- DRNKOVÁ, Barbora. Microbiology, immunology, epidemiology and hygiene: for medical disciplines. Prague: Grada Publishing, 2019. Sestra (Grada). ISBN 978-80-271-0693-6
- solen.sk - Acute respiratory infections in childhood. Solen. PharmDr. Ladislav Dubán, PhD. et al.
- Pediatriepropraxi.cz - Infectious conjunctivitis. Pediatrics for practice. Pavel Němec, MD
- linkos.cz - Adenovirus vectors in gene therapy. Regional Centre of Applied Molecular Oncology. Pjechová M. and spol.
- medicalnewstoday.com - What to know about adenoviruses. Medical News Today. Meredith Goodwin, MD
Adenovirus infection: what is adenovirus, what is its transmission and symptoms?
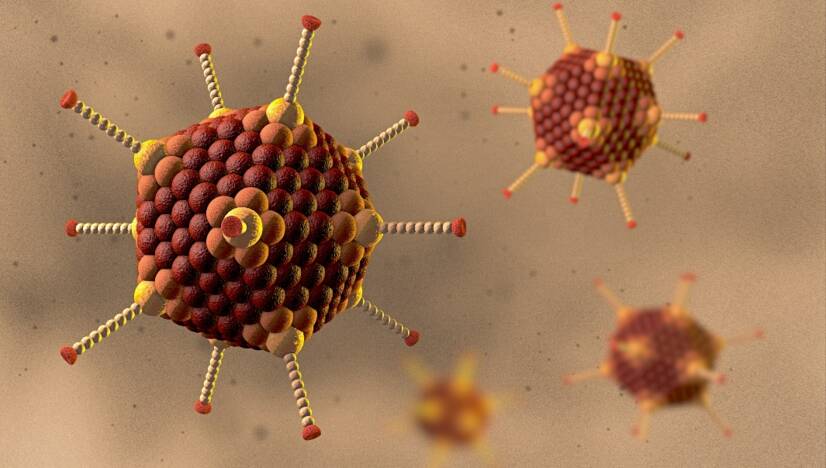
Adenoviruses cause mainly acute respiratory diseases in humans. However, they can attack various body systems. What is an adenovirus and how is the disease transmitted? What is the appropriate treatment and preventive measures?
Most common symptoms
- Malaise
- Thickening of the voice
- Abdominal Pain
- Headache
- Sore Throat
- Joint Pain
- Limb pain
- Eye Pain
- Pain when swallowing
- Fever
- Spirituality
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Purulent discharge from the eye
- Indigestion
- Full nose
- Eye irritation
- Cutting the eye
- Dry cough
- Muscle weakness
- Itchy eye
- Head spinning
- Tremors
- Fatigue
- Damp cough
- Vomiting
- Coughing up mucus
- Redness of the conjunctivae
- Winterreise
- Accelerated heart rate
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Increased body temperature
- Increased watery eye
Characteristics
Adenovirus infection is an acute infectious disease caused by a virus from the Adenoviridae family (adenoviruses).
Adenovirus infection is a relatively common disease, especially in young children.
Adenovirus attacks the primary respiratory tract, but can also affect the digestive, excretory or genital systems.
The first symptoms of infection, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, vaccination and many other interesting information - all this can be found in the article.
What is adenovirus?
A virus is a tiny particle made up of a protein casing. Inside the casing is stored hereditary information in the form of DNA or RNA.
An adenovirus is a virus of the DNA virus group. It is an uncoated double-stranded DNA virus with an icosahedral shape, approximately 60-90 nm in diameter. Up to 50 different subtypes of adenovirus have been identified.
Viruses need other (foreign) living cells in the body to reproduce.
A large proportion of adenoviruses cause respiratory disease by attacking the respiratory tract. Symptoms such as sneezing, stuffy nose, cough, sore throat and increased body temperature are common.
Although this viral disease is more typical of the colder months of the year, it can also occur in spring or early summer. Thus, unlike other respiratory viruses, adenovirus is not exclusively seasonal. It is relatively resistant to different surfaces and external environments.
Adenovirus vectors are among the most widely used carriers of genetic material in gene therapy, gene studies and immunotherapy.
Causes
In adenovirus infection, healthy host cells are attacked for their own viral replication. If left untreated and neglected, the virus can spread to other parts of the body and cause health complications such as pneumonia or intestinal infections.
Adenoviruses cause various types of infections, such as diseases of the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, conjunctivae of the eyes or, less frequently, the urogenital system. Adenoinfections of the nervous system or spread of the infection to other organs are also rare.
They occur at an increased rate in young children, but both adults and older individuals are at risk.
The incubation period of adenovirus infection is usually from 5 days to 2 weeks.
The source of infection is the infected individual. Adenovirus is transmitted from person to person by droplet transmission through secretions released mainly by coughing or sneezing.
Adenovirus is thus transmitted mainly through the air, more rarely through water and infected objects. Faecal-oral transmission and sexual transmission are also possible.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms depend on the infection with a particular type of adenovirus.
Adenovirus infection manifests itself according to the serotype of adenovirus involved. In most respiratory cases, the clinical symptoms are similar to the common cold, especially sore throat, cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis, fatigue and increased body temperature.
When the virus spreads, bronchitis and pneumonia can occur. This brings with it worsening of breathing difficulties, shortness of breath, chest tightness or coughing.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis affecting the conjunctiva of the eye is also relatively common. It is highly infectious through interpersonal contact.
However, if infection develops in the digestive system, abdominal pain, nausea, problems with defecation (diarrhoea) and vomiting are present. Increased body temperature, fever, lack of appetite and malaise are common.
Manifestations of adenovirus infection usually set in quite quickly.
In addition to the specific symptoms, less specific ones also occur. Examples of general symptoms are excessive fatigue, general weakness, headache, muscular pain, malaise and lack of appetite.
Common symptoms of adenovirus infection:
- Pain and redness of the throat
- Pain on swallowing
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Enlargement of cervical lymph nodes
- Swelling of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract
- Formation of mucus in the nose
- Sneezing and itching of the nose
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes
- Eyelid swelling and tearing
- Burning and itching of the eyes
- Headache and migraine
- Increased fatigue
- General weakness and malaise
- Increased body temperature
- Fever and chills
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal cramps
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty defecating
- Diarrhoea and watery stools
- Unappetite
Adenoviruses and the respiratory system
Respiratory disease does not last more than 10 days with appropriate treatment. However, some symptoms, such as coughing or increased fatigue, may persist for up to 4 weeks after the outbreak.
The risk of this respiratory virus is the spread of infection to the lower stages, namely the bronchi and lungs. Early initiation of treatment is therefore essential.
Hand in hand with the respiratory infection is the development of conjunctivitis.
Adenoviruses and conjunctivitis of the eyes
Adenoviral conjunctivitis causes local symptoms in the form of swollen eyelids, increased tearing, burning and itching of the eye. Redness of the conjunctiva is typical. A characteristic discharge from the eye is also present.
It is a highly infectious type of viral conjunctivitis. Respiratory difficulties are often associated, particularly due to swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Adenoviruses and the digestive system
Infections of the gastrointestinal tract are mainly accompanied by diarrhoea, watery stools, vomiting, nausea and abdominal pain.
Early regimen measures, adequate hydration and dietary modification are necessary.
Adenoviruses and the excretory system
In less frequent cases, adenovirus infection also affects the genitourinary system.
The symptoms are frequent urination, burning and unpleasant sensation when urinating and pain in the lower abdomen. Cloudy urine and the presence of blood in the urine are possible. A diagnosis by a urologist is thus necessary.
Urinary tract inflammation: what are its symptoms and causes + Prevention
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of viral diseases is primarily based on taking a comprehensive history of the patient and assessing clinical symptoms.
The doctor conducts a phonendoscope to listen to the chest (heart and lungs).
In the context of respiratory diseases, the doctor examines the upper airway by sight and the size of the lymph nodes of the neck by palpation.
Virus can be demonstrated by microbiological examination of a blood sample (or other sample). The presence of antigen or virus is then demonstrated.
Sputum (mucus) sampling from the throat and nose is also common.
If the extent of the virus is suspected, imaging of the lungs and bronchi in the form of an X-ray may be performed.
In the context of a particular type of adenoinfection, it is possible that the patient will be referred by the general practitioner to pneumology, gastroenterology, urology, ophthalmology and other relevant segments.
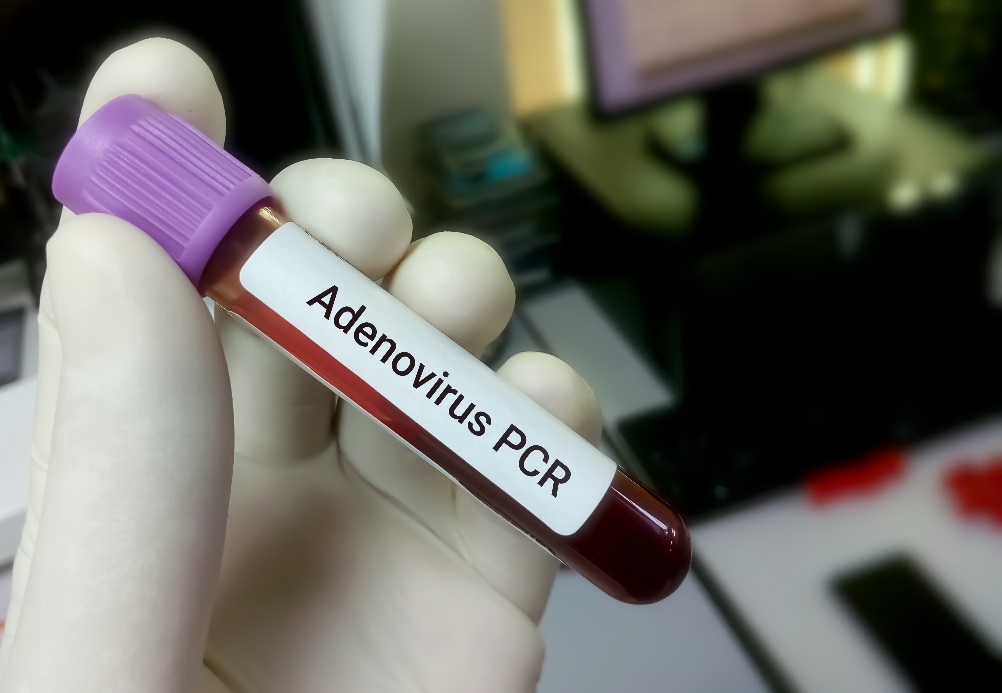
Adenovirus infections in children
Progress
Acute respiratory infections are among the most common diseases of childhood. ARIs account for about 50% of common illnesses in the first five years of a child's life, especially respiratory ones.
The incubation period of an adenoviral infection is approximately 2 to 12 days, with an average of 5-8 days. The disease usually starts acutely.
The first symptom is an increase in the general body temperature. The temperature rises gradually over the first few days and may reach a maximum of 39 °C (rarely 40 °C).
From the first days of the respiratory disease, a nasal discharge (snot) is present. The nasal mucosa is swollen and nasal breathing is difficult. The throat is slightly swollen and reddened, especially the tonsils and the anterior palatal arch. White plaque may be present.
What to look out for?
The main respiratory problems include shortness of breath and difficulty breathing, which is a more serious symptom in young children. A warning risk sign of respiratory problems is cyanosis - a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
Abnormally sleepy behaviour, difficult waking of the child, seizures and tachycardia (increased heart rate) are risk signs.
The parent should observe unusual warning signs and visit the paediatrician in time. The doctor's task is to rule out the risk of serious illness by examining and assessing the child's general condition. He or she opts for specialist treatment under professional supervision or self-medication at home.
Treatment
Treatment of adenovirus infection in children is mainly symptomatic. Relaxation of the nasal mucosa with drops containing sea salt intended for children.
Relief from coughing in turn by sufficient hydration, humidifying the surrounding air, keeping warm and possibly administering medicines for children prescribed by a doctor.
During ARI, adequate hydration of the child in the form of pure water, baby teas and honey-sweetened teas is important. In case of fever, it is advisable to give medicines containing paracetamol and ibuprofen, especially in the form of suppositories or tablets (depending on the age of the child).
However, the dose of antipyretics should be adjusted to the age and weight of the individual. Thus, consultation of the parent with the doctor is necessary.
Prevention of adenovirus infection
There is no 100% prevention for infection with viruses. However, it is possible to significantly eliminate the risk of transmission.
Thus, prevention consists in eliminating contact with infected persons, avoiding risky areas and observing hygiene measures.
The basic rule is clean hands.
A strong immune system and immunity are essential for overcoming viral illness. A regular, nutritious diet with plenty of vitamins and minerals (especially fruit and vegetables) is necessary.
Regular physical activity and support for the cardiovascular system are important. We must not forget about sufficient regeneration of the body and good quality regular sleep.
Important prevention of certain viruses is possible through vaccination, i.e. vaccines.
The basics of virus prevention:
- Avoiding contact with a sick person
- Adequate hand hygiene
- Observing hygiene measures
- Sneezing and coughing into a napkin
- Not touching mucous membranes (face) with dirty hands
- Strong immune system and defences
- Vaccinations (inoculations)
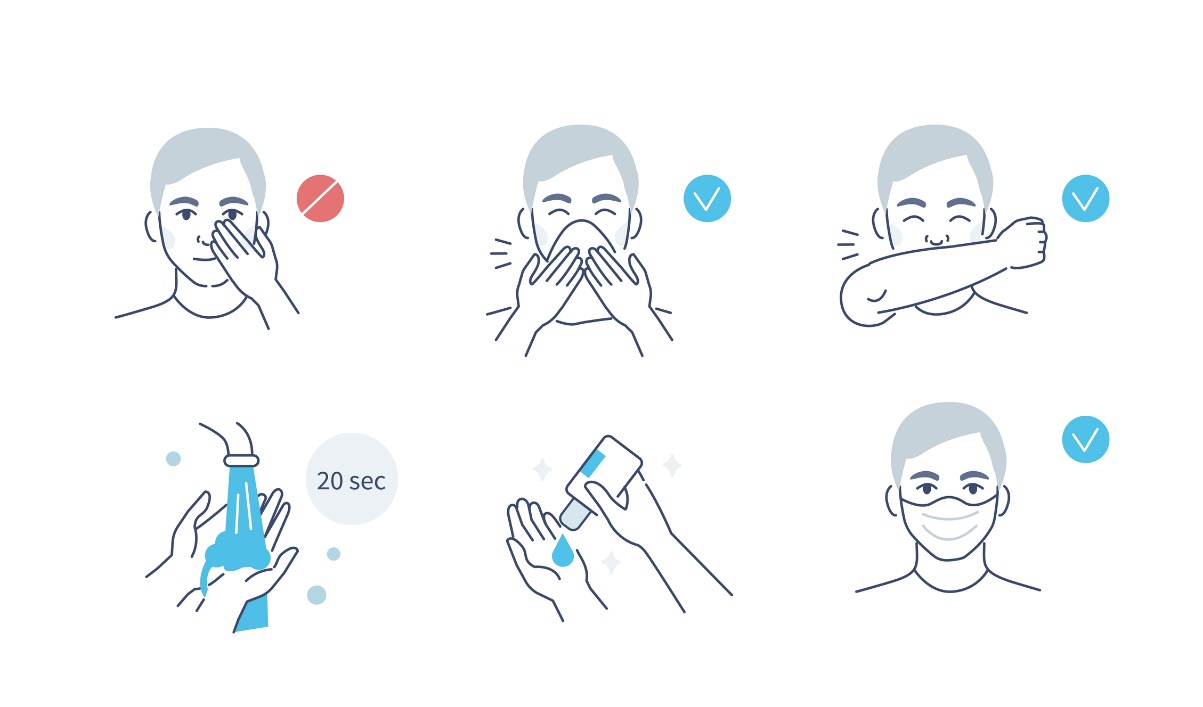
How it is treated: Adenovirus infection
Treatment of adenovirus infection: what drugs will help? Are antibiotics needed?
Show moreAdenovirus infection is treated by
Other names
Interesting resources
Related










