- Differential diagnostics of first contact: Zuzana Lomíčková
- Disease signs and symptoms: differential diagnosis: Lukáš Karel, Žák Aleš, a kolektiv
- Screening and diagnosis of breast cancer: for everyday practice: Daneš Jan, et al.
- Endocrinology for practice: diagnosis and treatment from A to Z - translation 7th edition: Herrmann Frank, Müller Peter, Lohmann Tobias, Wallaschofski Henri
- nhs.uk - What is gynaecomastia?
- healthline.com - What Is Gigantomastia?
- clevelandclinic.org - Enlarged Male Breast Tissue (Gynecomastia)
- mayoclinic.org - Enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia)
What does gynecomastia look like? Breast enlargement in men and its causes
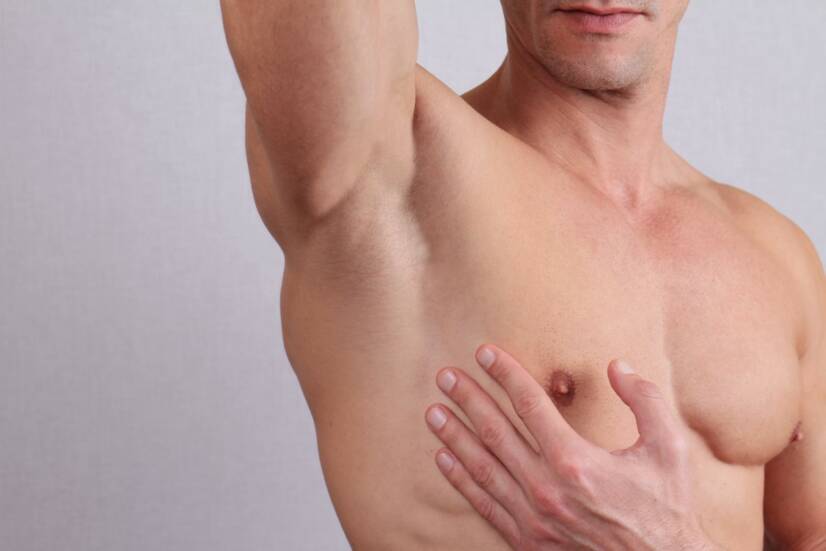
What does gynecomastia look like and what are the causes of breast enlargement in men?
However, it can affect men at any age.
The condition is related to various hormonal changes. In most cases, it is a benign condition, but the cause must be identified.
Gynecomastia is a unilateral or bilateral enlargement of the mammary gland in men due to excess estrogen and testosterone deficiency.
The breasts may grow unevenly.
However, breast enlargement does not always occur because of enlargement of the mammary gland. It can occur because of the deposition of increased fat around the breasts, and that is when we talk about pseudogynecomastia.
Pseudogynecomastia is also known as lipomastia. It occurs in obese men. It occurs symmetrically on both breasts. There is a palpable fatty tissue under the nipple which is soft.
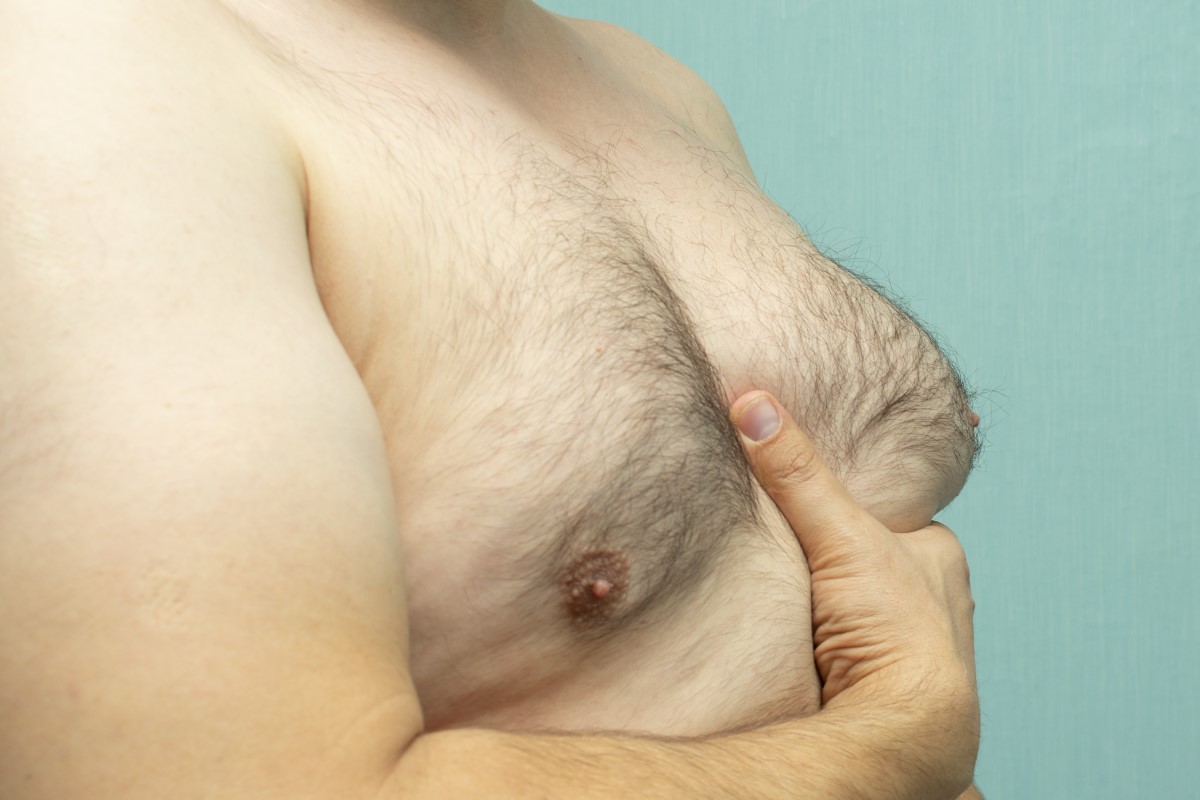
In general, gynecomastia is not a serious problem. In most cases, it is a symptom of another disease.
For men, however, this condition is challenging, mainly in appearance and psychological terms and because of the difficulty in coping with it.
Transient gynaecomastia often occurs in males after birth, due to persistent postnatal estrogens acquired from the mother by crossing the placenta. These themselves disappear during the first year of life.
Pubertal gynaecomastia occurs in up to 60% of 14-year-old boys. This is due to hormonal changes, due to an imbalance between estrogens and testosterone, especially during the period of rapid growth.
It can manifest as enlargement of either one breast only or both breasts at the same time. The breasts are often sensitive to touch and painful. By puberty, the condition corrects itself within two years.
In adulthood, breast enlargement in men is associated with another disease in 50% of cases.
Around the age of 50, it is mainly due to the influence of a decrease in testosterone.
Gynecomastia is a hormonal disorder. It is caused by an imbalance between free estrogens and androgens.
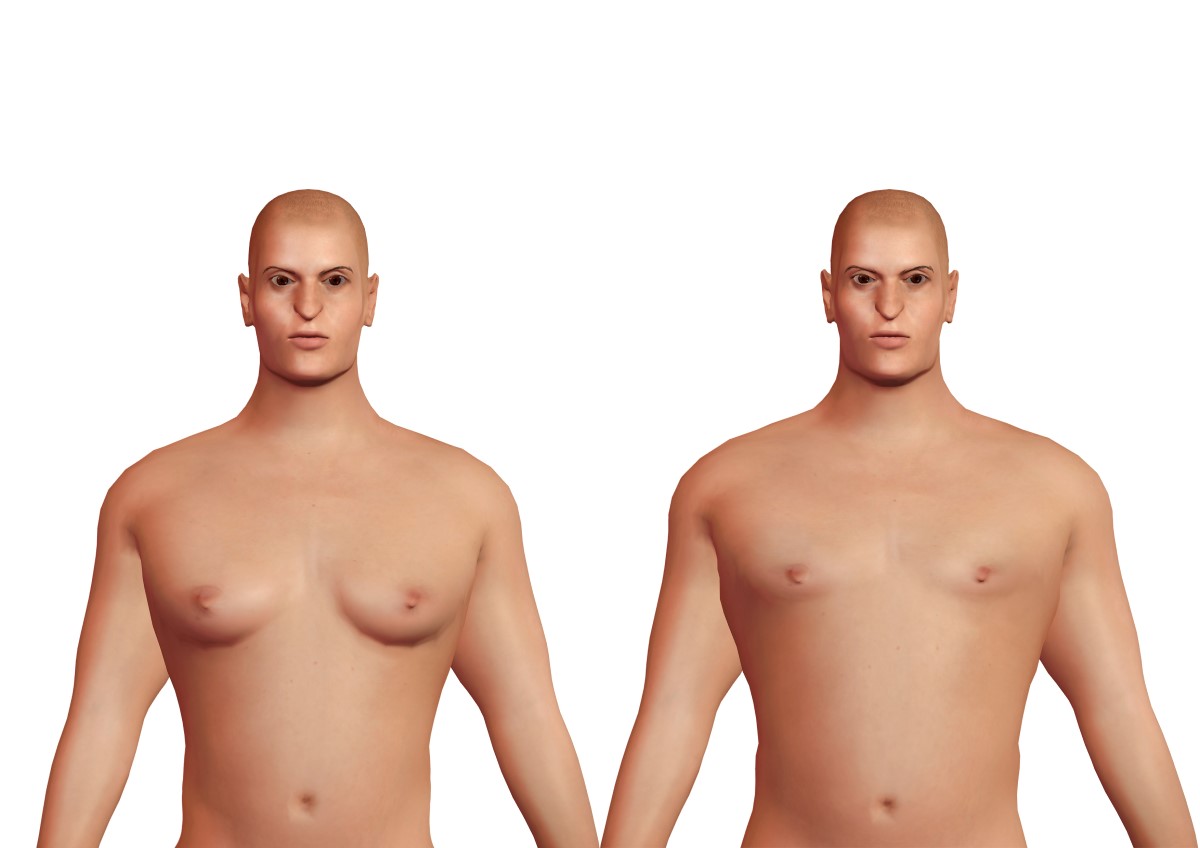
The cause may be physiological or pathological.
The cause may be the intake of estrogens or other female hormones.
The formation of estrogen or other substances similar to female hormones occurs in the case of testicular tumors.
The production of prolactin (a peptide hormone that stimulates the development and remodelling of the mammary gland) or human chorionic gonadotropin (occurring only physiologically in women during pregnancy) is increased by pituitary tumours and lung cancer.
Increased production of the hormone prolactin can also occur in people taking certain types of drugs or medications. In men, increased prolactin production also manifests itself in unexplained headaches, vision problems, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, loss of body hair and weight gain.
Decreased production of testosterone and other androgens occurs in the case of Klimnefelter's syndrome, lesions on the hypothalamus, liver diseases, neurological diseases.
Decreased testosterone production is also characteristic of pseudohermaphroditism (genital disorders with signs of one sex, with glands of the other sex), and also in congenital adrenal hyperplasia (enlargement of the adrenal glands with subsequent increased production).
Some drugs also cause breast enlargement in men.
Drugs that can cause gynecomastia
- Antiandrogenic drugs used in the treatment of prostate
- Anabolic steroids and androgens in the treatment of hormone deficiency
- Medications for AIDS
- ADHD medications containing amphetamine
- Drugs used in the treatment of anxiety, and this group includes diazepam
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Drugs for the treatment of obesity, which is treated by injections of human chorionic gonadotropin
- Antibiotics
- Certain drugs used for stomach ulcers
- Chemotherapy
- Drugs for heart disease such as digoxin and calcium channel blockers
Substances causing gynecomastia
- Alcohol
- Anabolic steroids
- Amphetamines
- Marijuana
- Heroin
- Methadone
In diseases where hormone regulation is affected
- Breast cancer in men
- Haemochromatosis (increased resorption of iron from the intestine and excessive deposition in the tissues)
- Idiopathic cause (arising from an unknown cause)
- Hypogonadism (a disorder of gonadal function in which testosterone production is reduced and infertility occurs)
- Ageing (hormonal changes occurring due to ageing, especially in overweight men)
- Tumours (testicular, adrenal, pituitary)
- Hyperthyroidism (the thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine)
- Hypothyroidism (reduced thyroid function)
- Kidney failure
- Dialysis
- Liver failure
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Inflammation of the liver
- Malnutrition and starvation
- Obesity
Herbal products affecting breast growth in men
These include herbal oils from tea tree, lavender, which are also used in shower gels, shampoos, lotions. Breast enlargement is probably due to weak estrogen activity.
Risk factors for gynecomastia
- Adolescence
- Older age
- Use of anabolic steroids
- Various diseases
Diagnosis mainly focuses on medications or drugs taken.
Bronze discoloration of the skin is a symptom of hemochromatosis. Formations on the testicles, neurological symptoms are observed.
Symptoms
Gynecomastia may appear by uneven enlargement of the breasts. There may be enlargement of only one, but also of both breasts.
It may start as a palpable lump located around the nipple, which may be painful.
Acute gynecomastia is characterized by pain and tightness in the breast due to swelling of the mammary gland. This stage may also be the initial symptom in breast cancer.
In inactive gynaecomastia, the breast gland is painless, but fibrous changes predominate in its structure, manifested by the multiplication and thickening of the tissue.
Pseudogynaecomastia, lipomastia, also called adiposomastia, is an enlargement of the breast due to the multiplication of fatty tissue in the breast. In pseudogynaecomastia, the mammary gland does not enlarge or grow. Fat in the breast increases, which may also be the result of weight gain. It is often found in obese men.
In breast cancer, breast enlargement is usually unilateral, with irregular borders. The breast is firm, has a rough consistency, is immobile, and is localized marginally. Other symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes and ulceration.
Other findings in the breast may be:
- Cyst - A cavity filled with fluid or other dense mass that is circumscribed from the surrounding tissue.
- Fibroadenoma - This is a benign disease of the breast. It forms a circumscribed, solid mass of varying size that grows slowly.
- Mastopathy - The formation of nodules and cysts in the mammary gland.
Symptoms are also classified by stage
Stage 1 - the mammary gland is palpable and inconspicuous to the eye
Stage 2 - breast enlargement, with a feeling of tightness, breasts are sensitive to touch and there may be a small secretion from the breast
Stage 3 - breasts are significantly enlarged, as in pubertal girls
Symptoms of gynaecomastia
- Breast pain, especially in adolescent boys
- Swollen breast tissue
- Breasts are sensitive to touch
- Nipples are also sensitive due to friction of clothing
- Discharge from one or both nipples
Seeing a doctor is essential if gynecomastia causes symptoms such as:
- A palpable lump in the breast
- Breast pain
- Unusual changes in the breast
- Itching in the breast or armpit area
- Discharge from the breast nipple
Treatment is mainly aimed at the underlying disease and the alleviation to elimination of breast enlargement in the male breast.
Gynecomastia can be treated with medication, surgery, as well as by discontinuing the drugs and illegal substances that caused the gynecomastia.
In the case of neonatal and pubertal gynecomastia, the breast enlargement disappears spontaneously, but it is necessary to exclude another nature of origin.
The treatment is mainly directed according to the cause of the occurrence
Hyperplasia is the multiplication of cells due to the use of certain drugs. The basis of treatment is the withdrawal of the drugs causing gynecomastia.
Hypogonadism is caused by insufficient production of male sex hormones. The treatment is the deployment of testosterone drugs.
Hyperprolactinemia is an increase in the level of the hormone prolactin in the blood. The treatment is to discontinue the medications that caused the breast enlargement. In the event that the man is not taking any medication, prolactin medication is administered.
Diseases with symptom "Breast enlargement in men"
Interesting resources










