Brain disorders
Brain disorders include

Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease is clearly one of the most common degenerative brain diseases. The most well-known feature of dementia is the gradual loss of memory.
Bleeding in the brain
Cerebral hemorrhage (cerebral hemorrhage) is divided into spontaneous and traumatic. Both conditions threaten a person's health and life. Why do they occur and how do they manifest themselves?
Brain abscess
An abscess is a pus-filled cavity in the tissue. It manifests as a circumscribed and encapsulated inflammation. The most common bacteria that form abscesses are staphylococci and streptococci.

Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy, also known by the abbreviated name CP, is a disorder of central motility control and a disease of the nervous system. The disease can be congenital or acquired. Various factors that affect the developing brain are involved in its occurrence. This is during intrauterine development, in the period during childbirth, but also in the time after childbirth.

Concussion
A concussion (commotio cerebri) is a transient disturbance of brain function. It is caused by external forces. It is referred to as a mild brain injury.
Edema of the brain - swelling
Edema of the brain refers to is swelling of the brain. This is a fairly common phenomenon with many causes.

Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a disease that mainly affects newborns and the elderly. It is an increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. The increased volume of fluid increases intracranial pressure, causing a number of characteristic symptoms. Diagnosis is rapid, using modern imaging tests. Treatment is so far only surgical.
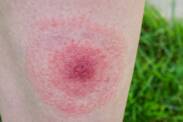
Lyme disease
Lyme disease is a multi-systemic infectious disease of bacterial origin. Humans become infected with this disease after being bitten by an insect. This spot is typically reddened by a large rash. It can take place in a lighter form. Chronic disease is sometimes treated for many years.
Meningitis
Meningitis, i.e. inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, is a neuroinfection. It affects the brain, the meninges, the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. The severity of the disease varies from asymptomatic to life-threatening.

Migraine is a seizure headache. In addition to pain, it is accompanied by other vegetative, perceptual and sometimes movement symptoms. It is quite common and occurs as a child. It affects more women. The precondition for its origin is a family occurrence.
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a chronic progressive disease of the nervous system.
Pseudotumor cerebri
Pseudotumor cerebri is a disease also known as idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is an acute multisystem inflammatory disease. It affects and damages connective tissues. It most often occurs in children of pre-school and school age. It occurs after recovery from a streptococcal infection of the upper respiratory tract and streptococcal angina.

Tick-borne encephalitis
The tick is one of the carriers of infectious diseases. Tick-borne encephalitis is one of them. Over the past 10 years, the number of cases has ranged from 50 to 108 per year.
Tuberculous meningitis
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease. Even today it is a common cause of death, especially in the developing world. But it is also common in developed countries.

Epilepsy
This disease is manifested mainly by recurrent epileptic seizures, but it is also accompanied by many other syndromes that complete the global clinical picture of the patient, such as cognitive disorders, depression, anxiety and other psychiatric complications.

Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder called narcolepsy is a serious problem that causes a variety of problems. Why does it arise and what are the impacts on human life?

Rabies
In the Middle Ages, it was thought to be demonic possession or a disease caused by cosmic phenomena. What is rabies, how is it spread, manifested and treated?









