- solen.cz - Pharmacotherapy of urge incontinence and overactive bladder. Solen. MUDr. Miroslava Romžová
- Everydayhealth.com - Frequent urination: symptoms, causes and treatment. Everydayhealth. Kathleen Smith, PhD, LPC
- pediatriepropraxi.cz - Polyuria as a clinical sign involved in early diagnosis of adrenal cancer. prof. MUDr Vladimír Mihál, CSc et al.
- TESAŘ, Vladimír and Ondřej VIKLICKÝ, ed. Klinická nefrologie. 2nd, completely revised and supplemented edition. Prague: Grada Publishing, 2015. ISBN 978-80-247-4367-7.
Frequent urination in both men and women: what are the possible causes? Can medication help?

More frequent urination for a small urge may not be anything serious. But it may signal a certain disorder or disease. How frequent urination is considered normal?
Frequent urination can be a symptom of a specific health problem. Sometimes it has a common, non-risky cause. Excessive urination frequency can make even the most mundane activities unpleasant.
Possible causes of frequent urination and the urge to go to the toilet, diagnosis, prevention, home help and much more interesting information can be found in the article.
What is considered frequent urination?
The body gets rid of waste materials from the body by urinating. Urine mainly contains uric acid, urea and unnecessary waste components. The bladder is an internal sac-like organ and should hold 600 ml of urine.
Filling the bladder increases the feeling of urge for a little need.
A healthy and normal frequency is considered to be urinating 6-8 times in 24 hours(when drinking approximately 2 litres of fluid per day). At night, a normal frequency of urination is a maximum of 2 times per night.
This is only an approximate figure.
Many factors contribute to urinary frequency. These include age, gender, drinking pattern, physical activity, energy intake/output, health status, drug therapy and others.
Frequent urge to urinate(professionally called pollakiuria) can be a common symptom of many diseases. It may not always be a disease of the excretory (urinary) system.
Polakisuria is the need for an individual to urinate more often than usual. Usually, it involves only small amounts of urine. It can occur during the day and night.
The frequent frequency of urination negatively affects normal daily activities, the quality of sleep and the overall comfort of the individual.
A healthy person has the bladder under control and is able to suppress the urge to go to the toilet. When there is an inability to regulate the leakage of urine, we speak of incontinence (spontaneous leakage of urine).
Excessive urination (6-8 times) does not always indicate a health problem. More frequent urination is natural when energy expenditure is high and when drinking excessive amounts of fluids.
With long-term problems and regular urination more than 10 times a day, the cause needs to be identified.
The frequency and approximate volume of urine excreted should be monitored. The need to urinate 15 to 30 minutes after the last visit to the toilet may indicate a health problem.
Possible causes of frequent urination
In case of non-specific symptoms, pain or burning during urination, it is a good idea to seek professional help from a urologist.
The cause of frequent urination is multifactorial. The urinary system is a complex system connected to other internal systems of the body. Possible causes are described below.
Excessive intake of fluids, alcohol and caffeine
If you drink more fluids than usual during the day, a higher frequency of urination is natural. Regular excessive drinking of fluids during the day can also be a problem. Approximately 2 litres of fluids per day is recommended. It depends on your weight, age and energy expenditure.
Beverages containing alcohol or caffeine can irritate the excretory system and act as diuretics. In the case of alcohol, the body gets rid of unnecessary fluids and pollutants by excessive urination. This condition is corrected in a short time.
The psychogenic factor
Increased stress, anxiety, excessive nervousness and emotional tension can cause an increased frequency of urination and stool. In occasional stressful situations, this is the natural "fighting" state of the organism.
With prolonged and regular stress, overactive bladder syndrome and a feeling of constant urge to urinate can develop.
Overactive bladder
Overactive bladder (also irritable bladder) is characterized by a high frequency of urination during the day and night. In the case of overactive bladder, urination occurs more than 8-10 times during the day.
Overactive bladder is more common in older people and in women.
Individuals with this syndrome feel the need to urinate when the bladder is filled to about half its volume. The degree of filling and the feeling of the urge to go to the toilet can be individual.
The cause of irritable bowel syndrome is mainly related to age, gender, psychological, excretory and reproductive health and other factors.
Pharmacotherapy (drugs and medicines)
Some medications are aimed at draining the body and increasing water excretion. These include medications for edema, high blood pressure, and kidney or liver disease.
Diuretics are medicines with a diuretic effect. They act directly on the kidneys and increase urine production.
Some natural herbs to support the lymphatic system and drain the body have a diuretic effect.
Infections and inflammations of the urinary system
In inflammatory infectious diseases of the excretory system, irritation of the bladder and urinary tract occurs. This is mainly manifested by burning and discomfort when urinating.
In this case, a specialist diagnosis by a doctor and determination of the causative agent of the infection by examination of a urine sample is necessary.
The inflammatory process can occur in the kidneys, bladder, ureters and urethra. Inflammation of the urethra is more common in women. This is due to the anatomically shorter length of the urethra. Exposure to cold and hypothermia can also lead to frequent urination.
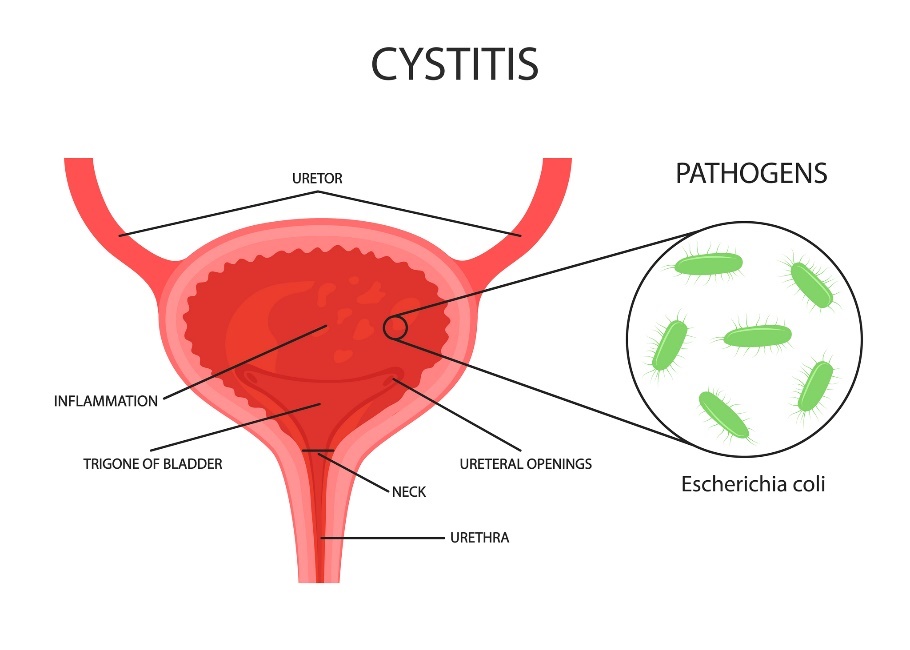
If neglected, the infection can progress to the bladder and kidneys. Bladder infection is technically called cystitis. It is caused mainly by bacteria Escherichia coli.
Excessive drinking, sufficient regeneration of the organism and pharmacological treatment prescribed by a urologist will help. It is necessary to pay attention to repeated inflammations of the urinary system.
Kidney (urinary) stones
Urinary (kidney) stones in the form of small stones are formed by insufficient dissolution of minerals and salts in the kidneys and urinary tract. They can also arise as a result of infectious inflammation and frequently recurring inflammation.
Risk factors include metabolic disorders, local factors, lifestyle and family history.
Concentrates travel through the urinary tract. They cause pain, discomfort and increased urge to urinate frequently. The pain caused by a urinary stone is referred to as renal colic.
Neurological disease
When the nervous system and its function is damaged, excretory system may malfunction. It may be a degenerative neurological diagnosis, stroke.or trauma.
Examples are spontaneous muscle contractions of the bladder and urge to urinate before filling. Diagnosis and treatment is determined by a neurologist.
Diabetes mellitus
A frequent urge to urinate is also present in diabetes mellitus (diabetes). Frequent urination, excessive thirst and dry mouth are often the first symptoms of diabetes.
The main cause is an increased amount of glucose in the blood. As a result, the kidneys have to increase the function of blood filtration and urine excretion.
Disorders of bladder emptying can occur. The bladder does not empty sufficiently and irritates to urinate again. When diabetes is suspected, it is necessary to see a doctor who will diagnose the level of glucose in the blood and urine.
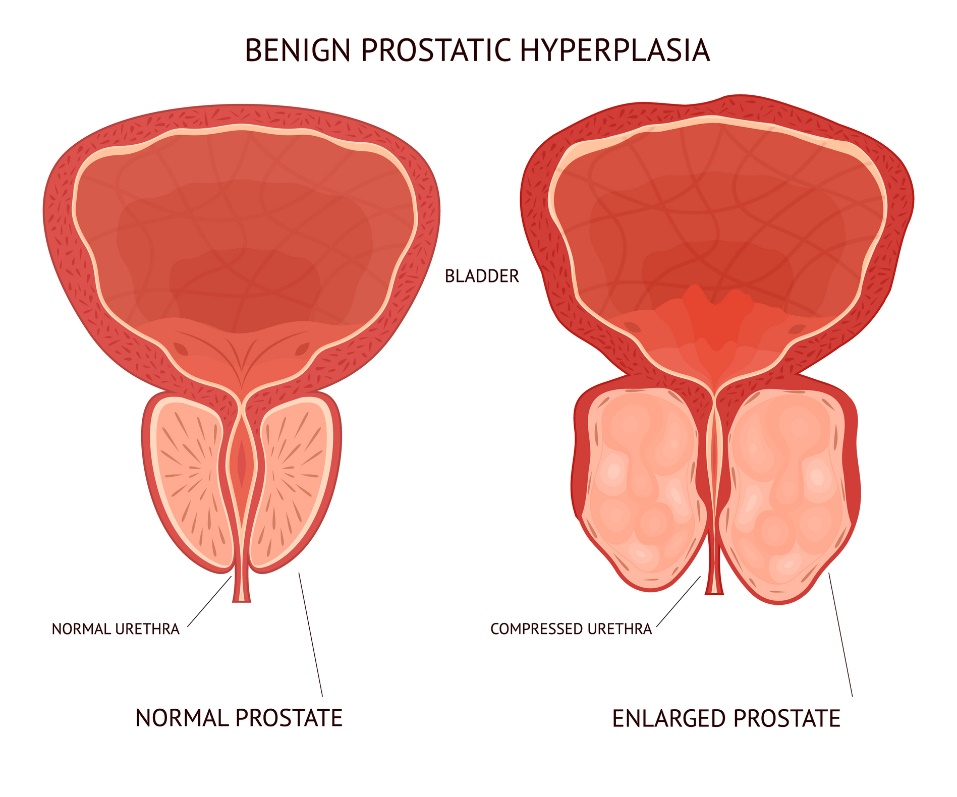
Prostate in men
After the age of 50, the prostate often enlarges. Its volume presses on the urethra. This causes incomplete emptying of the bladder and frequent urination.
The benign enlargement of the prostate is technically called benign prostatic hyperplasia (abbreviated BPH).
Treatment can be conservative in the form of drug therapy and lifestyle modification. Surgical treatment is also possible. The disease can be prevented by annual preventive visits to a urologist.
Pregnancy in women
Frequent frequency of urination during pregnancy is a common phenomenon. The growing fetus in the uterus gradually presses on the surrounding internal organs, including the bladder. It causes frequent urge to urinate.
With any unclear symptoms or unpleasant sensations when urinating, a visit to the gynecologist is necessary.
Mild incontinence (leakage of urine) may occur in the postpartum period. It is caused by the weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and abdominal wall by childbirth.
Other diseases
Frequent urination and the sensation to urinate is a multifactorial symptom. It mainly signals a disorder of the excretory, genital or nervous system.
Venereal diseases and sexually transmitted infections are also possible causes of frequent urination. They are accompanied by pain, burning, itching and discomfort during urination and intercourse.
The cause may also be psychological and psychosomatic. In both women and men, the pelvic floor and pelvic muscles are important in the prevention of incontinence and in the experience of sexuality.
Cancer is also a possibility, specifically benign and malignant tumours of the prostate, uterus, bladder and other surrounding areas. Therefore, a specialist diagnosis by a doctor (urologist) is always necessary.
Prostate cancer: causes and first symptoms. What is the prognosis of treatment?
An overview of the possible causes of frequent urination :
- infections and inflammation of the urinary tract
- pharmacotherapy (diuretics)
- excessive drinking of fluids
- alcohol consumption
- excessive consumption of caffeine
- urinary kidney stones
- kidney disease
- enlarged prostate in men
- pregnancy in women
- sexually transmitted diseases
- incontinence and weakening of the pelvic floor
- diseases of the nervous system
- psychological factors (anxiety, stress, tension)
- psychosomatic diseases
- overactive bladder
- oncological diseases of the pelvic area
- diabetes mellitus (diabetes)
- obesity
Frequent urination in children
Excessive urination or the urge to urinate troubles children in addition to adults.
Frequent urination in children should not be underestimated because of the risk of spreading infection to surrounding structures. This is especially true in the presence of infection.
Urinary tract inflammation is one of the most common problems associated with frequent urination in children.
It occurs mainly in girls because of the anatomically shorter urethra.
The risk factors include poor hygiene. Especially in smaller children, there is an increased risk of transmission of bacterial infection from around the rectum.
Frequent urination also occurs during adolescence. It is caused by a combination of cold, cold weather and inadequate clothing.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of frequent urination
The initial diagnosis of frequent urination starts with the general practitioner, who refers the patient to a specialist - a urologist.
The urologist will establish or exclude a diagnosis related to the urinary system.
In case of suspicion of other diseases , he refers the patient to the appropriate department(neurology, gynaecology, psychiatry, gastroenterology and others).
In the treatment of frequent urination caused by a disease of another system, the aim of therapy is to eliminate the cause. Pharmacological regimens for diabetes, medical or surgical treatment for neurological disorders, surgical treatment for oncological diseases...
The initial diagnosis consists of taking and laboratory examination of a sample of the patient's urine. Usually a blood sample is also taken. The urologist examines the patient by palpation, takes a history and assesses the clinical symptoms.
An instrumental ultrasound examination of the kidneys and relevant organs is appropriate.
In the case of infection and inflammation of the urinary tract, medical treatment with antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs is chosen. Treatment includes adjustment of lifestyle, drinking regime, diet and elimination of physical or mental stress.
In overactive bladder, the patient is often given anticholinergics to reduce bladder irritability by reducing local muscle contraction.
An adjunctive treatment for frequent urination is rehabilitation in the form of pelvic floor muscle strengthening and control.
For urological local problems, the cause is treated. An example is the treatment of kidney (urinary) stones. Therapy is regimen-based, medical and often surgical.
The prevention of frequent urination and urge to urinate consists in a change of lifestyle. It is primarily a matter of limiting the intake of alcohol, caffeine and foods and drinks with a diuretic and irritating effect (excessively spicy and hot foods, artificial sweeteners...).
The daily drinking regime should be approximately 2 l of fluid per day. It depends on age, body weight and energy expenditure.
It is advisable to limit fluid intake in the evening before bedtime. The frequency of nocturnal urination (technically nocturia) is reduced.
A balanced regular diet with sufficient vitamins, minerals, macronutrients (protein, complex carbohydrates, fats) and fibre is recommended. As part of the lifestyle, beware of cold and hypothermia. They have a negative effect on frequent urination.
Home strengthening of the pelvic muscles and pelvic floor is recommended. These include Kegel exercises aimed at isolated activation and contraction of the pelvic floor.
In addition to strengthening the muscles of the excretory system, the pelvic muscles support the experience of sexuality in women and erectile function in men.
When do I need to see a doctor?
- Frequent frequency of urination during the day and night
- Feeling of incomplete emptying
- Pain and burning during urination
- Smelly urine
- Nonspecific colour of urine, cloudy urine
- Presence of blood in the urine
- Incontinence (spontaneous leakage of urine)
- Increased body temperature and fever
- Any vague symptoms and pain
Diseases with symptom "Frequent urination"
- Chlamydia Infection
- Chronic pancreatitis - long-term inflammation of the pancreas
- Cushing's syndrome
- Cyst on the ovary
- Diabetes
- Enlarged Prostate
- Gonorrhea
- Haemochromatosis
- Hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Inflammation of the Ovaries and Inflammation of the Uterine Appendages
- Inflammation of the prostate - prostatitis
- Kidney stones
- Kidney inflammation
- Ovarian cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Puerperal infection - postpartum infection
- Incontinence - urine leakage
- Inflammation of the urinary tract
- Pituitary adenoma
Herbs used forFrequent urination
Interesting resources
Related










