- wikiskripta.eu
- google.sk
- mayoclinic.org - Petechiae
- healthline.com - What Causes Petechiae?
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Petechiae
Petechiae: What are they, why do they arise, how to recognize them? In children, beware!
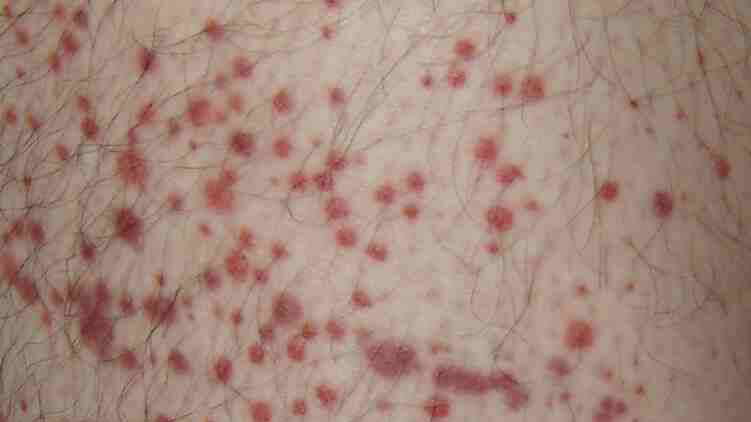
Petechiae are tiny blood eruptions the size of a pinhead. They occur in various diseases, which may also be infectious. Mechanical pressure or skin irritation is a minor cause.
They are approximately 3 mm in size.
Although they may resemble a rash, they do not protrude above the surface of the skin and do not lose their colour when pressed. The rash fades when pressure is applied to the surface.
Larger and more numerous petechiae are referred to as purpura.
A suffusion is a larger and more extensive subcutaneous haematoma (blood discharge).
Bleeding in petechiae comes from tiny blood capillaries (hair cells) that are located in the subcutaneous tissue, mucous membranes or tissues. Thus, in addition to the skin, they can also occur in the mouth cavity and mucous membranes. They are caused by the rupture of fine blood vessels and spillage of blood into the surrounding tissue.
Petechiae are a symptom, not a disease.
The cause of these small blood spurts may be minor mechanical irritation of the skin, subcutaneous tissue or mucous membranes. The blood vessels are disturbed by increased physical force. Blood penetration and spurting occurs.
Examples include the development of petechiae after strenuous vomiting or coughing, as well as when lifting heavy loads.
On the other hand, there are conditions that indicate various diseases, which are less or more serious, even critical and life-threatening.
Often petechiae and other skin problems come in advance of other symptoms, as the first subtle sign.
Therefore, it is not good to neglect this symptom. Early diagnosis and early treatment are of great resultant importance.
Want to know more about the causes of petechiae? Read on with us.
Petechiae as a result of mechanical damage
Blood capillaries are disrupted mechanically by pressure, pulling or other mechanisms. The wall of the tiny hairline cannot withstand the current increased load and ruptures. As a result, a blood spurt (bruise, bruise) is formed, which can have the shape and size of a pinhead.
Tiny dots of bleeding into the skin.
This often happens, for example, with a persistent and long-lasting cough or vomiting.
Increased pressure in these small blood vessels causes bleeding.
Examples include trauma mechanism, squeezing or punching, but also frequent minor bleeding when carrying heavy bags. Another is negative pressure, as in sucking (hiccups).
The presence of petechiae is also significant in crime, violence or murder. Petechiae are evidence and also occur in assault, kicking, handcuffing, pressure exerted on the mouth. They are also present in strangulation and suffocation.
They occur in athletic activities such as weightlifting and other strength sports. And increased pressure is also present in childbirth.
+ They can occur with skin irritation after shaving.
As a symptom of the disease
Often they come as a first and subtle symptom of even more serious to critical illnesses. This is when a medical examination should be sought immediately.
They often occur on the skin of the limbs, hands, feet, fingers, palms, face, around the eyes, on the chest and back, anywhere else on the body. But also on the mucous membranes in the mouth, tongue or palate.
In adults and children.
It signifies various blood (haemophilia and other bleeding disorders), vascular (inflammation of blood vessels), congenital, immunological, allergic, systemic diseases, inflammation, but also infectious diseases. And various other non-infectious diseases.
There are many causes...
The main signs of blood bruises of the petechiae type:
- sharply defined shape
- the size of a pinhead, approximately 2-3 mm
- do not protrude above the skin surface
- they are red, blue, even purple or brown
- do not change colour when pressed against the surface
- when spreading over large areas they are called purpura and when merging into larger areas they are called sufusions
Great care should be taken with children and babies
Two cases occur in children.
One of them is common and may not be serious. It is an accident. They are caused by mechanical pressure and action when the skin is injured, compressed and increased intensity is applied to the affected area.
The other side consists of diseases.
Infectious diseases such as infectious meningitis and encephalitis occur in childhood.
These neuroinfections are caused by bacteria or viruses.
Encephalitis is an inflammatory disease of the brain and meningitis is an infection of the meninges. Both are life-threatening and have a relatively rapid course.
And petechiae, along with a rise in body temperature and fever, are among the first warning signs.
The most serious condition is septicemia, meningococcal sepsis.
Read: What is blood poisoning (sepsis), what are its symptoms and how does it occur?
Petechiae are found on the trunk and around the navel, in the folds, in the armpits and groin, on the limbs and other parts of the body.
Symptoms are similar to flu. Petechiae and other neurological signs are associated:
- fever
- shivering, chills
- fatigue, weakness
- apathy
- petechiae
- muscle pain
- headache
- vomiting, persistent vomiting
- photosensitivity - excessive hypersensitivity to light, hiding from light in the dark
- neck stiffness and other meningeal symptoms due to irritation of the meninges
- disturbance of consciousness
Correct diagnosis is important
It is not only in children that early detection of the cause is important. Even in adults, petechiae can indicate an infectious cause that must be treated quickly. Otherwise, it can take an unfavorable and rapid course.
It is important to search for the basis of petechiae even in pregnancy.
Thus, an initial and early diagnosis is important, followed by special treatment. An example is a bacterial infection, for which early antibiotic treatment is important. This can save lives, equally in a child or an adult.
Petechiae usually occur as a few skin bruises.
If it is a solitary problem and no other problems are associated, one should look for the mechanical reasons mentioned above or after an injury.
If, however, it is a disease, the associated symptoms should be noted.
- checking the body temperature and the presence of chills, cough or fatigue?
- Is pain present?
- head in children behavioural changes, apathy, excessive sleepiness, irritability, nervousness
- is it an allergy?
- is shortness of breath present
- bruising on the body, even after a small wound - easy bruising
- frequent bleeding from the nose, gums and mouth
- menstrual disorders - heavy menstrual bleeding
- bleeding in the digestive tract, urine
- joint bleeding
- and others
The most common diseases with the occurrence of petechiae in the table + other causes
| Infectious | Non-infectious |
| Meningitis and encephalitis | Haemophilia |
| Infectious endocarditis | Thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopathies and thrombocytopenic purpura |
| Mononucleosis | Von Willebrand disease (vWD) |
| Fulminant hepatitis | Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC) |
| Haemolytic uraemic syndrome | Leukemia, aplastic anemia and other blood disorders |
| Dengue haemorrhagic fever | Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), Henoch-Schönlein purpura (vasculitis of childhood), polyarteritis nodosa (necrotizing vasculitis) |
| Hemorrhagic Hanta fever with renal syndrome | Kawasaki disease |
| Plague (pestis) | Rheumatic and systemic diseases, such as lupus erythematosus, celiac disease, Sjogren's syndrome |
| Scarlet fever, scarlatina | Cirrhosis of the liver, alcoholic hepatopathy, hepatic encephalopathy |
| Papular-purpuric gloves and socks syndrome - acute acute dermatitis = papulo-purpuric gloves and socks syndrome | Medications - medications to reduce blood clotting and prevent platelets from clotting (anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy), examples include acetylsalicylic acid, triclopidine, prasugrel, clopidogrel, ticagrelor, warfarin, etc. + Petechiae have also occurred after the use of other drugs such as analgesics, corticosteroids, steroids, antidepressants, sedatives, antibiotics, penicillin, etc. |
| Cytomegalovirus infection | Vitamin C deficiency - scurvy (vitamin C deficiency disease) Vitamin K deficiency |
| rubella | Toxic causes and poisoning, poisoning by fungi, toxins and other chemicals, especially for liver and vascular system failure and damage |
| Ebola, Yellow fever and others | Heat stroke, sunburn and sunburn of the skin + petechiae from allergies also occur |
|
Read also: Bacteria, viruses and other agents of serious diseases Vaccination, its importance before travelling abroad - foreign diseases | |
How to recognize petechiae
Interesting resources










