- curaprox.com - Information from CURAPROX
- medlineplus.gov - Bleeding gums
Bleeding gums: do you know the most common causes?
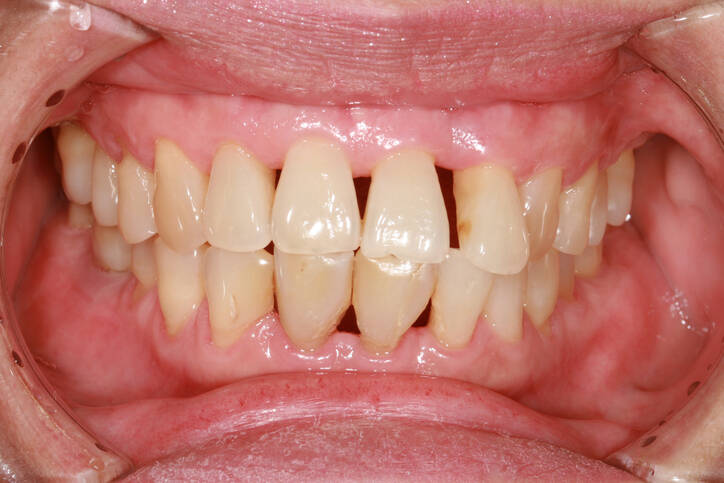
Bleeding is a problem that indicates inflammation or other diseases of the gums. For example, gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontitis. Its cause is also insufficient and improper oral hygiene. The risk is higher in diabetics, smokers and women due to hormonal changes.
Very often bleeding occurs after brushing the teeth or while eating.
Bleeding in gingivitis
Gingivitis is technically called gingivitis and is an infection. The infection forms on the gums, but also on the teeth. It is a bacterial infection of the plaque. The bacteria release toxic substances and the body defends itself by inflammation.
The affected area is red, swollen and pain is also present. The gum is both softer and more fragile. It is therefore more susceptible to injury, for example when brushing the teeth, which causes bleeding.
Gingivitis is mainly related to a lack of hygiene, which allows plaque to form. This is formed by bacteria that use sugars, converting them into organic acids. The acids then act on the enamel of the tooth, which they demineralise.
As a result, the enamel of the tooth softens, cavities are formed and tooth decay develops. Thus, gingivitis is also dangerous from this point of view. If it is left untreated and the bleeding gums are ignored, periodontal disease occurs.
Periodontitis as a cause
Periodontal disease is manifested by bleeding gums, but also by sensitive teeth. In the later stages, there is also wobbling of the teeth and pain. Periodontal scabs also form and purulent discharge from the gums may be present. Periodontal disease is a disease of the hanging apparatus of the tooth itself.
It causes degeneration of the tooth, the gum tissue develops a so-called tooth trunk and the tooth wobbles. Severe bleeding is also present. This is not due to inflammation, but rather to the disruption of the suspension system.
TIP: For more information, see the article on periodontal disease.
Bleeding in periodontitis
In addition to periodontal disease, bleeding gums are also present in inflammation of the hanging apparatus of the tooth (periodontitis). This is an inflammation located on the gum tissue adjacent to the tooth.
If this inflammation is ignored, it tends to spread to the root of the tooth as well. A gingival crease is also formed here. This is a kind of canal around the edge of the tooth that forms when the soft connective tissue of the gum around the tooth is disturbed. Food debris settles there and exposes the tooth socket.
As a result, the tooth wobbles and loosens. Bleeding gums are a symptom that should make a person visit a dentist to prevent further development of any of the possible complications.
An important part of any treatment is the need to change your approach to dental hygiene.
Hygiene and improper dental treatment
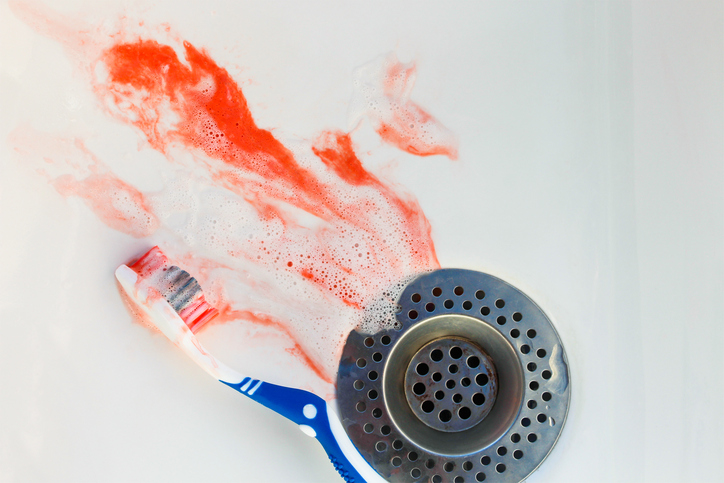

Bleeding can be a sign that a person should take more care with their dental hygiene. Even improper or inappropriate hygiene can cause gum problems and therefore bleeding. Other causes of bleeding can be a toothbrush that is too hard, or unsuitable dentures, bridges, crowns, braces or fillings.
Bleeding is a signal to see a dental hygienist. He or she can instruct you on how to change your brushing habits to prevent inflammation.
Other causes of bleeding gums
Difficulties with bleeding gums also occur in the case of diseases that are not directly related to the oral cavity and its mucosa. Inflammation of the lining of the mouth, and therefore the gums, is a risk factor for complications such as heart attack, atherosclerosis or erectile dysfunction.
With bleeding gums, it is important to think about:
- Diabetes
- liver disease, due to impaired blood clotting
- clotting disorders
- vitamin K and C, B12 deficiency
- iron deficiency, folic acid deficiency
- malnutrition
- leukaemia
Inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity and gums is more common in:
- diabetes
- smokers
- pregnant women
- during hormonal changes (menstrual cycle, menopause, pregnancy)
- improper nutrition
- use of certain medications (anti-clotting drugs such as warfarin, acetylsalicylic acid, heparin, some epilepsy drugs)
- chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- increased stress levels
- reduced immunity
- dentures and braces
- old age
Video about bleeding gums
Diseases with symptom "Bleeding gums"
Interesting resources
Related










