What are the causes of hair loss in women and men? (Alopecia)

The cause of this symptom is various skin diseases. It can be, for example, atopic eczema, but also purulent inflammations. Typically, it occurs in alopecia. Hormone levels, nutrient and vitamin deficiencies are also related. Obesity and radical dieting or starvation have a negative effect. It also occurs in inflammation of the liver or in its cirrhosis.
This hair loss is also technically called alopecia.
Other times, hair loss is only local, for example, on a particular limb or area of the body.
It may also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as a problem with the hair or nails or redness of the skin. It also appears as a single symptom.
Alopecia
Often, hair loss is caused by alopecia. Alopecia is an autoimmune disease that manifests itself in hair loss and hair loss in both men and women.
It can have various causes, either congenital or acquired. For example, improper lifestyle can cause hair loss.

Alopecia has several forms. The first type is complete, where there is a complete loss of hair on the head. It can also be universal, where there is a loss of hair on the whole body. The third type is local, where there is a loss of only some hair.
Alopecia is divided into:
- androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness)
- alopecia areata (hair loss and hair loss in clumps, for example in circles)
- alopecia universalis (loss of hair and hair on the whole body)
- alopecia totalis (complete loss of hair on the scalp, i.e. complete baldness)
- alopecia barbae (loss of hair on the chin and cheek in men)
- alopecia mucinosa (patches of hairlessness, loss of hair where it normally occurs, for example, loss of hair on the chest, thighs, calves or legs)
- traction alopecia (occurs after physical stress on the hair, for example poor combing technique, but also after pulling the hair)
- anagen effluvium (caused by drugs, chemotherapy, chemicals)
- scarring alopecia is hair loss with scarring of the skin
It is natural to lose 50-100 hairs per day. However, if the number of hairs lost per day is over 100, then there is a problem. With massive hair loss, up to 1000 hairs can fall out.
An adult has approximately 100,000 to 200,000 hairs.
The hair growth cycle is approximately 3-5 years, then falls out after a resting phase.
In one month, a hair grows approximately 1 centimeter.
Hair grows faster in summer than in winter.
Diseases and infections of the skin with hair loss
In various skin diseases and also in inflammatory or infectious skin diseases, there is a localized loss of hair. The local loss is only in a specific place. Infection of the skin may also be accompanied by suppuration at the site.
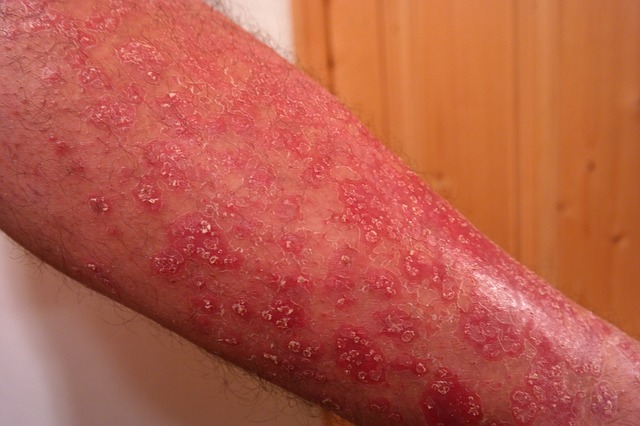
Examples of such diseases are:
- dermatosis
- inflammation of the skin due to mycosis or bacterial infection, pyoderma in purulent inflammation
- psoriasis
- tinea
- atopic eczema
- herpes zoster or shingles (neurological disease with skin manifestations)
Other causes of hair loss
Age, of course, also affects our hair and body hair. In older age, various hormonal changes occur. And these have a great influence in this case. Genetic predisposition or hereditary factors also affect the growth and renewal of hair or pubic hair. Loss of body hair may also be related to a disturbance of immunity.
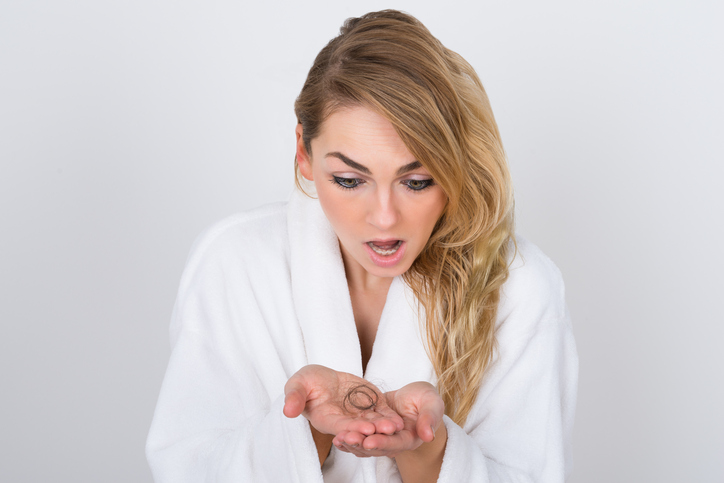

Hormonal changes
Hormone levels affect overall hair growth and hair growth. This is also the case, for example, if the thyroid and parathyroid glands are not functioning properly. There are also problems with elevated testosterone levels, as well as with menopause.
Neurological and metabolic problems
Loss of hair can also have neurological causes. For example, in diabetic neuropathy, a disease affecting the function and structure of nerves, a person usually loses hair on the arms and legs. This is particularly typical for men.
This disease is a complication of diabetes. People with diabetes also have problems with local hair loss. In addition to the neurological disorder, this also causes a problem with blood circulation. In the case of diabetes, it is referred to as diabetic angiopathy. Metabolic disorders also negatively affect this unpleasant symptom.
Problems with blood vessels
Several diseases of the veins and arteries are also manifested by hair loss. For example, the so-called tibial ulcers, which affect both veins and arteries. At the site of formation of this ulcer, there is both thinning of the skin and local hair loss.
The lower limbs are also affected by ischaemic disease, which affects the arteries, causing their narrowing and even complete closure. The limb becomes numb, painful and hairless.
Liver disease
Similarly, various problems with the liver are also manifested in the hair on the skin. For example, in the excessive deposition of iron in the tissues. This is typical of haemochromatosis. But also in hepatitis, this symptom occurs.
In cirrhosis, too, there is loss of hair. Cirrhosis is characterised by the death of the original liver cells and increased formation of connective tissue in the liver. This connective tissue replaces the original structure of the liver tissue, thus causing impaired function.
Medications, drugs and hair loss
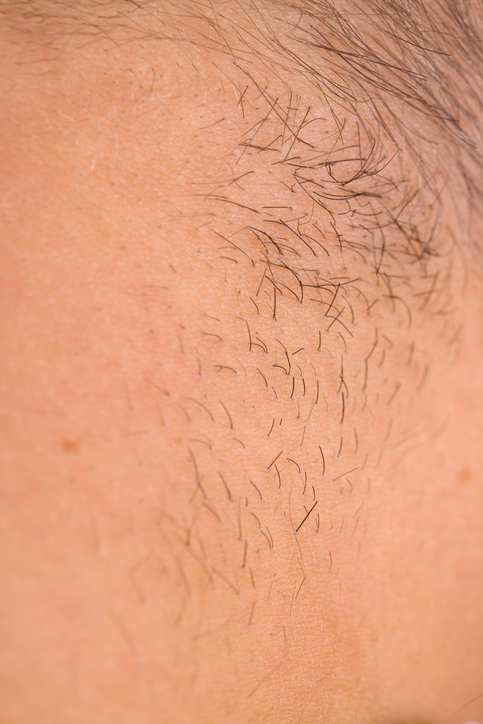
Loss of hair also occurs in the context of anticancer treatment, i.e. chemotherapy, which is a side effect and side effect of this form of treatment. Other drug causes include the use of contraceptives, cytostatics, certain psychiatric drugs or drugs for cardiovascular disease.
In the case of alcoholism, hair loss occurs for several reasons, especially if the aforementioned cirrhosis of the liver is present. Similarly, in drug addiction, it can occur, especially with cocaine abuse.
The cause can be undue stress or trauma
Slowed growth and also increased hair loss, locally or to a greater extent, can also be caused by psychological factors. Long-term stress, but also acute stress reactions can trigger hair loss or hair loss.
Similarly, post-operative conditions, serious injuries or extensive burns can also cause stress to the body. This is the case with shock conditions. Shock can occur, for example, with intense bleeding.
Eating disorders and nutrient and vitamin deficiencies
Slowed recovery and increased rates of hair loss and even loss of body hair also occur in cases of starvation. Deficiencies in B vitamins, vitamin D and vitamin E. But also in low levels of minerals and trace elements such as iron, zinc, magnesium or copper.
Similarly, an excess of vitamin A has a negative effect on the body. This can occur with supportive treatment with this vitamin. And in addition to anorexia, obesity or aggressive weight loss treatments also have a negative effect.
Therefore, a person who notices loss of body hair without any visible external cause should see a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis of one of the above-mentioned diseases.
Video about hair loss
Diseases with symptom "Loss of pubic hair"
Related










