The most common causes of tinnitus? Find them here in one place

It comes unexpectedly, lasts unpredictably long and we never know when it will recur. Unpleasant humming, ringing, ringing or whistling in the ears is a phenomenon that occurs repeatedly in association with certain situations and diseases. Yet we do not know much about the exact mechanism of its occurrence.
Article content
Tinnitus or whistling is often accompanied by headaches or dizziness. Sometimes the cause is obvious, other times even experts wonder about it.
Tinnitus auris (Latin: tinnire - to ring, whistle ⁄ auris - ear) is an unpleasant sound perceived only by the patient himself. For each one it has different intensity, frequency and also the specifics of the sound are different. Tinnitus is a symptom, never a disease. In this article you will find situations and diseases for which tinnitus is almost an integral part.
What is tinnitus?
Tinnitus auris is a subjective acoustic phenomenon perceived only by the patient himself. Each patient hears sounds in a different way. An individual in tinnitus recurrence perceives sound consistently in the same way (murmur, rustle, whistle, ringing, humming). It varies in intensity, duration and frequency.
Sound propagation
Sound is a mechanical wave (oscillation) propagating in a material medium that produces a sound sensation (the exception being hallucinations). We consider air to be the conductor for the most part (but also liquid and solid media). The conductor connects the source of the sound to the receiver (in our case, the ear).
We use the unit decibel to express the intensity of noise. We consider the human threshold of audibility to be 0 dB. Whispering is a sound equivalent to about 50 dB, traffic and loud shouting range from about 80 to 100 dB. Sounds above 100 dB are already unpleasant to the human ear.
Hearing aid
The ear consists of three basic parts. The cartilaginous part - the auricle (auricula) - together with the external ear canal form the so-called outer ear. The closed space in the temporal bone with the auditory system itself form the inner ear. These two interconnecting parts are separated by an oval connective membrane called the tympanic membrane (membrana tympani).
Behind it is the middle ear cavity (cavum tympani), which contains the three auditory bones (stapes, anvil, incus and malleus). The middle ear cavity already belongs to the middle ear, which is connected to the nasopharynx by the Eustachian tube.
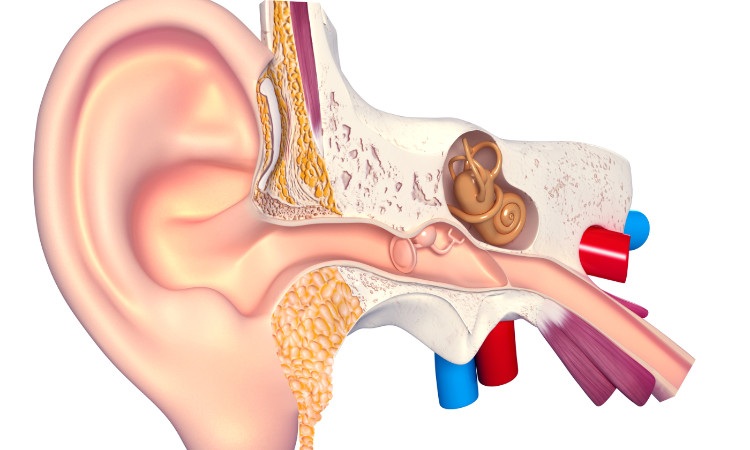
Inside the temporal bone there is a completely enclosed space in which the auditory system itself is located - the cochlea. In the cochlea is the organ of Corti. It is in the organ of Corti that the receptors of hearing are located.
The most likely causes of tinnitus are
This acoustic phenomenon occurs regularly in some of the same situations and with some of the same diseases in different people. It is an unmistakable fact that allows us to assume that these disease states and exposure to risky situations are the cause of its occurrence.
Acoustic (sound) trauma
Chronic acoustic trauma refers to damage to hearing caused by chronic noise and vibration. It usually occurs in people working for long periods in unsuitable working environments where they are exposed to permanent, persistent sound impulses of greater intensity. Chronic hearing damage occurs gradually. Most such hearing loss is preceded by tinnitus.
People at risk are workers who are exposed to excessive noise loads above 60 dB in the course of their occupation.
The ideal noise level in the working environment should be 40 dB and should not exceed this value. This includes, for example, those who work in night-time businesses, with chainsaws, grinders and other noisy tools.

Acute acoustic trauma is an unexpected, rapid sound impulse of very high intensity (more than 100 dB). It is of short duration. It causes a sudden change in the pressure acting on the ear structures and threatens to cause permanent tinnitus. In addition to tinnitus, permanent hearing damage (gunshot, explosion) or injury from a sudden change in pressure can occur.
If the sound is intense (180 dB), damage to the eardrum up to rupture occurs.
Barotrauma (trauma caused by a pressure wave)
Barotrauma is the mechanical damage to organs caused by air pressure. The pressure acts on otherwise incompressible organ structures, causing damage to them. It usually occurs simultaneously with acoustic trauma, because, for example, a bomb explosion is always accompanied by both sound and increased pressure.
Ear barotrauma includes damage to the eardrum, rupture of the eardrum, displacement of the auditory system (impingement of the tympanic membrane into the vestibular space, fracture of the ear bones), brain damage (brain laceration, swelling, bleeding).
Diseases of the ear

- A sebaceous plug (cerumen) can form in the ear when there is an overproduction of earwax, but also when there is a lack of hygiene or improper cleaning of the ear (e.g. with cotton buds). Sebum sticks to the tympanic membrane. This can cause a clogging of the ear, temporary unilateral hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Damage to the eardrum occurs as a result of acoustic sound trauma, barotrauma, mechanical damage/piercing of the eardrum during ear cleaning, but in case of trauma to the ear. At best, tinnitus, bleeding may occur.
In worse cases, the patient may permanently lose hearing on the affected side.
- Otitis media is an acute infectious disease of the middle ear caused mainly by bacteria, rarely by viruses. It is very typical of childhood. The disease is manifested by severe ear pain (sometimes bilateral), headache, purulent discharge from the ear, hearing loss, tinnitus, general weakness and fever.
- Inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis) is a rarer but also serious disease of the inner ear. Unlike otitis, it occurs predominantly in adulthood. The causative infectious agent is dominated by viruses (most commonly herpes). It may also arise as a secondary complication of head injuries. It presents with headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, balance disturbances and unilateral hearing loss to deafness.
Most of these inflammations leave no lasting effects.
- Otosclerosis means a change in the bone capsule of the inner ear as a result of a metabolic disorder. The bones of the inner ear (stirrup, anvil, hammer), which normally transmit sound, become immobile. Tinnitus is sometimes the first symptom of this process.
Subsequently, unilateral to bilateral hearing loss occurs.
- Diseases of the Eustachian tube: Bacterial inflammations fall into this category. They are usually transmitted from the nasopharynx, which connects the four-centimetre-long tube to the middle ear. Inflammation can spread to the middle ear. They are manifested by tinnitus, tinnitus and pain.
These include narrowing, obstruction, allergic inflammation, tumour and others.
Neurological causes
- Vestibular syndrome is a set of symptoms that arises from multiple causes when the vestibular apparatus used for balance malfunctions.
When the vestibular apparatus malfunctions, regardless of the reason for which it has formed, dizziness occurs. These may be accompanied by tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, general pallor of the patient and cold sweat.
- Meniere's disease refers to a disease of the inner ear in which there is an overpressure of its fluid. Specifically, this is an increase in pressure in the endolymphatic system of the inner ear.
The condition is characterised by a strong vertigo (vertigo syndrome) in ataxia, preceded by aura. There is a feeling of fullness in the ear, unilateral tinnitus on the affected side, as well as unilateral hearing loss (hypacusis).
- Stroke, or also cerebral ictus, stroke, apoplexy, belongs to the diseases of civilisation. It is caused by a blockage of a cerebral vessel by a blood clot, with consequent haemorrhage of a part of the brain and its subsequent infarction - ischaemic stroke. We also know of haemorrhagic stroke, which occurs as a result of rupture of a cerebral vessel with its further haemorrhage and pressure on the brain parenchyma.
Both can present with headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, visual impairment on one side, paralysis of half of the face and body, difficulty speaking, disorientation and disturbances of consciousness. Symptoms are individual to each individual depending on the size of the vessel, the type of stroke and the part of the brain it affects.
- Sclerosis multiplex or even multiple cerebrospinal sclerosis has an as yet unexplained cause. It is probably an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system in which the body's own immune system attacks the myelin sheaths of the brain and spinal nerve fibres. It is manifested by deterioration of the patient's neurological functions, instability of emotional state, muscle weakness often with convulsions, and coordination and movement disorders.
In many cases, vertigo, visual and hearing disturbances occur, in some cases accompanied by tinnitus.
- A tumour of the VIIIth cranial nerve (neurinoma acoustic) is a tumour affecting the acoustic nerve. Its growth and pressure on the surrounding area causes disturbances in the auditory pathways in the brain. It is manifested by pressure in the affected area, pain, hearing disturbances of varying degrees depending on the size of the tumour, and tinnitus.
In later stages, general symptoms typical of most cancers are associated.
- Neuroinfection is the collective name for bacterial as well as viral infections of the nervous system. It includes encephalitis, meningitis or a combination of the two called meningoencephalitis. These are serious infections. They can be fatal if not diagnosed in time and proper treatment is not initiated.
They present with severe headache, neck opposition, vertigo, tinnitus, photophobia, nausea, vomiting, high fever, chills, sweating and general weakness and alteration of consciousness.
Cardiovascular causes
.jpg)
- Arterial hypertension or elevation of blood pressure is known as a disease, but it can also occur as a secondary symptom of another disease or psychological condition. We consider high blood pressure to be >140/90 torr. When the pressure rises, the patient experiences headache, dizziness, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting, subjective sensation of impaired breathing. He is red in the face and has hot flashes, sweating, palpitations.
In each patient, the set of symptoms is individual and may not all appear.
- Increased intracranial pressure is observed in some disease states as a secondary symptom. The brain, in addition to being protected by the skull, is placed under a certain pressure in the cerebrospinal fluid. Due to injuries, intoxications, inflammations, or other diseases, such as hydrocephalus, this pressure increases.
The patient feels strong pressure, diffuse (full-body) headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, visual disturbances or squinting before the eyes, pressure or pain in the eyes and others.
- Atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries is a chronic disease of the arteries in which fat particles are deposited and form what is known as an atherosclerotic plaque. The lumen (diameter) of the vessel narrows, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the brain (cerebral hypoxia). The condition is often complicated by a blood clot getting trapped in the plaque. This leads to a re-narrowing of the vessel.
It is manifested by disorientation, disturbances of consciousness, psychological state, headaches, vertigo, tinnitus.
- Vascular malformations occur as early as infancy. Hemangiomas and other vascular malformations fall into this category. They can affect any blood vessel, in any part of the body. The most dangerous are high-flow ones, in which blood flows rapidly and under high pressure. They cause pain and bleeding.
Symptoms otherwise vary based on their localization.
- Aneurysms are arterial bulges - dilations. A blood vessel can dilate up to 1.5 times its normal thickness. A common cause is a weakening of the blood vessel wall, for example by atherosclerotic process, persistent high blood pressure or even smoking. The presence of an aneurysm can be considered a serious condition as the largest blood vessels, the arteries, are affected. The weakened wall can rupture and there is a risk of major bleeding.
An aneurysm in a closed cranial space causes pressure on the surrounding area, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances depending on its exact location, hearing disturbances with possible tinnitus.
Bone disease

- Everyone is familiar with dental diseases, mainly gingivitis, inflammation of the dental nerves and dental caries. Tooth pain can often be severe to unbearable in intensity, of a tearing nature, radiating to the ear, half of the head or even the whole head. It is accompanied by local swelling, sometimes with a suppurative process in the area of the tooth or an abscess.
The patient is attacked not only by pain, but also by tingling of the affected part, lying in the ear, tinnitus, vertigo or twinkling before the eyes.
- Diseases of the spine, especially of the cervical spine, often cause severe pain, which radiates to the surrounding area. In the case of radiation to the head, this is known as cervicocranial syndrome (CC syndrome).
It is dominated by a headache that is more intense and throbbing than the pain in the spine. Dizziness, fainting, tinnitus, tinnitus, nausea, sweating and vomiting are also present.
Paget's disease is one of the bone diseases characterised by local remodelling of the bones. Up to 70% of cases are asymptomatic. In some cases, the patient experiences pain in the affected area due to the pressure of the deformed bone. If the cranial part is affected, headaches are at the forefront, sometimes with an increase in its circumference and manifestations from the oppression of regional nerves.
These are, for example, the auditory nerve (hearing impairment, tinnitus), optic nerve (visual disturbances), oculomotor nerve (eye movement disorders), facial nerve (paralysis of half of the face) and others.
- Bone tumours, like Paget's disease, can occur in any part of the skeleton. If the skull is affected, they manifest in the same way as Paget's disease. Symptoms are caused by pressure on the brain, its blood vessels and nerves.
Injuries

- Concussion (commotio cerebri) is the most common condition after head injuries. It is a transient, functional injury whose symptoms usually resolve within 24 hours. After a severe impact, the injured person has a headache, a throbbing in the head, a feeling of a full or bloated head, and tinnitus.
These symptoms are accompanied by vegetative symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, pallor with profuse sweating.
- Injuries to the brain are variable. Injuries to the head and skull range from minor to fatal. They mainly involve compression of the brain, brain laceration, damage to the brain parenchyma, its rupture to cerebral haemorrhage. Their common features are headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting.
Depending on the severity of the condition, disturbances of vision, hearing (tinnitus), consciousness are added.
- Cerebral haemorrhage is the most serious post-traumatic complication. Depending on the intensity of the haemorrhage and the site of its occurrence, it presents with the same symptomatology as described for brain injuries in general. Cerebral haemorrhage is a life-threatening condition. Tinnitus is negligible. Depending on the rate of bleeding, the condition progresses. irreversible changes occur in the brain and the condition often ends in death.
- Fractures of the base of the skull occur only in severe injuries, such as car accidents or falls from a height. When the skull is fractured, it is certain that the traumatic event was extremely severe. It is often combined with cerebral haemorrhage or as part of other injuries in polytrauma (damage to two or more organs or organ systems). This injury is characterised by a high mortality rate.
Psychological causes

- Insomnia afflicts a large percentage of the world's population. Characteristic features are: prolonged sleeping interval of more than 30 minutes, disturbances in sleep depth, frequent awakenings during the night. It has many causes. Some of them can be corrected.
Patients suffering from insomnia wake up more tired than before falling asleep, malaise, headaches, tinnitus, physical inactivity, as well as immune disorders and, consequently, more frequent infections.
- Stress is a common phenomenon of modern times, as is insomnia, which in many cases is closely linked to it. Unpleasant situations arouse unpleasant feelings, often anxiety and fear. Patients exposed to permanent or very frequent and repeated stress have difficulty concentrating, their reactions are slowed down, they cannot express themselves well and quickly, and stammering occurs. They often have a strange feeling in the stomach, heart palpitations, rapid breathing, start to sweat, and are pale in the face.
There are also headaches, dizziness, tinnitus - usually in periods of rest as a result of stress.
- Depression is one of the causes of insomnia and sometimes a consequence of stress. More and more people are suffering from depression. The cause is usually a hopeless situation that has put the patient in a state of depression. The patient's mind is so preoccupied with the problem that he or she stops concentrating, seeks solitude, and interpersonal relationships are disturbed. Physical symptoms include palpitations, sweating, headaches, tinnitus, general weakness or trembling.
The frequency of symptoms is directly proportional to the degree of depression.
- Other psychiatric disorders besides the aforementioned depression may manifest themselves in the same way. This also applies to mental and personality disorders. In this case, tinnitus is also present.
We do not, however, include auditory hallucinations, which are common in many illnesses such as schizophrenia, paranoid psychosis and others.
Groups of people at risk of developing tinnitus
- People exposed to excessive noise (construction workers, night workers)
- people exposed to changes in pressure (divers, climbers, aviators, astronauts...)
- people with poor hygiene habits (earwax plugs, frequent ear infections)
- people suffering from the above-mentioned basic diseases (high blood pressure, infections, brain and skeletal tumours)
- people suffering from mental health problems (from stress to depression to serious psychological disorders)
- people at high risk of injury (working at heights with a risk of falling, racing drivers, professional drivers in general)
Prevention
Since we have an approximate idea of the situations and diseases in which tinnitus occurs as a concomitant phenomenon, we can prevent it to some extent:
- Elimination of sound phenomena
- not exposing ourselves to changes in pressure
- good hygiene habits
- treatment of the underlying disease
- psychotherapy for excessive stress
- safety and protection at work to minimise accidents at work
Treatment of tinnitus
- Ear surgery such as tympanoplasty - reconstruction of a ruptured eardrum.
- A noise generator is a device similar to a hearing aid. It generates noise and thus helps the patient to be less aware of their own tinnitus.
- Treating the underlying condition that causes tinnitus, such as treating high blood pressure, infection, tooth extraction.
- Relaxing music/antidepressants help with tinnitus arising from psychological causes.
Related