- terapiasvetlom.sk - which is arthritis
- akv.sk - information on rheumatoid arthritis
- mojareuma.sk - information on psoriatic arthritis
Arthrosis : How infectious or non-infectious arthritis, what are its symptoms?
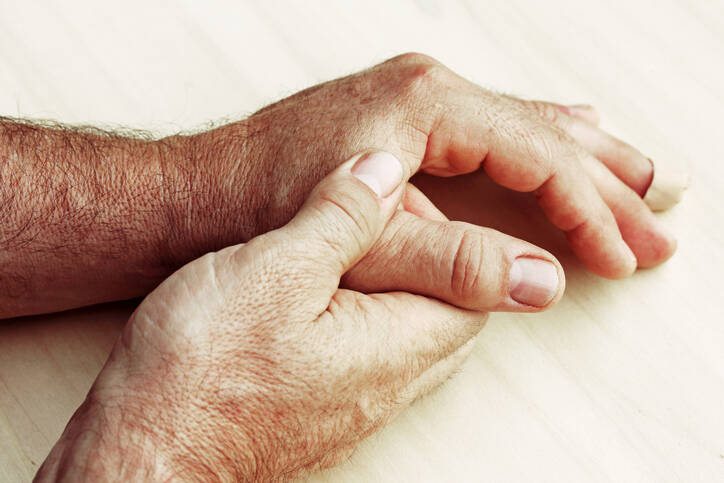

Arthrosis is an inflammatory disease of the joints. It can be infectious or non-infectious. It has several forms and is divided into rheumatoid arthritis, septic arthritis, or DNA disease. Each type has different causes. However, their common feature is pain, swelling, limited function, and joint damage.
Most common symptoms
- Malaise
- Chest pain
- Joint Pain
- Limb pain
- Leg Pain
- Eye Pain
- Heel Pain
- Painful Breathing
- Muscle Pain
- Flank Pain
- Groin Pain
- Fever
- Pain that Radiates into the Shoulder
- Pain under the Right Shoulder Blade
- Increased body temperature
- Nausea
- Head spinning
- Deformed nails
- The Hump
- Bone Pain
- Sweating
- Indigestion
- Swollen fingers
- Malnutrition
- Right Flank Pain
- Back Pain
- Bone thinning
- Dry skin
- Muscle weakness
- Pressure on the chest
- Fatigue
- Winterreise
Characteristics
Thus, the cause of arthritis is inflammation and not degenerative joint damage or wear. This is called osteoarthritis . Arthritis is divided into infectious and non-infectious . Subsequently, several forms of this disease are distinguished.
We know these forms of arthritis:
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis as an autoimmune disease
- psoriatic arthritis, also an autoimmune cause
- ankylosing spondyloarthritis, or Bechterev's disease
- juvenile idiopathic arthritis, also an autoimmune cause
- DNA, also known as llama, a metabolic cause
- septic arthritis, an infectious inflammation of the joint
- reactive arthritis is inflammation of the joint after another infection in the body (rheumatoid arthritis, for example after tonsillitis )
- Borrelia arthritis occurs after a tick bite as a complication of Lyme disease
Another method divides arthritis according to whether one or more joints are affected . They are technically referred to as monoarthritis , a disease of one joint, and polyarthritis . The second is a designation for affecting several joints.
Subsequently, arthritis can be classified according to which joint is damaged, namely:
- coxitis, which is inflammation of the hip joint
- gonitis, represents inflammation of the knee
- omarthritis, a sign for elbow inflammation
Non-infectious arthritis
Non-infectious arthritis is an inflammation of the joint that can be caused by autoimmune processes . When the immune system attacks its own tissues for pathological reasons. In this case, soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, cartilage, and thus joints.
Autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis , folk and rheumatism. It is similar with psoriatic arthritis . In children , this is a form called juvenile idiopathic arthritis . Non-infectious arthritis includes Bechterev's disease .
And DNA is a disease that affects the joints. And it is one of the non-communicable diseases. Thus, a non- infectious inflammation is one that does not cause a foreign pathogen , ie an infection. Whether a bacterium or a virus.
More information on DNA disease is in a separate article .
Osteoarthritis
This most common form of arthritis affects all freely moving joints.
Such as knees, hip joints, but also finger joints, wrists. The exact cause is not fully understood. But overload , genetic predisposition or age have a negative effect .
It most often occurs in old age , after the age of 65.
Risk factors for osteoarthritis:
- age from the age of 40
- family history, ie occurrence
- genetic predisposition
- overweight, obesity
- joint overload, such as a tennis elbow
- joint injury
- more common in postmenopausal women
- in men under the age of 45, the incidence is more frequent
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatism is an autoimmune systemic inflammatory disease .
It affects soft structures such as muscles, tendons and joints. It is more common in women. The age category it affects is relatively wide, from the 30th to the 60th year of life.
Severe forms of the disease affect the eyes, but also the lungs or blood vessels and the heart.
See also: Rheumatoid arthritis .
Psoriatic arthritis
It is also referred to as PSA or psoriatic arthropathy . Also an autoimmune disease that is chronic and occurs in people with psoriasis . And that's about 40 percent of cases.
It affects women as well as men.
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
The designation juvenile indicates that the disease affects childhood . Juvenile diseases are those that arose before the age of 16 . Otherwise, it could be described as childhood idiopathic arthritis.
Juvenile = juvenile, immature.
The word idiopathic further explains that its exact cause is unknown . But it is basically an autoimmune disease that is chronic and is involved in joint damage and disability.
Infectious forms of arthritis
As for infectious forms of arthritis , the inflammation may be caused by bacteria with streptococcus or a virus . And these are various viral diseases, such as herpes virus or hepatitis B virus. The infection can enter the joint with an open injury or from the environment, for example through the bloodstream .
Rheumatoid arthritis has a similar name to rheumatoid arthritis, however, the diseases are different, especially in terms of causes. The trigger is a previous bacterial infection in the body. Otherwise, these arthritis are also referred to as reactive .
They are classified as those inflammations of the joints that directly affect the joint, ie septic arthritis. But also inflammation that arose as a result of infection in another part of the body . As is the case, for example, with a complication of tonsillitis or Lyme disease .
Causes
- heredity
- genetic predisposition
- hormonal disorders
- poor lifestyle
- excessive mental load, ie stress
- allergy
- common infections, whether bacterial or viral
- weakening of immunity
- diabetes
- taking some medicines, such as corticosteroids (for asthma)
- cancer
Inflammation can also occur due to excessive physical exertion or due to older age . Sometimes there are difficulties in overweight people , but it is not always a directly confirmed connection.
Infectious arthritis, there are high-risk infections that, although originating in another part of the body, can spread to the joints.
And this is, for example, tonsillitis . But also various herpes infections . A typical infectious disease that has a common joint complication is Lyme disease . It is caused by insects, most often ticks.
Symptoms
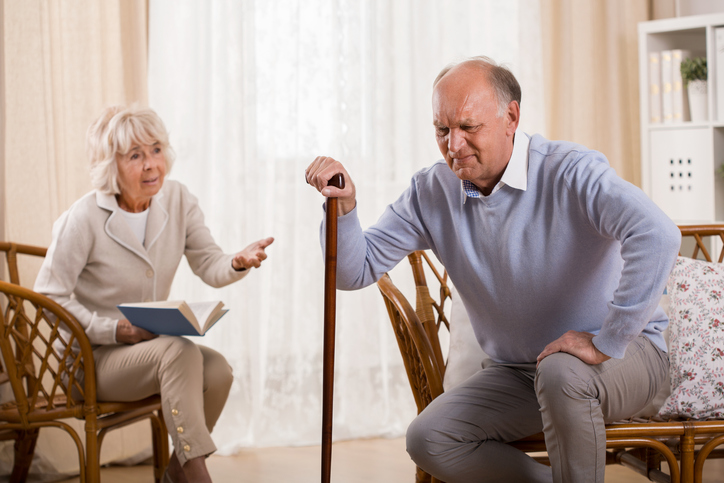

The most common manifestations of arthritis are joint pain , which is usually accompanied by swelling and stiffness .
In rheumatoid arthritis, morning stiffness also occurs , which subsides during the day. Attacks of excessive pain are sometimes present .
Symptoms of the inflammatory process also include reddening of the skin above the joint and increased body temperature . A person with arthritis has as a result of disease problems and difficulty walking , movement disorders of the joints .
Sometimes rheumatoid arthritis or DNA can cause mild deformations. Fatigue also occurs naturally, and in exceptional cases fever .
The table lists the most common causes of arthritis and their manifestations
| Title | Cause | Speeches |
| Osteoarthritis | multifactorial causes, age, congestion, obesity, injury, genetic predisposition |
4 degrees are indicated
|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | autoimmune inflammation |
|
| Psoriatic arthritis | psoriasis |
|
| Juvenile idiopathic arthritis | the cause is not exactly known, but includes, for example, autoimmune processes, some infections, genetic predisposition, stress |
|
| Ankylosing spondyloarthritis | autoimmune cause, genetic causes, infectious diseases |
|
| DNA | metabolic disorder, deposition of uric acid salts in the joints and their surroundings |
|
| Septic arthritis | tonsillitis |
|
| TBC | ||
| gonorrhea | ||
| rheumatic fever | ||
| mumps | ||
| urethritis | ||
| tooth decay, inflammation | ||
| infected injury near the joint | ||
| joint puncture | ||
| joint surgery |
Diagnostics
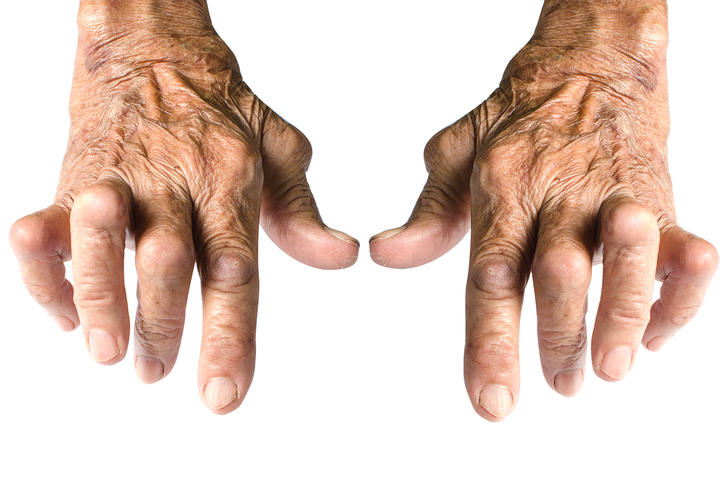
The diagnosis is based on the symptoms , and therefore on the anamnesis .
Joint pain and swelling and other associated symptoms may lead to a final diagnosis. Of course, a professional examination is important.
A general practitioner , rheumatologist or orthopedist cooperates in the diagnosis . Subsequently, other specialists, depending on the underlying cause and complications.
As can be seen in the table, different forms of arthritis also have different causes. The symptoms and their onset are also slightly different. If arthritis is due to an autoimmune process, the diagnosis of the underlying cause may be more difficult.
In arthritis caused by an infection in another part of the body, it is also important to know the underlying cause. Based on the correct diagnosis, a suitable treatment is then chosen. As the treatment is different for each type of arthritis.
The diagnostics also includes a laboratory blood test .
The doctor will perform a blood count or a serological examination of the blood, as well as a culture of blood or joint fluid. The rate of the body's response to inflammation is monitored, as well as various other components that may suggest something about a specific form of arthritis.
An X-ray imaging examination is also performed . This is due to possible deformations and observations of changes in the joint and its surroundings. In this case, it is possible to supplement the CT and MRI examination. Associated complications and difficulties on other body systems are investigated by the specialist. For example, an ophthalmologist, cardiologist, surgeon.
Course
As well as pain . She may react to warming up . And then it eases with movement . And the exact opposite is pain , which is exacerbated by movement . This type of pain is present in septic arthritis .
The characteristic pain, which also determines rheumatoid arthritis, is located in the area of the small joints of the fingers and toes. But also wrists, elbows, knees and ankles. In juvenile arthritis, the first to appear is a disorder of joint function , later pain and then swelling.
The swelling is usually present regardless of the underlying cause . For example, in psoriatic arthritis, it typically affects the entire area of the finger. And not just the area around the joint, as is usually the case with infectious inflammation.
Subsequently, skin manifestations often occur in arthritis . On the skin, it is possible to observe redness in the affected joint area, but also a local increase in temperature . A worse option is skin defects or other changes, such as its thickening.
The joint may not be damaged at an early stage . But usually long-term difficulties are also caused by its deformations. In rheumatoid arthritis and Bechtereva disease, the last stages are characterized by severe joint changes and reduced mobility.
Local symptoms occur together with general symptoms . Inefficiency, fatigue may be the first to occur . But also increased body temperature . Infectious arthritis is usually the cause of fever. Nausea is also associated.
As a result of the chronic persistence of these diseases, damage to other body systems occurs. For example, eye damage is common, especially in non-infectious arthritis. And others, for example, cardiovascular complications, a problem with the respiratory system or indigestion.
How it is treated: Arthrosis
How is arthrosis treated? Can it be stopped? Medications and lifestyle modification
Show moreExperiences with arthrosis
Arthrosis is treated by
Other names
Interesting resources










