Digestive disorders
Digestive disorders include
- Pancreatic disorders
- Oesophageal disorders
- Disorders of the gallbladder and bile ducts
- Liver disorders
- Gastric disorders
- Intestinal disorders
- Peritoneal disorders
- The category you were looking for was not found. Please try another one.
- List is empty.

Liver failure
Liver failure means that the liver is not adequately performing its functions. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate treatment.

Lactose intolerance
Consuming milk and lactose can cause health problems, especially digestive problems. What is the difference between milk allergy and lactose intolerance? What are the symptoms of dairy intolerance?

Non-specific intestinal inflammation - IBD
Nonspecific intestinal inflammation affects mostly young people between the ages of 20 and 35. The incidence of this disease is steadily increasing. The main representatives of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Why does inflammation arise and how does it manifest itself?
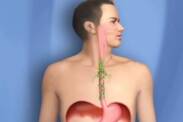
Oesophageal cancer
Oesophageal cancer is a dangerous and malignant disease that can be asymptomatic for a long time. Once the issues start appearing, it is indicative of a disease that is in an advanced stage. This malignant tumour is the sixth most common cause of death. It occurs three times more often in men than in women, and increasingly so.

Cancer of the oral cavity
Oral cancer is a serious cancer. It has a high mortality rate due to late diagnosis at an advanced stage. What are its first manifestations, prevention and treatment options?
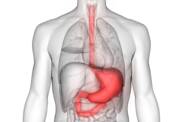
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most dangerous forms of cancer. It has a very high mortality rate and progresses rapidly and aggressively.
Peptic ulcer disease
A peptic, or gastric (stomach), ulcer is an open wound of the inner lining of the stomach. Pain is one of the symptoms. Why does it develop?

Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis affects the digestive tract. It is one of the most common diarrheal diseases of both children and adults.

SIBO - bacterial intestinal overgrowth syndrome
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (abbreviated SIBO) is a syndrome characterized by an increased or abnormal type of bacteria in the small intestine. It mainly causes problems with digestion and absorption. What causes SIBO and how does the disease manifest itself?

Cancer of the stomach
Gastric cancer is a cancer with a high mortality rate. What are its first symptoms and treatment options?

Teniasis
Teniasis is a parasitic intestinal disease caused by tapeworms. Worldwide, it is one of the most widespread parasitic diseases.
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is considered one of the most common parasitic diseases in humans.
Typhoid fever
Typhoid fever is an infectious fever. It is also referred to as intestinal fever because it affects the small intestine. The infection only attacks humans. It occurs mainly in areas with low hygiene standards, in poor countries and in areas with a high concentration of population.
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a long-term inflammatory disease of the terminal part of the large intestine, with possible spread to the whole colon. This autoimmune inflammation is characterised by bleeding, suppuration and ulceration of the intestinal mucosa. Its cause has not been clarified. It is characterised by alternating periods of calm and the onset of discomfort such as pain, diarrhoea and bleeding on stool.

Dyspepsia
Dyspepsia refers to a digestive disorder. It can be part of a variety of gastrointestinal diseases. Examples of problems include abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain and gas.

Hernia
The streak is a common disease and occurs in newborns, children, men, women and the elderly. The problem is a weakened abdominal wall.
Portal hypertension
Portal hypertension is serious for several reasons. Firstly, the causes that provoke it, and secondly, the complications that arise from it.

Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is a haemorrhagic infectious fever most commonly found in areas of Africa and South America, where it often causes epidemics and numerous deaths. The disease is virtually incurable. The only prevention is vaccination, which is compulsory when visiting these countries.









