- Jan Hugo and others - The Great Medical Dictionary
- wikiskripta.eu - Gastroduodenal ulcer disease
- wikiskripta.eu - Beryllium ulcer
- mayoclinic.org - Peptic ulcer disease
- verywellhealth.com - What are gastric and duodenal ulcers?
- healthline.com - Does a stomach ulcer cause pain?
- nhs.uk - Venous leg ulcer
- my.clevelandclinic.org - Leg and foot ulcers
- britannica.com - Ulcer
What is an ulcer, types of ulcers, their causes, symptoms and treatment?
An ulcer is a defect of the mucous membrane or skin (depending on its location). It can lead to various complications.
Characteristics - what are ulcers and what types are they divided into?
Ulcers in general
An ulcer (ulceration) is a defect of the skin or mucous membrane characterized by a failure of healing.
An ulcer is a breach or injury to the skin or mucous membrane. It is caused by the breakdown of the superficial epithelial tissue.
An ulcer may be superficial or deep.
It occurs in different layers of skin or other tissue (stomach, intestine...). It is a sunken base or crater surrounded by sharply demarcated edges. The edges sometimes protrude above the surface of the surrounding tissue.
The ulcer manifests itself mainly by pain.
The main causes of ulcers are infection, impaired blood supply, nerve damage or trauma. Sometimes ulcers are caused by vitamin deficiency (avitaminosis). Specifically, thiamine - vitamin B1.
Cancer can also lead to ulcer disease.
Tuberculosis or syphilis can lead to ulcers on any surface of the human body.
Other infections can lead to a skin ulcer.
Pressure ulcers are caused by weakening of blood circulation through the veins of the lower limb.
In patients suffering from diabetes, the blood vessels of the limbs and nerves are damaged. This is a predisposition to the development of a tibial ulcer.
In immobile patients, decubital ulceration, i.e. the development of pressure ulcers, may occur.
Peptic ulcers arise in the stomach and the beginning of the small intestine, in the duodenum (duodenum). They are caused by an imbalance in the composition of gastric juice.
The stomach and duodenum have a mucosal lining that protects them from digestion. However, sometimes, for various reasons, an imbalance occurs. The imbalance leads to the development of a gastric ulcer.
Sometimes ulcers form after burns or frostbite.
If a skin ulcer does not heal or is painful to the touch, the possibility of skin cancer should be considered. Age is then taken into account. Cancer is more common in this case in middle-aged patients.
Ulcers on the edge of the lower lip in older men are more likely to be cancerous. The prognosis should be taken into account and the disease should be operated on as soon as possible.
Sometimes ulcers are caused by viruses, especially those on the lips.
Ulcers in the mouth have a similar prognosis. They can result in cancer, but more often than not it is an infection.
Carcinogenic ulcers can also occur in the stomach, small or large intestine and rectum.
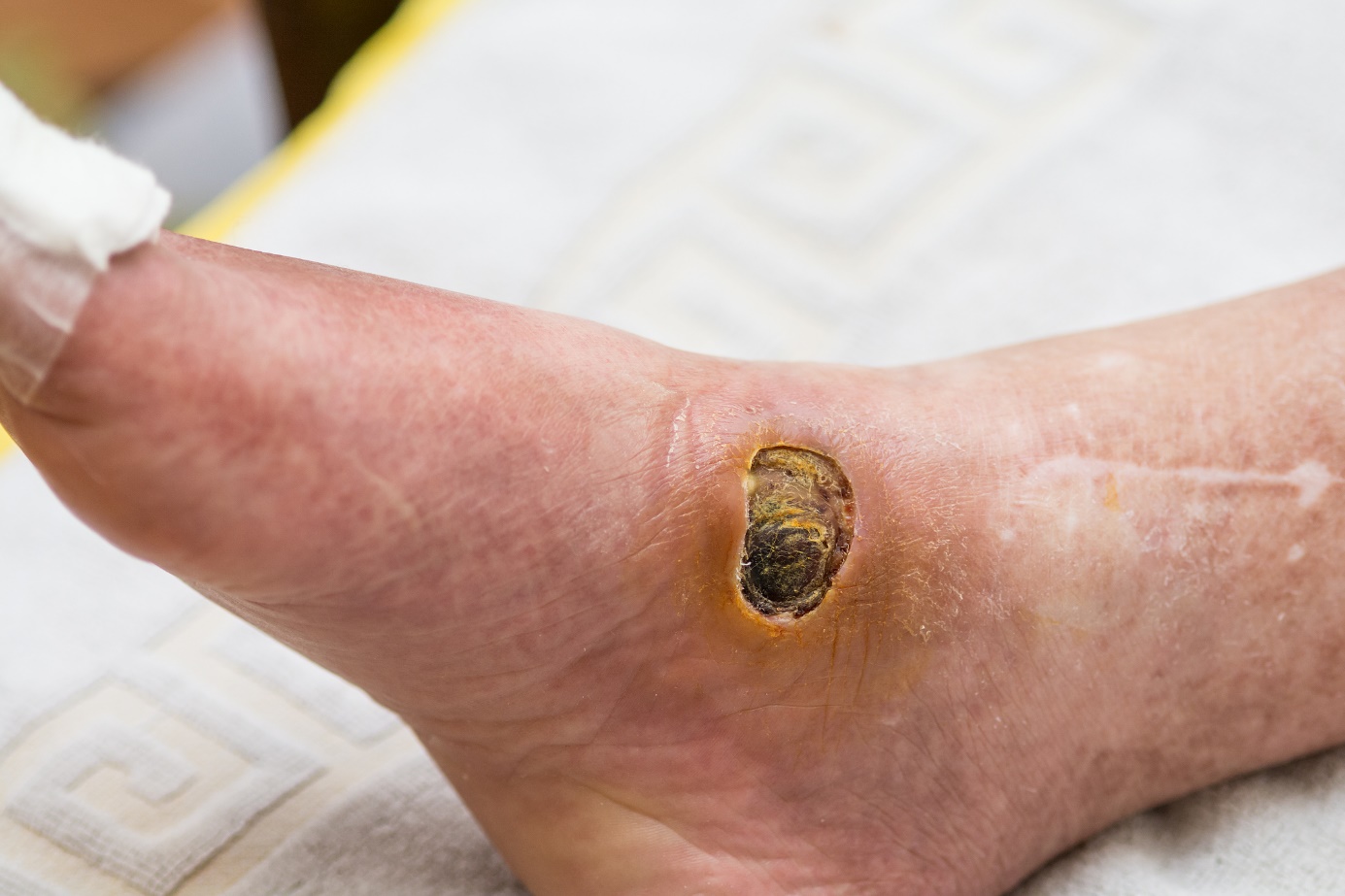
Ulcus cruris is a wound located between the knee and the ankle. The wound sometimes takes a long time to heal. The wound can produce purulent secretions. The tissue around the ulcer is also affected. It can be seen down to the bone.
People with varicose veins (varicose veins) are more prone to developing a tibial ulcer.
Mixed ulcus cruris occurs in diseases such as diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis.
There is also arterial ulcus cruris (ischaemic - non-bleeding, e.g. due to occlusion of a blood vessel) and ulcus cruris resulting from a malignant process (skin cancer).
In people with diabetes, ulcers on the foot and fingers occur as a result of diabetic neuropathy.
Sometimes it is necessary to amputate the toes or part of the foot. Ulcers are also associated with other diseases such as obesity or heart disease. Deformities and injuries are a prerequisite.
Tobacco and alcohol are risk factors for ulcers in general.
Ulcer disease of the tibia and leg is defined by a scale of six grades, from mild changes to gangrene. In the case of gangrene, amputation is necessary.
The skin is often dry, cracked, scaly, red and rash-like.
Complications of shin and leg ulcers are visible bone and a strong odor.
Ulcus durum (hard ulcer) occurs as an ulcer on the penis in the first stage of syphilis. It is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum.

Decay
Ulcers can arise in different places and have different causes.
Accordingly, they are divided into:
- Gastric and duodenal ulcer - in ulcerative disease of the stomach and duodenum, peptic
- Ulcus cruris - an ulcer typical of the tibia
- Ulcus durum - hard ulcer in syphilis
- Ulcer on the foot and adjacent toes
- Coracoid ulcer
- Ulcerative colitis - ulcerative disease of the colon
- Other - skin ulcers and subcutaneous ulcers localised variously over the body
- Read also more in the article Furuncle: what is a furuncle and subcutaneous ulcer?
Causes
Infection with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori can lead to a gastric or duodenal ulcer.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid can lead to a gastroduodenal (stomach or duodenal) ulcer.
Zölinger-Ellison syndrome can also lead to gastric ulcers. The pancreas in Zölinger-Ellison syndrome produces increased amounts of the enzyme gastrin, which stimulates the production of gastric juice.
Spicy foods and stress do not induce an ulcer, but worsen the condition when an ulcer develops.
Causes of ulcus cruris (pressure ulcer) are injury to the lower limb or stagnation of blood in the veins of the lower limb with lack of exercise. There is also an increase in blood pressure.
Causes of ulceration of the foot and adjacent toes are diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage), trauma, impaired blood supply through the blood vessels of the foot, cellulitis and overlapping infection or abnormally shaped toes.
For more interesting information, see the articles:
What health complications does diabetes cause? Even neglected and untreated
and
Diabetic foot as a complication of diabetes?
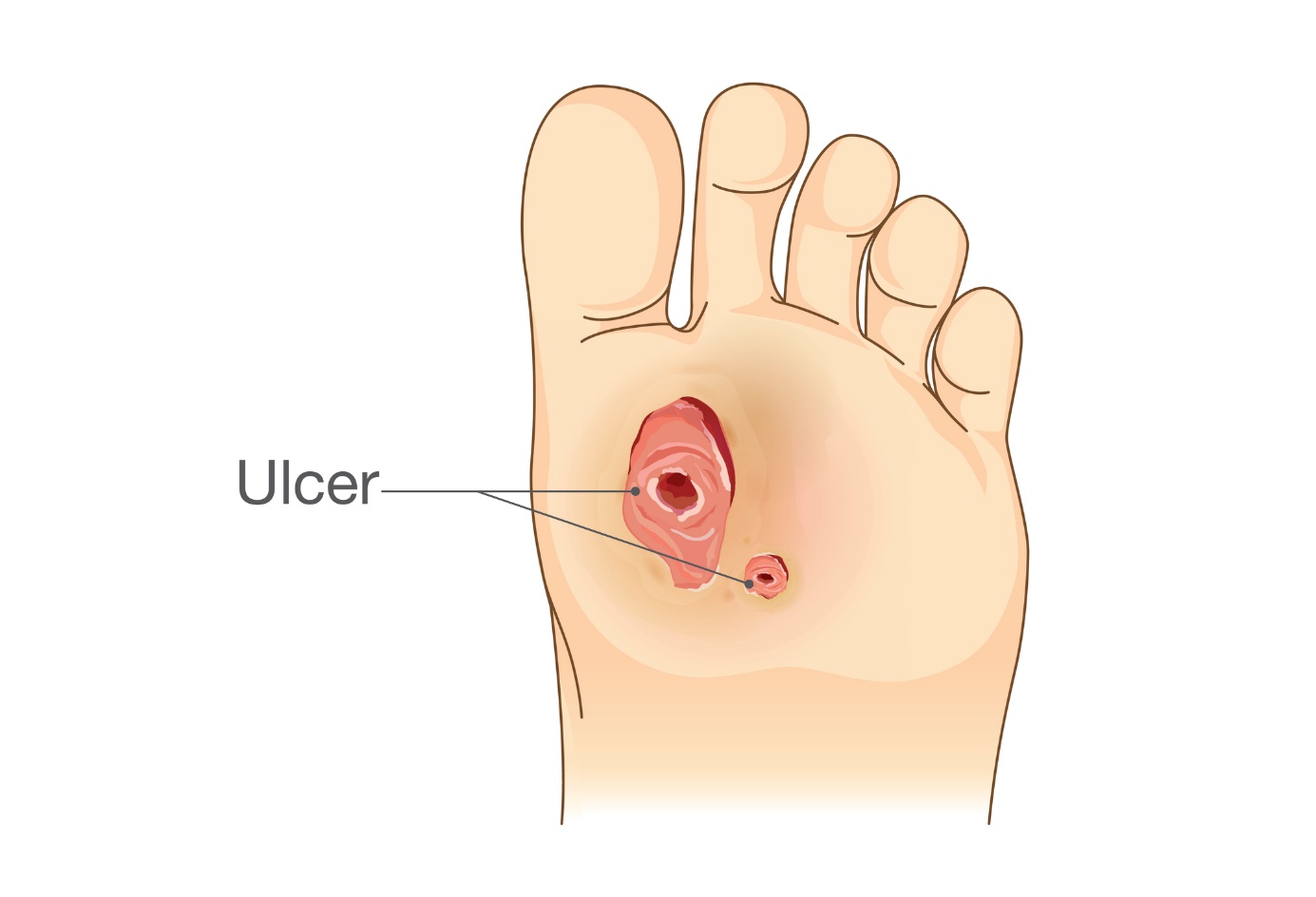
Manifestations
Many people with a tibial ulcer have no manifestations of the disease.
In gastroduodenal ulcer disease, there tends to be severe burning pain in the stomach area. This pain does not radiate. There is also a feeling of fullness or intolerance to fatty foods. Sometimes there is associated nausea (feeling like vomiting).
The pain may last for a few minutes, but also for hours or days.
Symptoms of gastric ulcer disease may include vomiting blood or black coloured blood in the stool. There is also a feeling of weakness or weight loss and changes in appetite.
Dyspepsia (altered digestion) also occurs in peptic ulcer disease.
Ulcus cruris (tibial ulcer) presents with pain, burning and swelling.
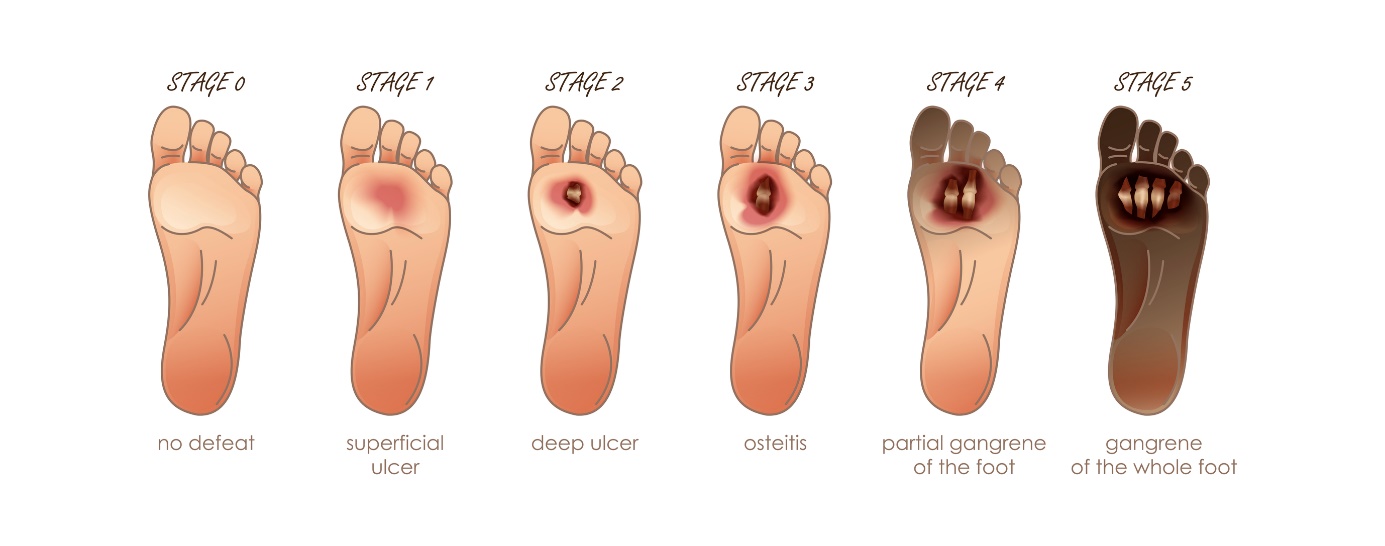
Interesting facts
A peptic ulcer is an injury to the lining of the stomach or duodenum (duodenum).
Predisposing factors for the development of peptic ulcer disease are increased intake of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, genetic predisposition and smoking.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is used to diagnose gastroduodenal ulcer disease.
Peptic ulcer can also occur in GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease).
The greatest risk is perforation of the stomach wall at the site of the ulcer.
Pain in peptic ulcer occurs between the umbilicus and the sternum.
Typically, a peptic ulcer occurs after the age of 80.
Ulcus cruris is more common in people who have had a deep vein thrombosis, trauma, osteoarthritis, paralysis, or are obese or immobile.
Ulceration of the tibia and leg can result in gangrene. The tissue in gangrene is black in colour and dead (necrotic).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) or X-ray (X-ray) is used to diagnose tibial and leg ulcers.
Shin and foot ulcers are generally not contagious. However, an infection that is transmissible from person to person can settle on the wound.
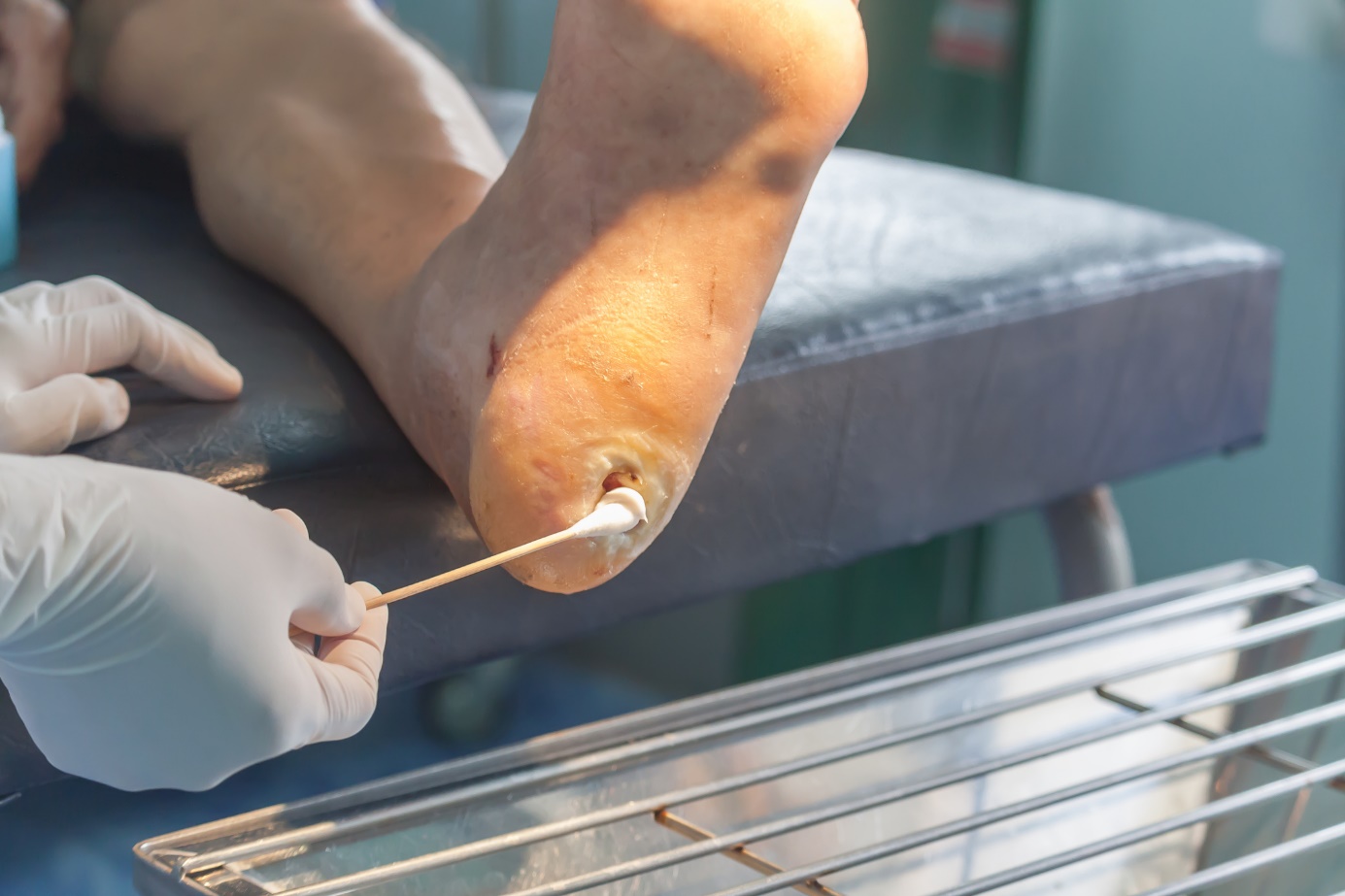
Prevention and treatment
The main goals of preventing tibial ulcer include limiting alcohol and cigarettes. It is important to avoid spicy foods and citrus fruits. In the literature, the authors add the condition of not eating two hours before bedtime.
If possible, completely discontinue the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, acetylsalicylic acid, etc. in patients with peptic ulcer.
Proton pump inhibitors are the first choice drug for patients with peptic ulcer. They reduce the production of gastric acid in the stomach. These include omeprazole and the like.
Sometimes antibiotic treatment is used when Helicobacter pylori infection is proven.
Surgical techniques are sometimes resorted to for peptic ulcer. However, there are also complications. Examples include perforation (puncture) of the stomach wall and bleeding.
Ulcus cruris is a treatable disease. Few cases are incurable. The main treatment approach involves cleaning the wound. Compression with an elastic bandage is also used.
Of the medications, antibiotics are used to prevent infection from entering the open wound.
Prevention of tibial ulcer consists in quitting smoking, losing weight and regular exercise.
Antiplatelet drugs (antiplatelet therapy), which prevent the formation of blood vessel blockages (thrombi) in the injured leg, also have a preventive effect.
Regular elevation of the limb above the level of the head while lying down is recommended.
Surgical treatment of tibial ulcers is also sometimes resorted to, especially in complicated courses.
Healing of tibial ulcer and leg ulcer takes weeks to several months. Sometimes it fails to heal.
Diseases with symptom "Ulcer"
- Alcoholism
- Basalioma - Basal cell carcinoma
- Bulimia
- Chlamydia Infection
- Chronic venous
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Esophagitis
- Furuncle, carbuncle and subcutaneous ulcer
- Leprosy - Leprosy
- Malignant melanoma
- Peripheral Artery Disease
- Post-thrombotic syndrome
- Raynaud Syndrome
- Syphilis
- Tiber ulcer
- Vasculitis
- Chronic venous
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Hemangioma
- Impetigo
- Scleroderma
- Mor










