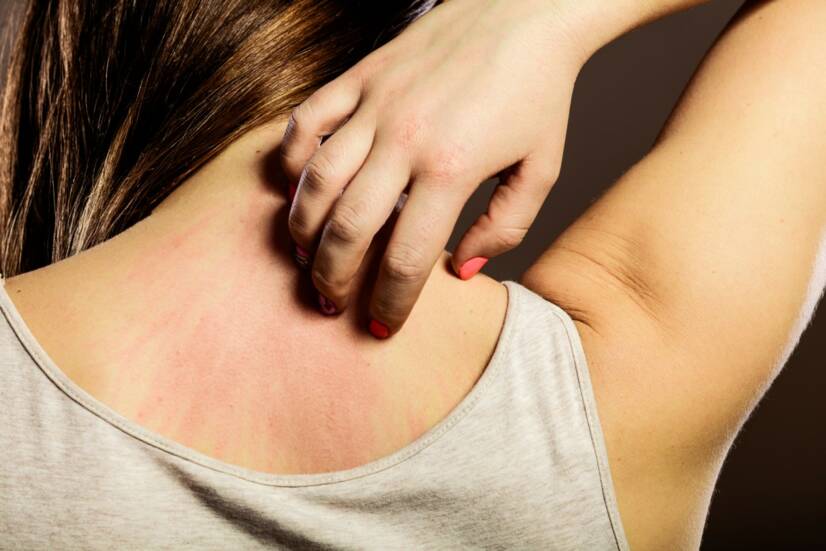
Reddened skin is a common phenomenon of increased emotional or physical stress. Excitement, stress, stage fright, nervousness, but also exercise or other physical exertion.
A person blushes for a variety of non-physical reasons.
And it's more of a cosmetic issue. Similarly with overly sensitive skin.
Sensitive and hypersensitive skin can be irritated by the sun, dusty environments, heat, or even cold. And some people have dilated blood vessels, either on the face or on the body.
However, minor cosmetic problems can be replaced by more serious ones that pose a threat of potential disease.
Sometimes as a precursor, sometimes directly as a symptom of disease.
The causes of skin redness represent a wide variety of both minor and more serious health problems. In this article we list the most common or major ones.
Read with us to learn more...
When redness is not caused by disease
Fragile and sensitive skin, but also the nature of the person.
Even in this way, the two main and most common causes that are not a manifestation of a disease could be divided.
Every day, people experience situations that increase their mental or physical effort. This results in increased activity of the cardiovascular system. And even the tiniest blood vessels in the facial skin become involved.
And thus...
You exercise, you exert yourself, you do manual labor. Or do you experience stress, agitation, excitement, fear? These emotional components have the same effect.
The result will be increased blood circulation to the skin, face and body. You may even feel a rush of heat to the face, head - nothing unusual and nothing morbid.
Quite normal.
In this case it is a mixed effect of vascular and nerve supply.
The reactive skin shows signs of redness, alongside which there is usually enlargement of small blood vessels. Although this is a temporary condition, it is possible that it will worsen or eventually become permanent.
And then, not only in women, this problem is an aesthetic and cosmetic obstacle.
Sensitive, reactive, hypersensitive skin, sensations of heat and flushing.
You ask:
What all can provoke this phenomenon?
Provocative factors include:
- Physical exertion
- psychological strain
- environmental temperature, heat and cold, especially sudden changes and transitions
- humidity and excessively dry environments
- windy weather
- dusty and polluted environment, especially in the city
- sunlight
- lack of fluids and dehydration
- food and fluids - spicy, hot, pungent foods, but also carbonated drinks
- alcohol
- chemicals and daily hygiene products
- hormonal changes, including the menstrual cycle in women
- mechanical irritation, pressure on the skin, pulling, rubbing, shaving
Redness of the facial skin after shaving - due to mechanical irritation.
But also in the armpits or groin and lower legs.
With the appearance of pain or itching.
Factors such as age and dryness of the skin are also important. It is natural that age makes the skin drier, less elastic and therefore more susceptible when exposed to other factors.
Skin pigmentation, phototype, ethnicity and overall lifestyle are also associated.
Redness as a possible symptom of the disease
Excessively red skin can, of course, be a sign of a health problem. This can be both minor and serious.
In addition to the aesthetic aspect, other unpleasant symptoms can also be associated with itching, swelling, but also general symptoms such as an increase in body temperature to fever, fatigue and others.
Cuperosis is one of the terms that refer to the enlargement of tiny blood vessels located in the superficial layers of the skin. You may also come across the term telangiectasia.
These enlargements can be localised on a small scale, for example on the nose, cheeks and other parts of the body. Sometimes, however, they can form larger areas and cover a substantial part of the mentioned areas.
The blood vessels are small, like a spider's web, or larger, merging into flat areas.
Teleangiectasias may be red, deep red, purple or blue in colour.
Similarly, dilated veins can be found in the subcutaneous tissue. These are known professionally as venectasia, or also as spider veins.
Read also the article
Broomstick veins.
Cuperosis does not have a precise cause of occurrence.
It has a multifactorial basis. Factors such as heredity, genetic predisposition, disorders of the vascular wall and therefore connective tissue and elasticity of blood vessels are involved in triggering the problem.
External factors such as UV radiation (sun), cold, heat, dryness, wind, dust and pollution as well as stress, activity or alcohol are provoking factors.
A complication is the increased permeability of the vascular walls and their cracking. This exacerbates this cosmetic problem.
Over time, the vascular pattern can become wider and more prominent.
Various cosmetic products, skin hydration and sufficient protection from irritation are helpful in solving the problem. Of course, a sufficient drinking regime and a balanced diet with sufficient vitamins and minerals will also help.
The skin benefits from collagen, zinc, selenium, copper, vitamin C, E, A, B complex, beta-carotene (provitamin A).
Interesting articles:
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It occurs more often in women after 30 to 40 years of age.
It affects women 3 times more often.
It usually affects the skin of the face and especially the forehead, nose, cheeks and chin. Not so often the skin of the chest, décolleté, scalp or around the ears.
The redness is caused by dilation of blood vessels, which is temporary at first. Flushing (recurrent outbreak of symptoms) at a later stage develops into a permanent form.
Pimples, i.e. rashes (papules), also appear on the surface of the skin. The rashes may be filled with purulent contents. Secondary bacterial contamination from injury or skin breakdown is a risk.
The most serious complication of the disease is the nodular transformation of long inflamed skin and thickening of the sebaceous glands.
Typical is the cauliflower-like thickening of the skin of the nose, which is technically referred to as rhinophyma.
No, rhinophyma is not a manifestation of alcoholism.
Apart from these two examples, skin problems are varied.
Dermatosis = general term for skin disease.
It combines more than 600 different skin diseases.
Skin inflammations have a variety of origins. They are divided into external and internal. Examples are pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, yeasts (mycoses), but also many internal diseases. Even autoimmune and congenital.
The aforementioned factors such as sunlight, temperature changes, food or alcohol are also a trigger for problems.
The table lists some other causes of skin redness
| Allergies |
Allergic - an overreaction to an allergen such as food, drugs, chemicals, cleaning or hygiene products, disinfectants, etc.
Contact dermatitis - may not indicate an allergic reaction, just irritation due to skin contact with an irritant or allergen
Eczema - allergic or atopic
Symptoms...
The skin is red, irritated, with or without rash or blisters (there may be no skin protrusion above the surface), itching, burning, with swelling or scaling
|
| Urticaria |
Urticaria - may occur independently of the allergic reaction, with redness and local swelling, which produces typical swelling of the skin above the surface, as in the case of urticaria burns, itching is also present
At least once in a lifetime in 20-30% of the population
May have a variety of causes
|
| Swelling | Can also be present alongside allergy, but also for many other conditions, soft tissue swelling, so-called Quincke's oedema can also accompany redness |
| Medication | For side effects or allergy |
| Diaper dermatitis |
In young children who wear diapers
The skin is exposed to irritation from urine and stool, being in a moist environment
The rash is at the diaper overlay sites, is red, moist and warm to the touch, itchy
|
| Effect of heat and cold |
Thermal injuries such as burns, scalding, chemical exposure or frostbite and skin damage from hypothermia, but also skin burns from excessive sun exposure, sunbathing
There are 3 degrees of damage, which are classified based on the extent and depth
- Grade - superficial redness
- degree - blistering
- white to dark/light brown skin or sunburned skin
Symptoms include redness, swelling, blistering, pain, burning, skin is subsequently dry and heals according to the extent of damage
|
| Cellulitis |
Not like the commonly known orange skin, but like inflammation of the skin cells
The skin is red, swollen, painful, with or without discharge, the skin is hot to the touch, tender, tense
Associated complaints such as fever, fatigue or nausea, etc. may be present
|
| Spála | Scarlatina - as a severe infectious disease with fever, tonsillitis and skin seeding and rash |
| Lupus | Systemic lupus erythematosus - an autoimmune disease that has a rich variety of symptoms
Cutaneous manifestation - reddened butterfly-shaped skin on the face (butterfly exanthema)
- facial redness in the area of both cheeks, joining on the nose
|
| Herpes | Shingles or the more common herpes simplex - caused by viruses |
| Psoriasis | Psoriasis as an autoimmune disease, in addition to redness, the formation of scales is typical |
| Borreliosis | Lyme disease - after a tick bite
It has a number of manifestations, but the typical one is a circular skin rash
- migratory erythema, i.e. erythema migrans at the site of the tick bite
- the erythema may disappear and appear elsewhere on the body
Read also:
|
| Rashes |
They appear in a variety of forms, as one or more rashes, small large, swollen
Examples are furuncle, skin abscess, acne |
| Scabies |
A parasitic skin disease caused by the scabies mite, the parasite creates tiny passages in the skin where it lives and lays its eggs
The disease is infectious and is therefore transmitted from person to person
|
| Roses |
Erysipelas as an inflammation caused mainly by streptococcus or staphylococcus bacteria
In addition to redness, general discomforts such as fever, chills, tremors, weakness, fatigue, lack of appetite are associated
|
| Inflammation of the veins |
Redness on the legs for...
Thrombophlebitis - inflammation of the superficial veins, whereby redness appears on the skin, the risk is the formation of thrombi, i.e. blood clots that can travel like an embolus through the blood vessels and cause embolism and non-blooding of another distant organ, an example is embolism to the lungs
Inflammation of the skin on the leg...
Similarly, problems with the blood vessels of the lower limbs can form a tibial ulcer, which forms a deep skin defect with problematic healing
|
| Other |
Redness of the skin can also accompany conditions:
|
The table lists only some of the problems that may accompany this symptom.
In the event of an acute course, persistence of problems or association of more serious problems, it is necessary to seek specialist examination by a general practitioner, skin doctor or other specialist depending on the cause identified.