- prolekare.cz - The role of nutrition in the prevention of cognitive impairment in older age
- prolekare.cz - Effect of oxidative stress on male fertility
- prolekare.cz - The use of vitamin E in the prevention of venous thromboembolism in women
- healthline.com - How Can Vitamin E Oil Help the Appearance and Health of My Face?
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Vitamin E in dermatology
- jamanetwork.com - Yellow Nail Syndrome Response to Vitamin E
- ods.od.nih.gov - Vitamin E
Vitamin E and its effects. How is deficiency or excess manifested? + Food sources

Vitamin E is a known antioxidant. What other effects does it have? Can we overdose on it? Where can we find it?
Article content
Vitamins E belong to the group of fat-soluble vitamins. The human body cannot make them. Therefore, they must be taken in through the diet.
Vitamin E was first described in 1922 by the scientist Herbert M. Evans and his assistant Katherine Bishop. In 1936 it was given the name tocopherol.
Vitamin E has eight basic forms. Specifically, 4 tocopherols (alpha, beta, gamma, delta) and 4 tocotrienols (alpha, beta, gamma, delta). Both groups have similar biological activity. Alpha tocopherol is considered the most potent.
Vitamin E is considered an important antioxidant. It is very important for the proper functioning of the human body.
It protects cells from the harmful effects of free radicals. It protects low-density lipoprotein cholesterol-rich (LDL) proteins from oxidation.
Gamma-tocopherol affects platelet aggregation. It also has an effect on blood vessel dilation. It is also involved in nucleic acid metabolism.
Vitamin E is responsible for normal growth, development and function of muscles. It is important for the proper function of blood circulation. It also affects the function of the nervous and digestive systems.
Vitamin E protects the human body against various diseases:
- slows down the development of cataracts
- prevents atherosclerosis
- is used as an adjunctive treatment for fertility disorders
- protects the body from the toxic effects of cigarette smoke

The effect of vitamin E on our organism
1. Vitamin E and its role in the prevention of cognitive disorders
The results of some studies show that approximately 15 to 45% of patients with dementia suffer from malnutrition.
Patients who suffer from dementia and malnutrition at the same time have a more rapid progression of dementia. They respond less well to treatment and have an increased mortality rate. This suggests that maintaining the patient's nutritional status is an integral part of dementia treatment.
In the case of Alzheimer's disease, nutritional deterioration occurs in the earliest stages. Low levels of vitamin B, vitamin C and vitamin E have been reported in these patients.
You might also be interested in.
The causes of low levels of the above vitamins are varied. In the following section, we will discuss some of the explanations.
Patients suffering from dementia are unable to choose a sufficiently varied diet containing various vitamins. In these patients, there is a reduced synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid.
It is believed that dementia patients have an increased consumption of vitamins by the brain affected by neurodegeneration.
Docosahexaenoic acid is a biologically active omega-3 unsaturated fatty acid. Its main source is fish. It contributes to normal brain function and normal vision. It also contributes to the maintenance of normal heart function.
Have you heard of the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet is based on a high intake of fruit, vegetables, pasta, fish and olive oil. Various spices (rosemary, oregano, thyme), garlic and onions are used in the preparation of dishes.
Moderate consumption of wine with meals is also recommended. The intake of dairy products and meat is limited.
According to some studies, the Mediterranean diet reduces the development of dementia, Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. It has a protective effect on cognitive decline in old age.
The cognitive protective effect of the Mediterranean diet is explained by several mechanisms:
- the anti-inflammatory effect of a higher intake of omega-3 fatty acids
- the effect of antioxidants (vitamin C and vitamin E) in reducing oxidative stress
2. What is the effect of vitamin E deficiency on our eyesight?
In the eye, vitamin E deficiency is manifested by swollen eyelashes, cataracts, age-related macular degeneration and atrophy of the eye movement muscles.
One of the risk factors for age-related macular degeneration is a lack of antioxidants in the diet.
Their deficiency leads to a slower removal of toxic free radicals, which are produced in the retina in the process of light processing.
3. Vitamin E and its role in the prevention of venous thromboembolism in women
Thromboembolic disease of venous origin is the third most common cardiovascular disease. It has been shown that the incidence of venous thromboembolic events was reduced in women who took vitamin E.
Vitamin E is known to have an anticoagulant effect. It can inhibit vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors and reduce platelet adhesion.
A study was conducted abroad to test its effect on the incidence of cardiovascular disease. The research lasted ten years.
It involved 39 876 women over the age of 45 who took either vitamin E at 600 IU every other day or a placebo.
The conclusion of the research was that vitamin E may reduce the risk of venous thromboembolism in women who have a genetic predisposition.
You might be interested in: thromboembolic disease, why does it occur, how is it related to pulmonary embolism?
4. Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men. It mainly affects American and European men. Nutrition plays an important role in the etiology of this disease.
The results of several scientific studies have shown that vitamin E can reduce the risk of prostate cancer in smokers.
In patients who took 50 mg of vitamin E, the incidence and mortality rates were reduced by 30 to 40%. A reduced risk of prostate cancer metastasis was also noted.
5. Vitamin E and male fertility
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species are very important for the proper function of sperm. Their positive effect only occurs at certain concentrations. Above a certain level, they act in the form of oxidative stress.
Their negative effect leads to cell damage. It is believed that 30 to 80% of cases of male infertility are due to oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
The role of antioxidants is to maintain such concentrations of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species that cell damage is prevented.
The antioxidant protective mechanism consists of:
- preventing the formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
- trapping and scavenging the radicals produced
- repairing damaged molecules
Antioxidants that provide the above mechanisms include vitamin A, vitamin C and vitamin E.
Other substances that support proper sperm function include uric acid, coenzyme Q10, taurine and hypotaurine, carotenoids (ß-carotene), flavonoids, L-carnitine, melatonin and pyruvate.
Taking antioxidants leads to:
- reduction of lipid peroxidation
- an increase in sperm motility
- an increase in sperm count
- improvement of sperm morphology
- reduction of sperm DNA fragmentation
6. Vitamin E and skin care
Vitamin E has been used in dermatology for more than 50 years. Its main role in skin care is to protect against oxidative stress.
Its effects include:
- slowing the signs of ageing - softening wrinkles
- reduction of hyperpigmentation
- protection of the skin from UV rays
- promotes cell renewal and regeneration

In practice, a cream containing vitamin E and D-panthenol is often used. It helps to reduce the signs of ageing. It reduces the appearance of wrinkles. It has a moisturising and antioxidant effect. It protects the skin from the harmful effects of free radicals.
An oil containing pure vitamin E is also a popular form.
Its effects include:
- soothing the skin after shaving, waxing and after sunbathing
- hydration
- protection against redness
- regeneration
- leaves skin supple
Other applications include a body lotion containing vitamin E. It spreads well on the skin and leaves it supple and fresh. It maintains the youthful appearance of the skin, hydrates it and slows down the aging process.
Vitamin E products are also used in hair care. Vitamin E is mainly used to prevent hair loss and to add shine to the hair. It makes it easier to comb the hair. It improves the overall quality of the hair.
Have you heard of yellow nail syndrome?
Symptoms of this disorder include slow nail growth, yellow nails, lymphedema and chronic respiratory disorders (chronic bronchitis, sinusitis). Vitamin E is taken at a dose of 1000 IU once a day for 6 months.
Yellow toenails and fingernails. Aesthetic defect or health problem?
What are the food sources of vitamin E?
Major sources of vitamin E include vegetable oils, nuts, whole grain cereals, avocados, broccoli and leafy greens.

The following table lists sources of vitamin E
| Foods | Milligrams (mg) per serving |
| Wheat germ oil (1 tablespoon) | 20,3 |
| Sunflower seeds, dry roasted | 7,4 |
| Dry roasted almonds | 6,8 |
| Sunflower oil (1 tablespoon) | 5,6 |
| Safflower (thistle) oil (1 tablespoon) | 4,6 |
| Dry roasted peanuts | 2,2 |
| Corn oil (1 tablespoon) | 1,9 |
| Broccoli (cooked, ½ cup) | 1,9 |
| Soybean oil (1 tablespoon) | 1,1 |
| Kiwi (medium) | 1,1 |
| Mango (chopped, ½ cup) | 0,7 |
| Tomatoes (medium) | 0,7 |
| Spinach (raw, 1 cup) | 0,6 |
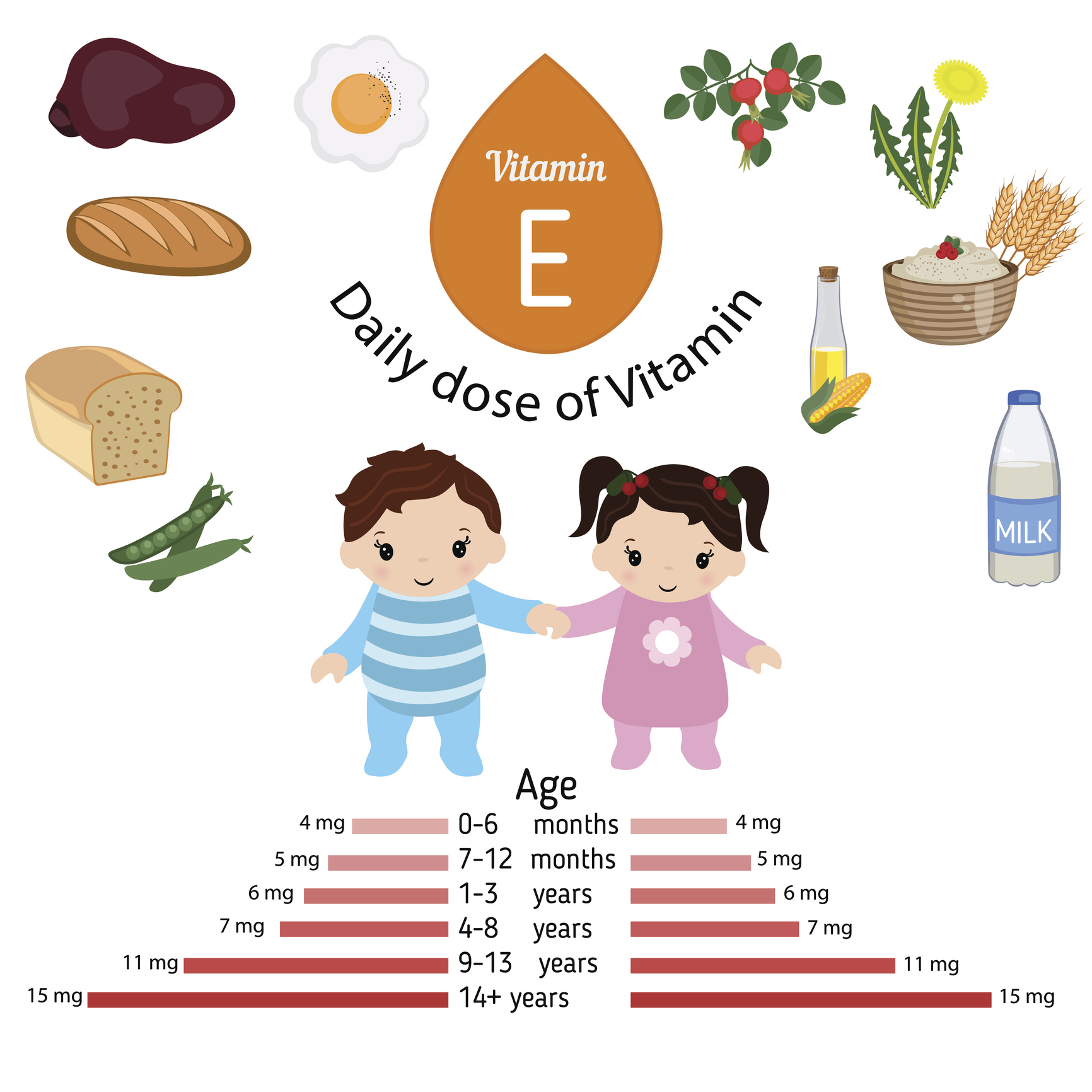
The recommended daily allowance of vitamin E depends on the age and physiological state of the person. In particular, on its intake from the diet.
For example, the recommended daily dose (15 mg) can be obtained from 170 g of canned tuna in oil. In 50 g of almonds, approximately one third of the recommended daily dose of vitamin E is found.
Alpha-tocopherol has the highest biological activity. It is also referred to as natural vitamin E. It is found in natural food sources.
In commercially produced preparations, so-called synthetic vitamin E is used. This is actually a racemic mixture of all 8 isomers of alpha-tocopherol.
The level of vitamin E in the human body depends on the intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The results of scientific studies have shown that a high intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids negatively affects vitamin E levels.
In practice, vitamin E is often combined with vitamin C to reduce its degradation. The two vitamins are appropriately supplemented in their proportions.
The following table shows the combinations of vitamin E available in pharmacies
| Combinations | Application form | Effects |
| Fish oil + vitamin E | softgel |
|
| Coenzyme Q 10 + vitamin E | caspula |
|
| Selenium + zinc + vitamin E | tablets |
|
| Vitamin D3 + vitamin E | capsules |
|
| Coenzyme Q10 + vitamin E + selenium | capsules |
|
| Vitamin D 3 + vitamin E + inulin | capsules |
|
| Magnesium + vitamin B6 + gentian + ginkgo + vitamin E | tablets |
|
Vitamin E needs the presence of pancreatic enzymes and bile acids to be absorbed into the blood. Because it belongs to the group of fat-soluble vitamins, the human body builds up reserves of it. For this reason, its reduced level is not immediately apparent.
Vitamin E deficiency can manifest itself:
- anaemia
- shortening of the survival time of red blood cells
- fertility problems
- degeneration of the gonads
- nerve and muscle disorders (gait disturbances, degenerative changes in peripheral nerves)
In pregnant women, reduced vitamin E intake can lead to spontaneous abortion or premature birth. In newborns, vitamin E deficiency causes haemolytic anaemia, oedema and thrombocytosis. Higher levels of vitamin E can lead to sepsis.
How does excessive intake of vitamin E manifest itself?
Excessive intake of vitamin E manifests as:
- gastrointestinal disorders
- general fatigue
- muscle weakness
- inappetence
Interesting resources
Related










