- The miraculous journey into life: Rainer Jonas
- Langman's Medical Embryology: Thomas W. Sadler
- anat.lf1.cuni.cz - Introduction to embryology - the development of organ systems. Petr Valášek
- nhs.uk - You and your baby at 4 weeks pregnant
- whattoexpect.com - 4 Weeks Pregnant
- verywellfamily.com - Week 4 of Your Pregnancy
- healthline.com - 4 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tip an More
Week 4 of pregnancy: skipping my period. Am I pregnant?
The fertilised egg finishes its journey and joins the uterus this week. It attaches to it, which is called implantation or nesting. Some women only find out they are pregnant now when they miss their periods.
Article content
4th week of pregnancy, nearing the end of the 1st month.
Now a new stage in your life will also begin and your body will start to change over the course of 36 weeks.
Pregnancy is counted from the first day of your last period, not from the day of conception.
You can read more about the length of pregnancy in the article:
How long does pregnancy last? How many days, weeks and months?
Most women with unplanned pregnancies do not even know they are pregnant at this time, that a fertilized egg has nestled inside them and a new life is beginning to grow.
How is your baby developing in early pregnancy?
The blastocyst has completed its journey from the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it has attached itself to the wall of the uterus and become firmly embedded in it. This will take another 8 months.
The uterus accepts the egg and doesn't treat it as a stranger.
The cells of the fertilized egg are likely to produce some kind of genetic codes that signal the mother's body their shared genetic code. They say "I am your baby" and so the lining of the uterus allows its nesting and important contact.
Your baby has begun to change from a clump of cells called a blastocyst into an embryo.
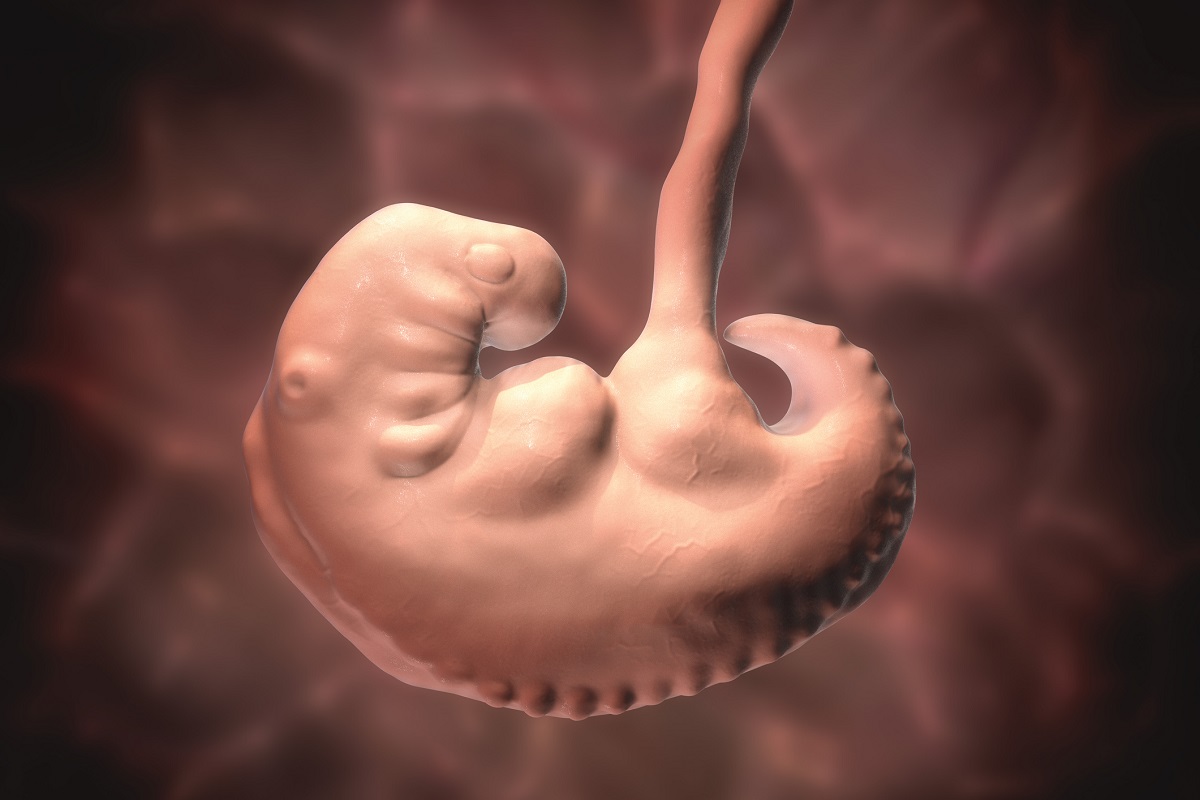
Now comes the period of development and growth. By the end of the pregnancy, the fetus must have developed organs, limbs, a heart and a brain. By the time it is born, it has eight months to grow, gain weight, its organs must be formed, perfected and fully functioning.
In order to develop, the fetus needs to be well supplied and nourished.
Immediately after attachment in the womb, a great cell division takes place.
One part forms your baby and the other forms the placenta.
At week 4, the fetus begins to make contact with the mother's body. It is in a sac called the amniotic sac, which is filled with fluid. Inside the sac is the embryo.
The outer amniotic sac develops into the placenta. Cells from the placenta attach to the uterus and create a rich blood supply. This allows the placenta to nourish and oxygenate the fetus.
The uterus responds immediately to the nesting. It begins to produce fats and carbohydrates at the nesting site so that the embryo can take them in and develop.
Around the nested egg, cavities form, which leak the mother's blood in the small amount needed to supply the baby. This period is short. The embryo grows rapidly. Tendrils and fibres develop, penetrating deep into the uterine wall. These develop into the placenta, which will nourish the growing foetus until birth.
The embryo becomes an embryo around day 12 after fertilisation, when the amniotic sac forms. Along with the amniotic sac, the yolk sac forms, which later integrates into the digestive tract of the fetus.
The embryo still takes nourishment from the yolk sac, which is attached to it. In a few weeks, the placenta will fully develop, which will supply and nourish the fetus.
The embryo and its cells multiply rapidly. Each of the cells contains the genetic program that will develop into a human being.
The embryonic period
The embryonic period runs from the third to the eighth week of development.
It is the period when the three germ leaves give rise to the tissues and organs of the embryo.
At the end of the embryonic period, the major organ systems are formed
There are three layers in the inner part of the embryo. From each of them, different parts of the fetal body develop.
- From the inner layer, called the endoderm, develops the lining of the respiratory, urinary and digestive systems, the stomach, liver, pancreas, bladder
- The middle layer, called the mesoderm, develops the cardiovascular system, heart, blood vessels, muscles, bones, genitals
- The outer layer of ectoderm will form the brain, nervous system, skin, hair, nails and tooth enamel
In the next 6 weeks, the fetus will begin to develop organs, nervous system and connective tissue.
You can read more about fetal development in our article:
Pregnancyby weeks: How does pregnancy and fetal development work?In it you can read how your baby is growing and developing, what symptoms of pregnancy may accompany you and what examinations await you in the clinic.
The development of twins
The first signs of pregnancy may be stronger if you are expecting twins. There is a higher level of hormones in your body. You may think you are pregnant for a longer period of time. The first symptoms have already started.
Nothing may be visible on an ultrasound at this time yet. There is no way to confirm a multiple pregnancy yet, but high levels of hCG and progesterone may suggest that more than one new life is developing in your uterus.
Changes in a woman
Approximately 25% of women experience bleeding during implantation of the egg into the uterus.
This usually manifests itself as light bleeding. This may occur before you expect your period. Therefore, some women who used to have light periods may mistake implantation for menstruation and not know they are pregnant.
In most cases, they will miss their periods.
When menstruation is missed or when even light spotting is suspected to confirm pregnancy in the early stages, it is advisable to use a home pregnancy test. The pregnancy test is highly sensitive to elevated levels of hCG in the urine early in pregnancy.
As early as day 12 after fertilization, the egg produces the hormone hCG. After 4 weeks, hCG levels range between 5 and 426 mlU/ml.
If you have used a pregnancy test and two lines appear, even though the second line may still be faint and not as clear as a neonate, we can most likely welcome you to the club of expectant mothers.
You can use our pregnancy calculator to calculate your due date based on your last period.
Immediately after confirming the pregnancy with a pregnancy test, a woman will visit her gynecologist to confirm the pregnancy. The doctor will take blood for a pregnancy hormone test to confirm the pregnancy.
Sonographically, the gestational sac is only visible from the 4th-5th week of pregnancy. Even though a little person is developing inside you, it is still only a few millimeters long at this week. It is very difficult to observe by sonography.
You can read more about ultrasound in pregnancy in the article:
Ultrasound in pregnancy: fetal size, what is fetal biometry?
Simultaneously with the development of the fetus, the mother's breasts begin to produce milk. Your breasts are sensitive to touch and enlarged.
You may experience early pregnancy symptoms, often similar to premenstrual syndrome, including bloating, abdominal cramps, mood changes, and a feeling of tightness in the breasts.
Read also:
No, false, possible or certain first signs of pregnancy. When do they appear?
Other moms-to-be experience nothing at all. It's individual for each woman and for every single pregnancy.
What we recommend
- The most suitable form of vitamin supplementation is over-the-counter prenatal vitamins in the pharmacy. They are precisely put together for the requirements of the pregnant woman and her developing fetus.
- If you don't want to take vitamins in tablet form, try to prefer a balanced diet with sufficient vitamins and nutrients needed for fetal development.
- Supplement with vitamin D, which you can supplement with sunshine. Vitamin D maintains healthy teeth and bones, and helps absorb calcium from the diet. Vitamin D is found in milk, egg yolk.
- Supplement omega-3 fatty acids. They are a major component for brain and retinal support and are also important for fetal brain development.
- Folic acid, which belongs to the group of B vitamins, has a positive effect on proper fetal development, on proper cell division, promotes the growth of germ tissues during pregnancy and helps blood formation. You can find it in leafy greens, peas, asparagus, but also in avocados, eggs, nuts.
- Vitamin A is needed for vision, bone growth and fetal development. It is found in spinach, broccoli, carrots, lettuce, eggs.
- For sensitive breasts, wear a comfortable and supportive bra.
- Avoid smoking, both active and passive, and alcohol.
- If you feel tired early in pregnancy, try to sleep during the day.
You might be interested in:
Gallery


Interesting resources
Related










