- THAM, Tony C. K., John S. A. COLLINS and Roy SOETIKNO. Urgent gastroenterology. Translated by Helena HARTLOVÁ. Prague: Grada Publishing, 2017. ISBN 978-80-271-0157-3.
- solen.sk - Treatment options for digestive disorders. Solen. PhDr. Marta Martinčeková
- solen.cz - Functional intestinal disorders and their treatment. Solen. Peter Minárik and Daniela Mináriková
- healthline.com - Diarrhea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments. Healthline - Valencia Higuera
How (not) to eat in acute diarrhoea + Appropriate diet + Causes

Almost every person occasionally has digestive problems that force him to spend some time in the toilet. Acute diarrhea, pain or discomfort in the digestive tract. What are the possible causes of diarrhea?
Article content
Diarrhea affects newborns, children and adults, and the elderly.
Diarrhoea is a condition where there is an increased frequency of defecation. Defecation is sudden, stools are watery and runny.
The accompanying phenomenon is often pain in the abdomen and nausea.
The etiology of diarrhea, symptoms, appropriate diet, vitamin/mineral supplementation for diarrhea and many other interesting information can be found in the following article.
What is diarrhea and what are its most common causes?
Diarrhoea is technically called diarrhoea. Diarrhoea is defined as defecating more than three times a day, with the stools being thin and watery.
It is a defence mechanism of the body, which in this way tries to get rid of harmful and unwanted substances from the digestive tract.
Diarrhoea is divided according to its duration into acute and chronic.
Chronic diarrhoea can last for several weeks or months.
Chronic diarrhoea is mainly caused by chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract (e.g. ulcerative colitis), infections or systemic diseases such as celiac disease.
Acute diarrhoea is mainly caused by dietary error, inappropriate eating habits or due to viral/bacterial infection.
Short-term diarrhoea is in most cases caused by poorly digested food, improperly modified diet or a possible allergic reaction to some component of the ingested food.
Short-term traveler's diarrhoea is also specific and occurs when travelling to foreign countries with different hygiene standards. It is mainly transmitted by contaminated water.
Possible causes of acute diarrhoea:
- Bacterial infections
- Viral infection
- Parasitic infection
- Reaction to a dietary error
- Improper eating habits
- Reaction to spoiled food
- Reaction to poorly prepared food
- Reactions to drug therapy (e.g. antibiotics)
- Food intolerance and allergies
- Stress and emotional strain
- Menstruation and PMS
- Food poisoning
- Psychogenic factor
- Stress, anxiety and nervousness
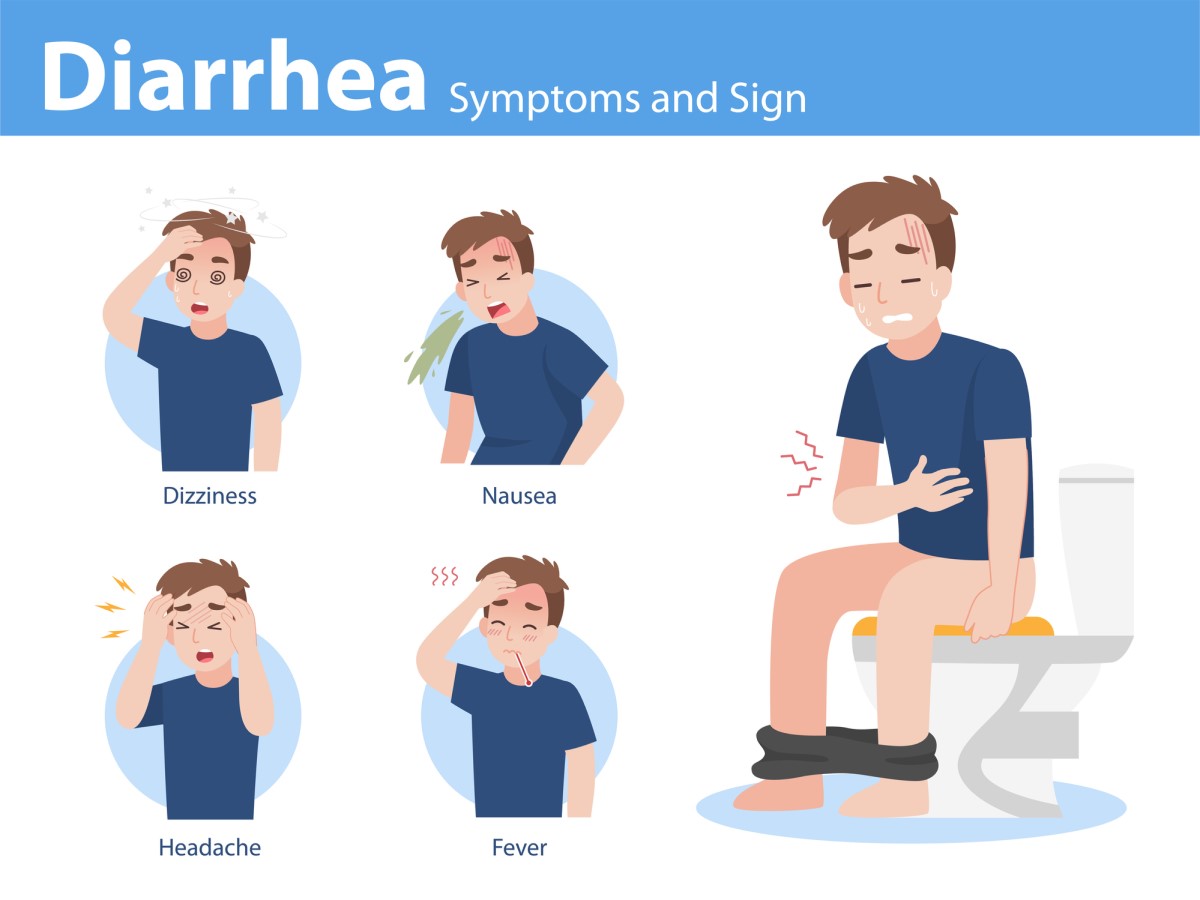
Manifestations and symptoms of acute diarrhoea
The main symptom of diarrhoea is frequent loose stools with the urge to perform a large meal.
Nausea, bloating, cramps and pain in the abdomen and lower abdomen are common. It is possible to experience only one symptom, but also a combination of them.
Possible symptoms and manifestations of diarrhea:
- Nausea
- feeling sick, vomiting
- dizziness
- general weakness
- abdominal pain
- headache
- abdominal cramps
- a feeling of bloating and flatulence
- dehydration
- frequent urge to perform a great need
- thin and watery stools
- large stool volume
Treatment options or how to stop diarrhoea?
Diarrhoea can cause a particularly rapid loss of fluid from the body. There is a risk of dehydration (lack of water in the body). Diarrhoea needs to be addressed immediately as dehydration can have serious consequences.
Read also:
What are the symptoms of dehydration? Do you know the causes? How to rehydrate the body?
Why is dehydration dangerous in children? What are the symptoms?
Treatment with fluids is key, ideally in the form of plain water, unsweetened mineral water, sweetened/herbal teas or electrolyte drinks. In more severe cases, fluids can be given through intravenous infusion therapy.
Increased drinking is necessary to prevent dehydration of the body.
Home treatment consists of a resting regime without physical and mental exertion.
It is necessary to follow certain dietary measures and avoid mistakes in the diet.
If the cause of your acute diarrhea is a bacterial, viral or parasitic infection, your doctor may prescribe medical treatment in the form of antibiotics (or antiviral drugs) after a professional diagnosis.
A gastrointestinologist will diagnose another cause for these digestive difficulties.
When is it appropriate to seek professional help?
Seek medical help if:
- Acute diarrhoea lasts an unusually long time
- You have a body temperature of 38 °C or higher
- You have stools containing blood
- You have stools containing pus
- You have black and tarry stools
- You feel unwell and have doubts about the symptoms
Appropriate diet and dietary measures for acute diarrhoea
The aim of a modified diet for diarrhoea is to eliminate foods that are difficult to digest and, on the contrary, to replenish missing vitamins and minerals (potassium, sodium, calcium...).
Rehydration with unsaturated mineral waters, plain water, tea or ionic drinks is essential.
The glucose intake is important, so it is advisable to sweeten the water taken. For large-volume dehydration diarrhoea, electrolyte ion drinks can be used to hydrate and nourish the body.
Beware, artificial sweeteners have a laxative effect and are therefore not suitable in diarrhoeal disease.
Natural herbal aids in the form of teas promote better digestion and relieve painful cramps. Examples include chamomile, lemon balm, St. John's wort, calendula, sage or lemon balm.
It is not recommended to drink coffee, alcohol or lactose-containing dairy products. Caffeine promotes fluid excretion and thus worsens the symptoms of diarrhoea.
The diet should not be overloaded with heavy spicy fatty foods, dairy products and large amounts of fiber.
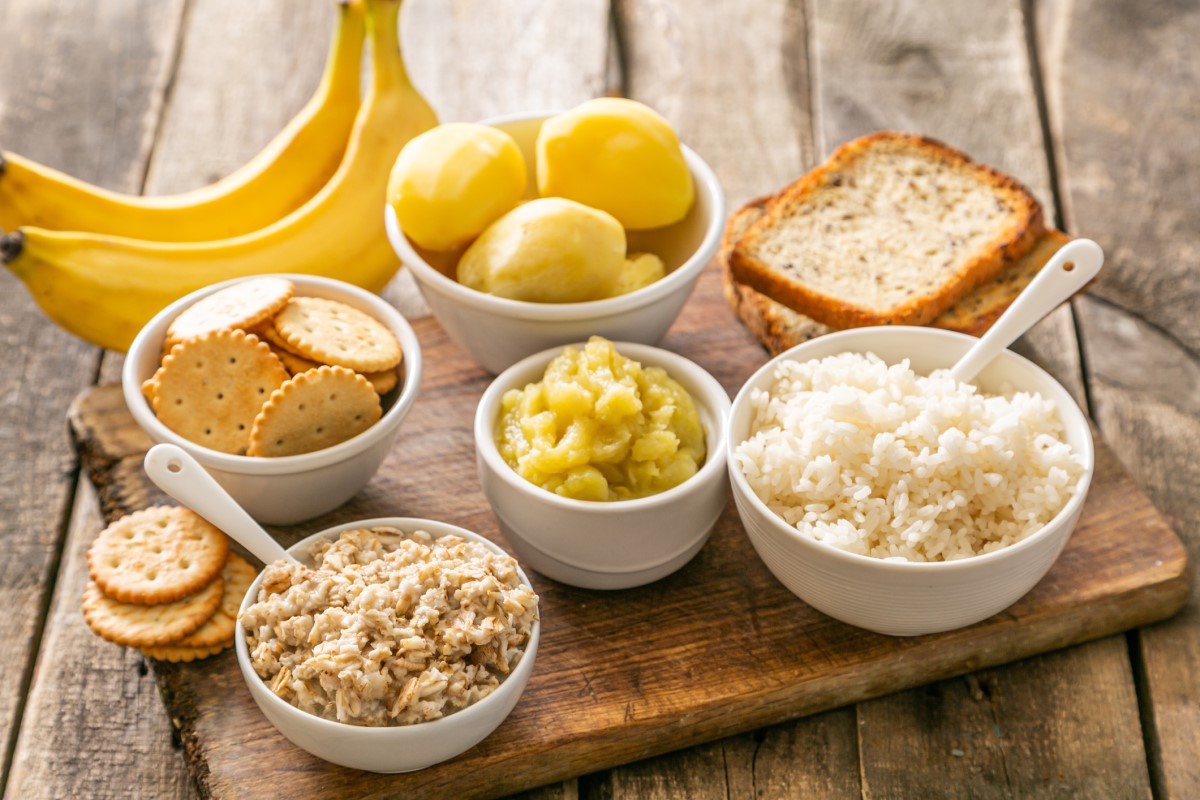
On the other hand, biscuits/biscuits, old white bread, banana, carrot, apple, boiled potato or broth are good choices.
If you suffer from acute diarrhoea, it is advisable to follow the diet for at least 3-5 days. However, if the diarrhoea is of infectious origin, it is necessary to follow the dietary recommendations of your doctor.
It is recommended to eat food slowly and gradually in smaller portions.
Which diet is appropriate or inappropriate?
Suitable foods:
- White rice, potatoes (high starch content)
- fruit (apple, banana, blueberries)
- carrots
- white bread, biscuits, cookies
- pure broth (chicken, beef)
- lean meat in the natural way
- baby food
- tea (black, herbal, fruit, rooibos...)
Inappropriate foods:
- Fatty, hard to digest foods
- fried foods
- spicy foods
- excessively acidic foods
- dairy products containing lactose (yoghurt, cottage cheese, porridge...)
- fatty meat and fish
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils...)
- whole grain cereals
- lots of high-fibre vegetables (kale, cabbage)
- coffee and alcohol
- energy drinks
- artificial sweeteners
- food ingredients with intolerances

Medications, vitamins and minerals (dietary supplements) for diarrhea
In diarrhoea, there is a high loss of fluids, vitamins and minerals. It is therefore necessary to support health by increased nutrient supplementation also in the form of dietary supplements.
A varied and balanced diet is a sufficient source of vitamins, but sometimes it is necessary to take supplements, especially for recurrent diarrhoea.
In diarrhoeal diseases, it is advisable to supplement with minerals such as sodium, potassium, calcium or zinc.
Over-the-counter preparations for the suppression of diarrhoea are based primarily on the principle of a substance that has the ability to thicken the stool and thus eliminate frequent defecation. Some medicines increase the resistance of the intestinal mucosa.
Among the basic remedies for diarrhea are charcoal and probiotics. However, it should be mentioned that charcoal affects the effects of other drugs. Therefore, it is important to observe a certain time interval between their use. It can also reduce the amount of excessive gas in the digestive tract, thereby eliminating nausea and a feeling of bloating.
To restore the bacterial balance in the digestive tract, it is advisable to reach for probiotics. When diarrhea occurs, the number of probiotic bacteria in the digestive tract is reduced. Probiotics and prebiotics supply the necessary microorganisms to the digestive tract to promote a balance of the right bacteria.
Read more:
Probiotics: When to take them? How to choose the right ones?
It is advisable to consult a pharmacist when choosing a specific medicine. When diarrhea lasts more than 3 days, it is necessary to seek professional help from a doctor. It is also necessary to alert the patient to notice pathological changes such as blood and mucus in the stool.
Further information also in the articles:
Interesting resources