- "Esophagitis – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org.
- "Esophagitis-Topic Overview". WebMD.
- "Esophagitis". Johns Hopkins Medicine.
- "Understanding Esophagitis". WebMD.
- "Upper Gastrointestinal (UGI) Series". WebMD.
- "Inflammation, Not Acid, Cause of GERD, Study Suggests".
- Farivar M. "Los Angeles Classification of Esophagitis". webgerd.com. Archived from the original on 2015-01-30. Retrieved 2010-10-27. In turn citing: Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. (August 1999). "Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification". Gut. 45 (2): 172–80.
- Laparoscopic bariatric surgery, Volume 1. William B. Inabnet, Eric J. DeMaria, Sayeed Ikramuddin.
- "Esophagitis". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library.
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), 2013. Metoclopramide: risk of neurological adverse effects. Drug Safety Update 7 (1), S2. Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, 2014. Domperidone: risks of cardiac side effects. Drug Safety Update 7 (10), A1. Moayyedi, P., Santana, J., Khan, M., et al., 2011. Medical treatments in the short-term management of relux oesophagitis. Cochrane DB Syst. Rev. 2011 (2), Art. No. CD003244.
- Kirkham, EN; Main, BG; Jones, KJB; Blazeby, JM; Blencowe, NS (January 2020). "Systematic review of the introduction and evaluation of magnetic augmentation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease". The British Journal of Surgery. 107 (1): 44–55
Esophagitis - Inflammation of the Oesophagus
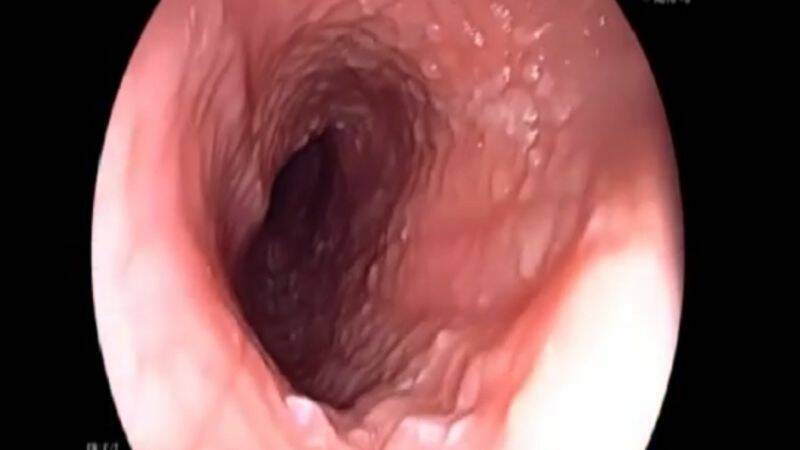
Photo source: Getty images
Esophagitis is treated by
Other names
Esophagitis










