- POIRIER, Nicole. Intermittent fasting: quick and tasty recipes for health and weight loss. Translated by Denisa ŠTRBOVÁ. Prague: Alpha Book, 2021. ISBN 978-80-87529-63-8
- SVAČINA, Štěpán. Clinical dietetics. Prague: Grada, 2008. ISBN 978-80-247-2256-6
- medicalnewstoday.com - The ultimate beginner's guide to intermittent fasting. Medical News Today. Miho Hatanaka, RDN, L.D.
- healthline.com - Pros and Cons of 5 Intermittent Fasting Methods. Healthline. Cecilia Snyder, MS, RD
Weight loss and intermittent fasting: what is it?
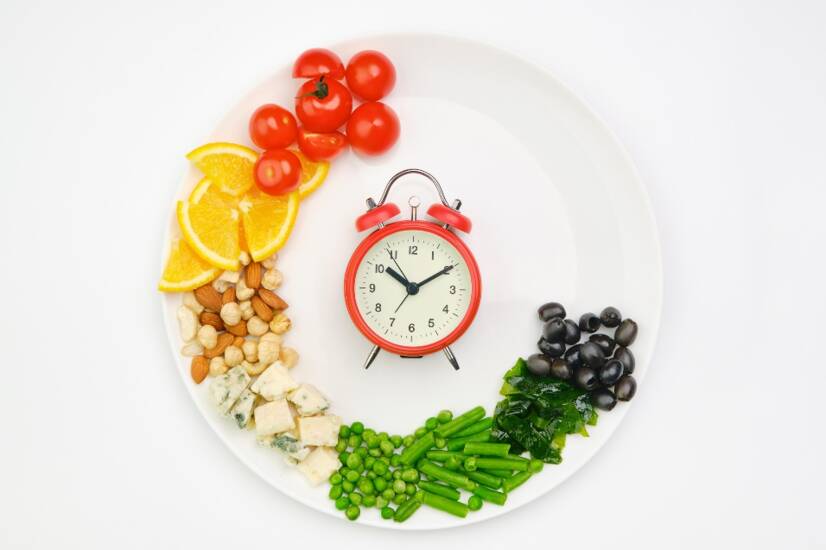

Intermittent fasting, otherwise known as intermittent fasting, is a relatively popular way of eating and losing weight. What is the main principle of intermittent fasting? What are its benefits and who should avoid it?
Article content
Intermittent fasting has become a well-known method of dietary modification in recent years. This system is based on a period of eating followed by a short fast.
It does not have to be exclusively a reduction diet, as intermittent fasting is also presented as a long-term method of eating.
The advantages, disadvantages, exact principle, methods, results and many other interesting information can be found in the article.
The principle of intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting means time-limited eating. It is known by the acronym IF.
It is not exclusively a diet that restricts certain types of foods or macronutrients in the diet.
Rather, it is a way of eating that determines when foods are eaten.
An intermittent fasting diet consists of a period of eating and a period of deliberate calorie restriction. Thus, the individual does not restrict him/herself during the eating period and eats in a normal but healthy manner.
During the fasting period, on the other hand, he/she consumes nothing except unsweetened beverages (water, tea, coffee...).
The basic idea of intermittent fasting is to reduce the amount of calories consumed, which in turn leads to weight and fat loss.
Since the key to weight loss is a caloric deficit, IF is just one of the ways to achieve your dream figure and shed excess pounds.
Intermittent fasting is a relatively simple way of eating that is popular with a large number of people around the world. Many studies also confirm the beneficial health effects of short-term "fasting".
Intermittent fasting in practice
The basic principle of IF in practice is the regular alternation between periods of fasting and periods of normal eating.
It's all about the times we eat. Of course, it also depends on what foods we eat.
An IF diet should be healthy, wholesome, nutritious and high in vitamins, minerals, protein and fibre.
The best way to start intermittent fasting is to gradually add more hours of fasting into one 24-hour day.
Intermittent fasting offers a variety of time-based eating methods:
- The 16/8 method (the most commonly used)
- The 5:2 method
- The eat - stop - eat method
IF 16/8 method
This most commonly used method involves skipping breakfast and reducing the meal time to 8 hours.
In real practice, this means that the individual eats, for example, from 12:00 to 20:00, and the last meal is followed by a 16-hour fasting period from 20:00 to 12:00 the next day. The individual will therefore sleep through a large part of the fast.
In the beginning, it is common to experiment with different times to see which time period works best for you. Time windows are individual due to employment, sleep hygiene, or personal preferences.
However, you can adapt this schedule to your own needs. If you can't imagine starting the day without breakfast, you can skip dinner. Conversely, if you don't feel like eating in the morning and like to eat in the evening, skip the breakfast period.
The important thing is to follow the 16/8 ratio.
However, for beginners, it is advisable to start with a shorter fast and gradually add hours of fasting to feel physically and mentally well.
This method is the most natural way of intermittent fasting. This diet is also known as the leangains protocol made famous by fitness expert Martin Berkhan.
During the fasting period, it is necessary to take in plenty of fluids, especially plain water, mineral water or unsweetened teas. Unsweetened coffee is also allowed.
However, even intermittent fasting will not do wonders for excess kilograms if an individual consumes excessive calories during an eight-hour meal and "catches up" by eating during the fast.
A calculator can help you calculate your calorie requirements:
- Calculating BMR - Calculator: What is my basal metabolic rate?
- Calculator: daily calorie intake TDEE - energy requirement + calculation
IF method 5:2
When eating according to this reduction method, the individual chooses two arbitrary days in one week on which to limit the calorie intake of the diet to 500-600 kcal per day.
On the remaining five days of the week, he/she eats a normal but healthy diet.
The reduction in caloric intake again creates a caloric deficit, which in turn leads to weight loss and fat reduction. Again, the results are valid only if the individual does not compensate for the fasting period by overeating and does not replenish the calories 'lost' during the fasting period.
This method is more suitable for people who know their calorie intake, energy expenditure and are mentally and physically stable.
This is why the 16/8 method is the most popular with ordinary people. It is more natural, similar to a normal regime and less drastic at the beginning.
How to lose weight in a healthy way? Diet for weight loss. Beware of nonsense diets
IF eat - stop - eat method
In this case, it is an intermittent fast that the individual keeps for 24 hours once a week.
A significant disadvantage of this method is that 24 hours can be quite mentally and physically demanding for many people.
In practice, an eat-stop-eat regime looks like no food intake from the evening of the first day to the evening of the second day. Or from breakfast on the first day to breakfast on the second day.
The goal is to go 24 hours without eating. Coffee, water and other non-sweetened liquids without calories are allowed.
As with the previous methods, it is not recommended that an individual take in excessive calories the day after the fast in what is called binge eating and overeating.
This method is mentally and physically demanding. Therefore, it is suitable for experienced fitness individuals who know their body, energy intake and expenditure.
For beginners, it is possible to start with a fast lasting only 16 hours.
How to lose weight at home and healthily? Suitable diet, exercise and supplements
Advantages and disadvantages of intermittent fasting
Benefits
During fasting, several internal processes take place in the human body at the cellular level. Cell renewal, metabolism and reactions take place that reduce the oxidative effect on cells and thus strengthen their protection.
The reparative process of removing damaged cells and metabolites is technically called autophagy.
During fasting, the body begins to burn off stores and substances that were previously unnecessary and redundant. Temporary fasting can aid in the regeneration of the digestive tract as it is "cleansed" and is in a so-called resting mode.
Blood sugar levels fall and growth hormone and noradrenaline levels rise. These processes lead to an acceleration of metabolism and loss of body fat.
However, fasting is not starvation.
It is important to note that there is a difference between fasting and starvation. During a short-term fast, the body must be in good physical and mental condition. Conversely, during a fast, the body is forced to survive by using up vital tissues and supplies.
The benefits of a properly set intermittent fast:
- Prevention of cardiovascular disease
- Promoting metabolism and fat loss
- Cell repair (autophagy)
- Regeneration of the digestive tract
- Support weight loss
Disadvantages
If the fast is prolonged or starts too early in the day, there is a risk that the individual will feel hungry when falling asleep. The feeling of hunger may subsequently impair the quality of sleep due to a reduction in blood sugar levels.
Poor quality sleep subsequently leads to nervousness, lack of concentration and excessive fatigue. Therefore, the 16/8 method is suitable for beginners and the general population.
Improperly set intermittent fasting can have a negative effect on the digestive tract in terms of constipation, indigestion or bloating. The main risk is an insufficient supply of nutrients, especially vitamins, minerals and protein.
Excessive hunger, abdominal bloating, nervousness, irritability and low mood are common. However, after a certain period of time, the body gets used to fasting and readjusts to a given eating rhythm.
If these negative physical and mental feelings persist for a long time, intermittent fasting may not be the best option for you.
Possible risks and disadvantages of intermittent fasting:
- Nervousness and irritability
- Fatigue and lack of focus
- Poor sleep quality
- Insufficient nutrient intake
- Low blood sugar
- Negative effect on digestion
- Disruption of the menstrual (ovulatory) cycle
For whom is intermittent fasting not suitable?
This way of eating is particularly not suitable for pregnant women, malnourished individuals, diabetics and those with eating disorders.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding require a woman to have a regular intake of nutrients necessary for the proper development of the baby.
Intermittent fasting is also not recommended for women who are currently trying to conceive. If they do not receive enough of the necessary nutrients during the fast, undesirable changes in the menstrual and ovulatory cycles may occur.
Fasting is not suitable for people with diabetes, hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) and blood pressure problems. Some sources state that intermittent fasting can increase insulin sensitivity and alter blood sugar control.
Intermittent fasting is also not suitable for the elderly (seniors) and children during the growing season.
If you are unsure about the combination of the IF diet and your diagnoses, medical condition or drug therapy (medication), consult a professional.
Intermittent fasting and weight loss: does it work?
The basis of body fat reduction is a caloric deficit, and therefore lower energy intake than expenditure.
Intermittent fasting, thanks to the fasting window, eliminates calorie intake from the diet and thus reduces energy intake.
Thus, it can be said that this type of diet has some benefits and has helped many individuals with weight and fat reduction. However, as with any other diet, the calorie deficit rule must apply.
Therefore, if an individual were to eat an intermittent fasting system but was not in a caloric deficit, there would be no reduction in body fat.
Interesting resources
Related