- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - A Systematic Review of the European Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed: Trends in Illegal Food Supplements for Weight Loss, Dorottya Koncz, Barbara Tóth, Orsolya Roza, Dezső Csupor
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - The best drug supplement for obesity treatment: a systematic review and network meta-analysis, Nader Salari, Samira Jafari, Niloofar Darvishi, Elahe Valipour, Masoud Mohammadi, Kamran Mansouri, Shamarina Shohaimi
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Anti-Obesity Drugs: A Review about Their Effects and Safety, Jun Goo Kang, Cheol-Young Park
- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Medications for weight loss, John P Mordes, Chao Liu, Shuhang Xu
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Off-label drugs for weight management, Ed J Hendricks
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Complementary and Alternative Therapies for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review, Pei Lin Lua, Nurul Afiedia Roslim, Aryati Ahmad, Mardiana Mansor, Myat Moe Thwe Aung, Farrahdilla Hamzah
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - WEIGHT LOSS MEDICATIONS IN THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY AND HYPERTENSION,Jordana B. Cohen, Kishore M. Gadde
- addictioncenter.com - Diet Pill Abuse, Addiction, And Treatment
- mayoclinic.org - Prescription weight-loss drugs
- healthline.com - 12 Popular Weight Loss Pills and Supplements Reviewed
- ema.europa.eu - European Medicines Agency - Medicines
Diet pills: how do they work and what are the risks? + Restricted substances

The road to your dream weight takes time, patience and, last but not least, a strong will. One way to make it easier and shorter is to use weight loss products. What products are currently available on the market? Does it make sense to use them and, most importantly, are they safe to use?
Article content
How do diet pills work? Their meaning, effect and important warnings about restricted, "banned" substances.
Probably all of us have tried to lose some weight at some point. The goal is to feel good physically, but most importantly mentally.
Maybe it's just a seasonal mania during which we put all our efforts into achieving the momentary goal of having a dream body weight.
In some cases, it is a long-term or even lifelong effort using a variety of methods. Less and more accessible methods.
Maintaining a reasonable body weight is one of the important aspects affecting the health and overall quality of life of every person.
It is therefore essential to maintain a good lifestyle and to engage in sufficient physical activity wherever possible.
There are now dozens or even hundreds of different guidelines available that promise at least to maintain a stable body weight, and at best to reduce it.
In general, however, it is advisable to adopt a few rules and make them part of your daily routine.
These should be, for example, the following steps:
- Eat adequate portions of food at regular intervals.
- Eat plenty of vegetables and fruit.
- Choose healthier food alternatives and avoid fast food.
- Drink plenty of water, preferring unsweetened drinks.
- Be active, engage in physical activities and get plenty of exercise.
It probably comes as no surprise that the number of people who are overweight or even obese is increasing alarmingly every day. Of the total population of adults over 18, up to 39% are overweight and 13% are obese.
And it is not just developed countries with relatively high incomes that are affected. Countries that are still considered to be developing are also affected.
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), we are overweight if our body mass index (BMI) is ≥ 25 and obese if our BMI is ≥ 30.
The greatest risk of overweight and obesity to humans is their negative impact on health.
They increase the risk of life-threatening diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, musculoskeletal, liver and kidney diseases. They are also associated with higher mortality.
The path to effective weight loss is not a short-term and often not an easy one.
Interventions in an established lifestyle, including dietary changes or increasing the frequency of physical activity, can be quite challenging. The desired results are slow to come and the person loses motivation.
This leads to a relatively early return to business as usual or a search for a quicker and easier way to lose weight.
Therefore, in the hope of success, we very often reach for helpers such as dietary supplements or drugs directly.
Useful calculators and articles:
- BMI index calculator.
- Waist to Hip Ratio Calculator.
- Calculator: BMI for children - Is the child overweight, ideal weight or underweight?
- Overweight and obesity in children, adolescents and young adults. What to do about it?
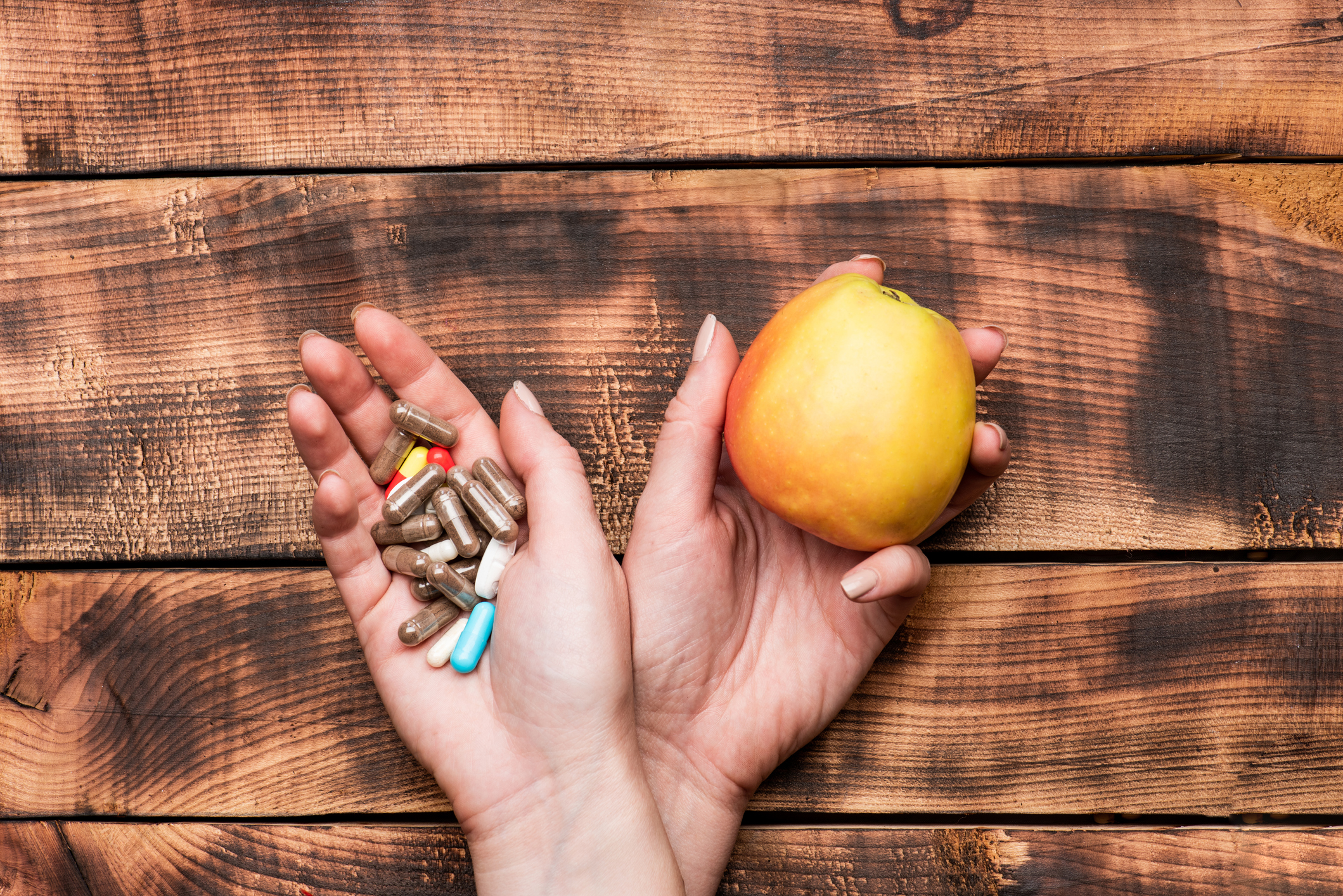
Dietary supplements vs. weight loss drugs
Nutritional (food) supplements are additions to our normal balanced diet. They can be vitamins, minerals, trace elements, amino acids, fibre or plant extracts that provide nutrients for our bodies.
They are not intended to treat or prevent disease and must not be used as a substitute for a varied diet.
The placing on the market of food supplements is not (unlike medicines) subject to such strict approval by national regulatory authorities. Their safety is primarily the responsibility of the manufacturer.
When trying to lose weight, the right dietary supplements can help us achieve the desired effect, but always in combination with other lifestyle adjustments.
The second category is weight loss drugs. These are called anorectics.
Unlike dietary supplements, these drugs are strictly controlled for safety (they have safety clinical studies that have been developed and approved).
The drugs have a biological effect in the body. They can also reduce weight by various mechanisms.
Due to their nature, weight loss drugs are almost always prescription only.
They are used exclusively for patients who are diagnosed as overweight or obese, for whom lifestyle changes including dietary modification and physical activity are not sufficient or who cannot undergo surgical treatment.
Dietary modification and increased physical activity are still the treatment of first choice for both obese and overweight patients.
The important fact is that the effectiveness of weight loss drugs is limited and very individual. In some people they can have a very good effect, in others they are ineffective. In the worst cases they even cause side effects.
Based on the above aspects, there are differences in the availability of these drugs on the markets in different countries. While in Europe some drugs may be approved by the relevant authority, in other countries you will not find them. Of course, the reverse is also true.

How do weight loss products work?
Weight loss products, whether we are talking about medicines, dietary supplements or certain foods, usually work in the following way.
They may act on the central nervous system (the brain), or they may act elsewhere in the body.
In the brain, these substances can produce a feeling of satiety or suppress appetite.
Some are able to improve and speed up the functioning of metabolic processes, thus allowing increased energy expenditure.
Others act directly in the digestive tract, where they prevent the absorption of certain food components, such as fats. They act by binding to certain food components or by affecting the activity of digestive enzymes.
What are the risks of taking them?
It's important to remember that taking medicines or dietary supplements unwisely to reduce your weight can carry certain risks.
Although dietary supplements are more affordable compared to prescription drugs, this does not mean that there are no health risks associated with their use.
Before starting to take any product, you need to consider its benefits, the possible occurrence of side effects or the development of dependence.
Nor can it be relied upon that if a product is natural, for example of plant origin, it cannot be dangerous.
Therefore, the best way is to consult a doctor before taking these products, ideally before starting to use them.
This applies not only to medicines but also to food supplements, which often lack the intervention of a doctor or pharmacist.
In such cases, the doctor helps the patient to assess his or her overall health.
He assesses whether the patient is overweight or obese. He finds out the possible causes of increased or excessive body weight.
He/she recommends the next course of action, i.e. chooses the most appropriate regimen or prescribes treatment. He/she always takes into account the patient's age, gender, severity of the condition, general health, possible complications, psychosocial factors and takes into account the patient's preferences.
He also assesses the presence of other diseases, which is a key factor in deciding on the right treatment.
If the doctor decides to treat with medication or other products, he or she must carefully weigh the benefits and risks of this treatment.
There are certain groups of patients who may not take any medications or dietary supplements designed to reduce weight.
Examples include:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Women who are trying to conceive
- People who are allergic to certain ingredients in a medicine or dietary supplement
- Patients with glaucoma, cardiovascular disease, overactive thyroid or liver problems
- People who are at risk of developing addiction
The most common side effects of weight loss medications and dietary supplements include:
- Abdominal discomfort
- nausea and vomiting
- constipation
- cough
- dizziness
- fatigue
- headache
- dry mouth, changes in taste
- sleep problems to insomnia
Serious and dangerous side effects include increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, liver and kidney damage.
They can also cause addiction.
The occurrence of side effects, including serious ones, is also largely due to a person taking these products in the wrong dose. Often, he or she is overdosed.
This is also due to the fact that the method and appropriateness of taking these preparations is not consulted in advance with a doctor or pharmacist.
Incorrect dosage or abuse of the preparations leads to side effects such as insomnia, hallucinations, dizziness, vomiting, skin rashes, itching, swelling of the lower limbs, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, or discolouration of the urine or stools.
The development and emergence of dependence is mainly related to the fact that these products induce feelings of euphoria and energy. This increases the likelihood of developing dependence on these feelings and on the product that induces them.
However, biological factors, environmental factors, family background, etc. are also involved in the development of addiction.
Other risks of taking dietary supplements for weight loss include their interaction potential.
They can interact with other medications that a person is currently taking. This can lead to a change in the effect of the treatment. They also interact with certain food ingredients or other dietary supplements.
In the case of herbal food supplements, there is a risk that the effect and mode of action of the active ingredients is not well described and known.
Historically, several drugs have been used to treat overweight and obesity in recent decades. Currently, only a few of them are on the market.
This is mainly due to the fact that drugs approved and used in medical practice in the past have been found to have serious side effects.
These were mainly significant heart and cardiac damage, liver damage or psychological disorders (insomnia, depression, anxiety, suicidal tendencies).
For safety reasons, these drugs have been withdrawn from the market and are currently no longer available.

Which substances are effective in reducing weight?
Several active substances are currently approved and used in the European Union for weight reduction purposes.
Orlistat, liraglutide, semaglutide, setmelanotide and the combination of naltrexone and bupropion are approved as active substances in medicines.
Orlistat
Orlistat is a substance that acts in the digestive tract. It blocks the enzymes responsible for digesting fats in food.
Specifically, gastric and pancreatic lipases, whose function is inhibited in this way. Blockade of lipases leads to the inability to digest certain fats. The fats are not absorbed from the digestive tract but are excreted from the body undigested in the faeces.
This aids weight loss.
Orlistat does not affect appetite. It is usually available in oral dosage forms.
The use of orlistat is associated with the possible occurrence of stomach discomforts such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, urge to pass stool to stool incontinence, presence of fats in stool.
These discomforts are usually alleviated if high-fat foods are not consumed.
Serious risks include liver damage manifested by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, itching, dark-coloured urine, abdominal pain or loss of appetite.
Orlistat may also interfere with the absorption of other medicines or fat-soluble vitamins.
Liraglutide
Liraglutide was primarily approved and used as a medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes because it increases the production of the hormone insulin in the pancreas.
Later on, its other effects - peripheral and central appetite suppression and prolongation of gastric emptying interval - were also identified.
It is currently used in higher doses to promote weight loss as an adjunct to lifestyle modification. It is administered by injection.
Digestive problems such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and constipation may occur when taking liraglutide. Also increased heart rate, lack of appetite, fatigue or dizziness.
Semaglutide
Semaglutide acts by the same mechanism as liraglutide. It induces a feeling of satiety, thereby delaying hunger and reducing the amount of food taken. It is given by injection.
Headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation or abdominal pain may occur when taking semaglutide.
Combination of naltrexone and bupropion
The fixed combination of the drugs naltrexone (an opioid receptor antagonist) and bupropion (an antidepressant) acts on the parts of the brain that control food intake and regulate feelings of pleasure and pleasure related to food intake.
It therefore acts as an appetite suppressant, reducing the amount of food intake and increasing energy expenditure.
The most common side effects of the combination of these drugs are nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, constipation, dry mouth.
The product should not be used by patients with liver and kidney disorders, patients with untreated high blood pressure, and patients with certain psychiatric disorders.
Setmelanotide
Setmelanotide is a drug used to control the feeling of hunger in patients with a genetic disorder in which their brain cannot regulate the feeling of hunger. It prevents overeating because these patients do not have a feeling of fullness in their stomach after eating.
Herbal preparations and dietary supplements
The effectiveness of weight loss drugs is highly individual, is associated with the occurrence of side effects and in many cases, there is also limited availability for obvious reasons. Therefore, other means of weight loss have begun to be sought.
People have started to look for alternatives, especially in nature. But not every natural product is safe.
Even in the case of natural preparations or various dietary supplements, there is still a risk of their undesirable or even harmful effects on the human body. Therefore, they should always be approached with common sense.
Examples of natural ingredients that have been shown to promote weight loss are chitosan, carnitine, capsaicin, glucomannan, conjugated linoleic acid or synephrine.
Among plants, these include green coffee, green tea, Garcinia cambogia, sugar stevia or Hoodia gordonii.
Chitosan
Chitosan is a polysaccharide that is formed by the chemical reaction of deacetylation from chitin. Chitin forms part of the outer skeleton of insects or crustaceans.
It acts by reducing the absorption of fats and cholesterol from the diet into the body while increasing the rate of fat excretion. In addition, its other beneficial effects on blood pressure and blood fat content have been described.
Chitosan may cause side effects such as bloating, indigestion, nausea and heartburn. Allergies may occur in some users.
Its interaction potential is considered negative. For example, it interacts with warfarin or affects the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Carnitine
Carnitine is a substance involved in the natural metabolism of humans. Its function is to transport fatty acids into the mitochondria where they are used for energy production. It is also involved in the excretion of metabolic wastes from cells.
This helps in weight loss.
It has only very mild side effects - diarrhea, nausea or abdominal pain.
Capsaicin
Capsaicin is an alkaloid that is responsible for the hot taste of peppers. One of its many effects is to promote fat burning and increase the body's energy expenditure.
As a result, it finds application in weight management and obesity prevention.
Its use may be associated with mild indigestion, sweating, hot flushes and rhinitis. It may interact with drugs used to treat high blood pressure.
Glucomannan
Glucomannan is a polysaccharide obtained by extraction from the tubers of the Amorphophallus konjac plant. It is considered a soluble form of dietary fibre.
It contributes to weight loss in several ways. It increases the viscosity of the intestinal contents, speeding up the passage time of digested food through the small intestine. Absorption through the intestinal walls is thus limited in time.
In addition, glucomannan slows down gastric emptying and also increases energy loss.
Digestive problems such as bloating or diarrhoea may occur when taking it.
Conjugated linoleic acid
Linoleic acid and its isomers are to some extent involved in the genes responsible for fat metabolism in the body.
This acid occurs naturally in beef and dairy products.
The efficacy and safety of its use in humans have not yet been sufficiently evaluated and described. In animals, its use has been associated with changes in liver function and insulin resistance.
Synephrine
Synephrine is an alkaloid found in citrus fruits, particularly bitter orange (Citrus aurantium).
It is involved in reducing appetite and increasing fat burning in the body.
The risk of its use lies mainly in its adverse effect on the heart, causing an increase in blood pressure and heart rate.
Green coffee
Green coffee refers to the unroasted beans of the Arabica coffee plant (Coffea arabica). The roasting of coffee beans results in the loss of a large number of active substances, one of which is the heat unstable chlorogenic acid.
Chlorogenic acid in particular has beneficial effects on weight loss. It lowers the amount of lipids and glucose in the blood, lowers blood pressure and also reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Green tea
The name green tea refers to the unfermented leaves of the Chinese tea plant (Camellia sinensis). The most important substances that play a role in weight loss are polyphenols. The most abundant and also the most effective of these is epigallocatechin-3-gallate.
In combination with the other content substance caffeine, they contribute to weight control, especially in those people who normally consume only low doses of caffeine daily. The effect is to increase heat production and fat metabolism.
High doses of green tea can have an adverse effect on the liver.
Garcinia cambogia
The main content of this tropical citrus fruit is hydroxycitric acid, which reduces the production of fatty acids, lipids and also reduces appetite.
However, despite its relatively promising effect, studies show the occurrence of adverse effects on the liver, leading in some cases to inflammation and liver failure.
Sweet stevia (Stevia rebaudiana)
This plant, native to South America, has long been used not only for sweetening but also, for example, to relieve heartburn.
Today, stevia is used as a low-calorie alternative to conventional sweeteners.
Hoodia gordonii
This is an African succulent similar to the cactus that was consumed by indigenous people to suppress their appetite.
Studies have found effects associated with its use such as nausea, vomiting, skin sensitivity disorders, increased blood pressure and rapid heart rate.

Substances whose use has been restricted
In the past, many other substances were available and used. However, due to the serious side effects they caused, they are no longer used, at least in the European Union.
Amphetamines
Amphetamine and its derivatives were first used for weight reduction purposes as early as 1930.
Their effect is to stimulate the release of the neurotransmitters noradrenaline and dopamine, thereby increasing their levels in the brain. In this way, they can suppress appetite.
Examples used include phenylpropanolamine, fenfluramine, dexfenfluramine or amfepramone.
The greatest danger of these substances is the rapid development of addiction (within a few weeks) and, not least, serious cardiac complications.
Their use is currently restricted.
Phentermine
Phentermine causes the release of the neurotransmitter noradrenaline in the part of the brain responsible for regulating the feeling of hunger. This suppresses the appetite.
It is also used in combination with another drug, topiramate, which reduces appetite and increases energy expenditure in the body.
It is currently no longer used because of serious cardiovascular and psychiatric side effects (anxiety, depression, attention and memory problems).
Lorkaserin
Lorkaserin is a substance that acts as a serotonin receptor agonist. It mimics the function of the neurotransmitter serotonin and thus activates receptors that are normally activated by serotonin.
Its action induces a feeling of satiety after eating and reduces the feeling of hunger before eating.
Due to its serious side effects, such as the risk of depression, tumours and heart valve damage, its use is currently not permitted.
Sibutramine
Sibutramine is a substance that blocks the uptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine by nerve cells. This increases their levels in the brain. In addition to its antidepressant effect, its weight loss effect has also been used for a long time.
It induced a feeling of satiety after eating, which helped patients to reduce the amount of food intake.
Sibutramine has been found to cause serious cardiovascular side effects, namely increased blood pressure, increased heart rate and even stroke. For this reason, its use is now completely restricted.
Rimonabant
Rimonabant acts as an antagonist of cannabinoid receptors, which are found in the nervous system but also in fat cells. It has a significant effect on weight loss.
However, it also caused significant psychiatric side effects such as depression, anxiety and suicidal thoughts and is therefore no longer used.
A similar scenario occurred with taranabant, which acts by the same mechanism as rimonabant.
Use of off-label weight loss substances
There are many other drugs and active substances that are known to have a beneficial effect on weight loss but have never been approved for this use.
We talk about off-label use when:
- the drug or other substance is used for purposes other than those for which it was primarily approved and authorised
- the medicine or other substance is used at a different (usually higher) dose or for a different duration than that for which it was primarily approved and authorised
The drugs most commonly associated with off-label use for weight loss include antidepressants, called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Also, some drugs used to treat diabetes, such as metformin, pramlintide, exenatide or dulaglutide.
The greatest risk of off-label use of drugs or other substances is the high likelihood of side effects of which the user may not even be aware. The consequences of such use can be life-threatening.
Interesting resources
Related