What can cause yellow whites of the eyes?

The whites of the eyes are normally white in colour. In the case of disease, they may be yellow. This is also the case, for example, in liver failure. Gallstones are another example. The condition is worse in the case of malignant disease. They can be seen even in newborns.
In addition, bilirubin can also be elevated in other diseases. For example, in Gilbert's syndrome or Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Usually, there are other symptoms besides yellowing of the whites of the eyes. If this is not the case, it is best to see a doctor anyway to diagnose the yellowing.
Hepatitis as a cause of icterus
Most often, yellow whites are associated with hepatitis, or jaundice of the infectious type. Professionally, this symptom is called icterus, and there is a characteristic yellowing. The skin and mucous membranes become discoloured, and yellow whites in the eyes are also present.
This yellowing is caused by the aforementioned bilirubin, which is present in the blood at elevated levels in cases of jaundice. Hepatitis is not a skin disease but an infectious disease of the liver. The liver is attacked by a viral infection which causes it to malfunction.
There are several types of hepatitis viruses. The most common are types A, B and C. While type A is the least severe, type B can already progress from acute hepatitis to chronic hepatitis. The most risky in this respect is type C, which in most cases progresses to the chronic stage.
In any case, the disease is quite protracted. Medication treatment is necessary, depending on the specific type of disease and the virus that caused it. Hospitalisation is necessary, mainly for a thorough diagnosis and also to determine the extent of the impairment of liver function.
Bile problem and icterus
A bilirubin problem can also be caused by other diseases. A good example is the obstruction of the bile ducts. A stone in the bile ducts but also in the gallbladder can cause obstruction.
This causes a disruption in the outflow of bile from the liver. Subsequently, this accumulation of bile over the obstruction causes a number of symptoms. In addition to the typical pain that occurs with gallbladder stones, yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes are associated as well.
Failure of liver function
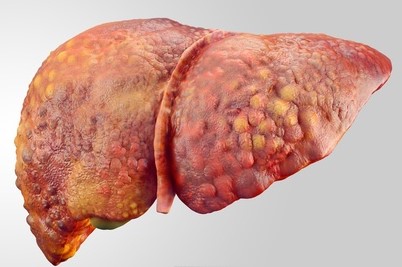
Hepatitis is not the only reason for liver failure. One of the symptoms of liver failure is just icterus, for putting the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, organs, mucous membranes and also in the skin or whites of the eyes.
The liver function fails in cirrhosis, tumor and also by the action of toxins. Such poisoning occurs, for example, after eating poisonous mushrooms.
It occurs in alcoholism, which is the cause of cirrhosis. But also after an overdose of paracetamol, which is the active substance of some drugs for pain or high body temperature.
Paracetamol is also contained in some combination cold and flu preparations. Therefore, the package information and dosage should be read carefully.
Paracetamol overdose
Paracetamol is an over-the-counter medicine for lowering body temperature, fever. In addition, it has an effect against pain. Paracetamol is the name of the active substance. The medicine is produced by different manufacturers and each manufacturer will give its own name to the medicine. There is a risk of overdose if you are not careful.
Paracetamol contains various drugs, combination drugs, mainly for flu symptoms and colds. It is important to try not to exceed the recommended dosage. With an overdose, there is a risk of liver failure.
In a healthy person, the toxic dose when taking paracetamol is 140 mg per kilogram of body weight. This toxic dose is also referred to as the hepatotoxic dose. In people such as alcoholics, but also in people with chronic liver failure, the dose for liver damage is even lower. Likewise in people taking drugs from the group of antiepileptics.
The risk of liver damage increases with alcohol ingestion.
Example: A person has a body weight of 70 kg. 70 kg (body weight) x 140 mg (toxic dose) = 9 800 mg of paracetamol, which is actually 9.8 g of paracetamol. This means that taking approximately 20 tablets is a hepatotoxic dose.
The following symptoms occur in paracetamol overdose:
- pain in the upper abdomen
- feeling like vomiting
- vomiting
- after 48 hours, signs of liver failure (icterus and yellow-coloured whites of the eyes)
- impaired brain function
With increased red blood cell breakdown
Icterus also occurs when red blood cells break down if hemolysis is present at an increased rate. Increased red blood cell breakdown can be caused by several causes. It can be caused by exposure to toxins, poisoning, snake venom, heavy metals (lead), as well as some diseases. Read more about hemolysis.
Other causes
Yellow whites of the eyes are also a symptom of other diseases. For example, in tumors in the liver, in yellow fever, in disorders of blood supply and circulation directly in the liver, or in genetic or toxic liver disorders.
Among the genetic disorders for which yellow whites of the eyes are a fairly typical symptom is Gilbert's syndrome. This syndrome is also characterized by elevated bilirubin levels. In this case, it is unconjugated bilirubin that is free and enters the liver.
Here it should be conjugated (merged) by the enzyme. However, if there is a disorder of the liver and the enzyme in it, this bilirubin is present in the blood. Typical is yellowing of the whites of the eyes.
Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a relatively rare inherited and genetic disorder. It causes problems in the metabolism of bilirubin specifically by mutating the enzyme that conjugates bilirubin in the liver.
Disruption of this enzyme leads to impaired conjugation, and bilirubin cannot be excreted from the body by bile. It accumulates in the body and in the blood. As a result, there is an unnatural yellowing of both the skin and the presence of yellow whites of the eyes.
An example of when the whites of the eyes lose their color is also a malignant process of the conjunctiva or melanoma of the eye. Melanoma has several forms. It appears on the surface of the eye, in the conjunctival area, but also in the inner part of the eye.
The type of melanoma that occurs in the inner part of the eye is dangerous, mainly because of its hidden form and late diagnosis. The risk of developing it is already from the age of 25.
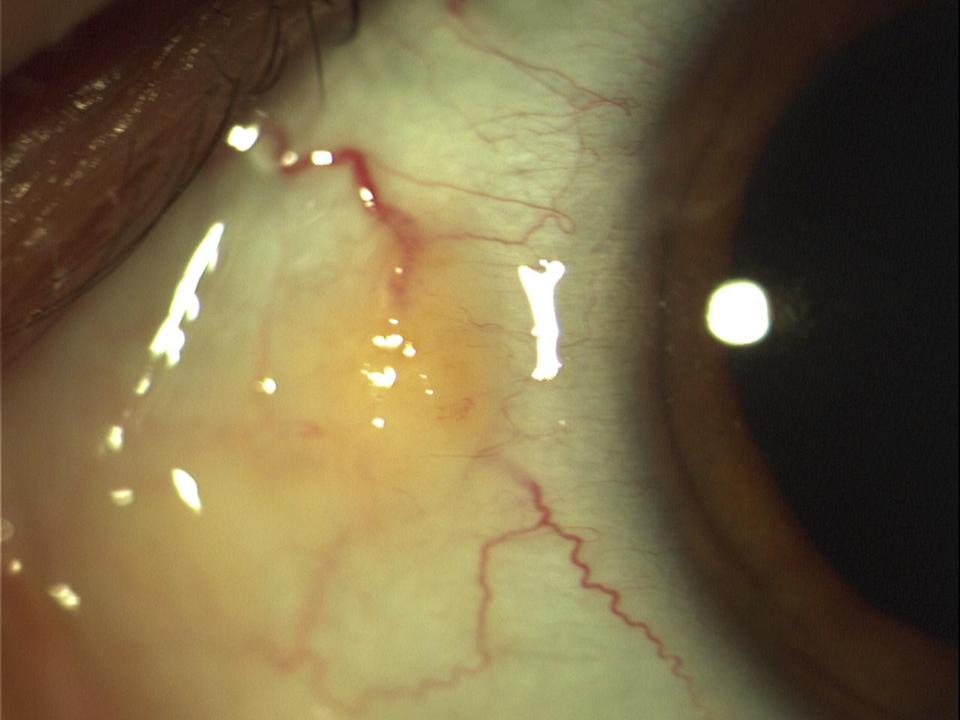
The partial discolouration of the white of the eye is caused by pinquecula and pterygium, both of which are hyperplastic changes of the conjunctiva. The former is triangular in shape and typically pale yellow in colour. The latter is similar, but more grey in colour.
A good example of when the color of the whites of the eyes changes is also poor lifestyle and eye fatigue. Unbalanced diet, increased consumption of salty, spicy, fried food and alcohol. Fatigue, prolonged computer work, lack of sleep, dry air.
However, discoloration and yellowing is not as pronounced as in liver disease or other diseases. The whites of the eyes lose their white colour and may have a faint yellow tint.
Neonatal icterus
It is also referred to as neonatal jaundice. It does not indicate a disease in this period. The child before birth (fetus) has a different hemoglobin, also referred to as fetal hemoglobin. This begins to change to what is called adult hemoglobin before birth.
It is present in approximately 45-65 % of newborns. Bilirubin is also produced in this case. This is conjugated in the liver and then excreted in the bile. If the bilirubin levels in newborns are high and persist for a long time, this condition can lead to health problems.
Video about jaundice
Diseases with symptom "Of yellow-white eyes"
Interesting resources










