- wikiskripta.eu - general information about teeth
- stomaklinik.sk - information about periodontal disease
Teeth wobbling: what are the causes (in adults and children)?
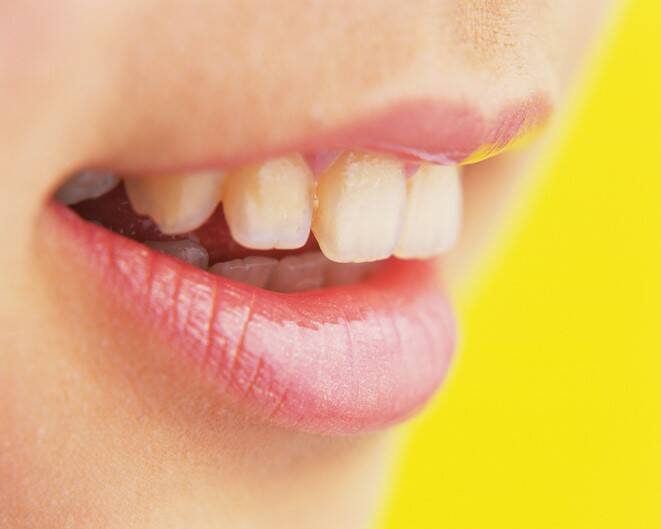

Milk teeth in children loosen naturally to be replaced by adult, permanent teeth. But in an adult, this is a phenomenon that indicates a disease. Neglect can mean serious complications.
Very often it is a symptom of an inflammatory or infectious disease in the oral cavity.
In this case, it is necessary to seek professional medical treatment from a dentist who can determine the cause of the wobble. Of course, external influences and causes that are not related to the oral cavity must be ruled out before the visit itself.
In childhood
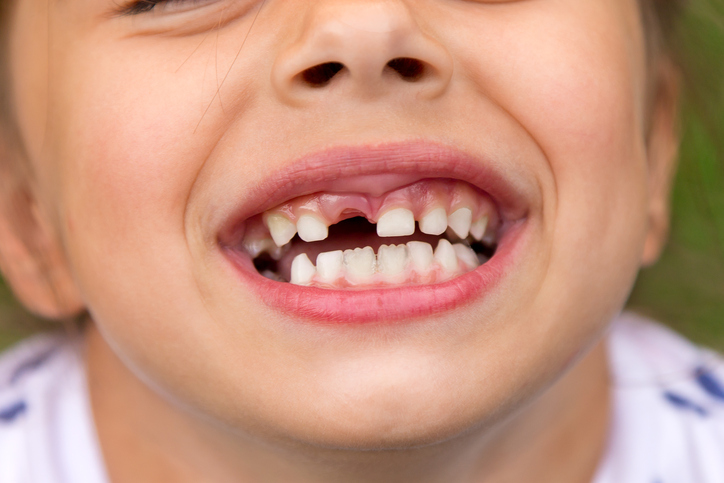
In children, tooth wobbling is caused, for example, by the natural replacement of milk teeth by permanent teeth. Milk teeth begin to wobble and later fall out. The front teeth are the first to begin to wobble. The child then begins to grow new teeth, which are already a permanent part of the dentition.
In adults
In adults, tooth wobbling can be associated with, for example, tooth decay that has spread to the root and may have caused isolated inflammation. This has not spread to other teeth and the tooth has begun to wobble due to the inflammation.
Such an unstable bed can occur in the event of complications after a tooth repair. But even if a person ignores the symptoms of tooth decay, it will subsequently spread up the root to the tooth and into its suspension apparatus.
Gingivitis as a cause
But if the rocking of the teeth is extended to several teeth within the oral cavity, there is already a suspicion of an inflammatory process in the gum. Gingivitis is very widespread, it is divided into:
- gingivitis
- periodontitis
- periodontitis
- periodontal atrophy, the most serious condition
Gingivitis
The gum (gingiva) is part of the hanging apparatus of the tooth. It surrounds the teeth. In gingivitis, symptoms are present:
- swelling, swelling of the gingiva and a change in its shape.
- pain
- redness
- bleeding
- sometimes pus formation, swelling
- in some cases the body temperature may rise
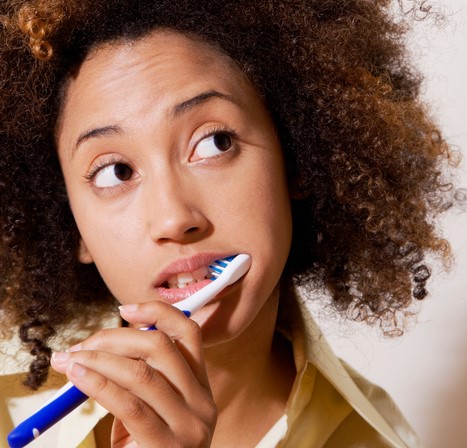

Tooth decay is very often caused by gingivitis, which is caused by plaque formation. This is caused by poor or improper dental hygiene.
Dental plaque is also made up of bacteria that can get into the tooth and gums and cause inflammation, pain and, of course, tooth wobbling. Also, the infection can spread to other teeth in the area. That is why in this case it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible, who can examine and treat the teeth.
Parodontitis
Inflammation of the attachment apparatus of the tooth is called periodontitis. It is an inflammation that is located in the area of the gum, where it adheres closely to the tooth. Often this inflammation tends to spread directly to the root of the tooth.
This causes a weakening of the stability, recession of the gum, and this can also cause the tooth to wobble. Gradual destruction of the hanging apparatus, the development of a pathological tooth decay, and the exposure of the tooth cusps. Gradually, if the condition is not addressed, the tooth becomes loose.
Periodontal disease
Paradentosis is also related to a similar case. Because this condition is also a disease of the hinge apparatus of the tooth. Here, however, there is no inflammatory spread, although the stability is also disturbed in this case. This results in tooth wobbling.
Periodontal disease is also characterised by bleeding gums, especially when cleaning the teeth. In periodontal disease, the disease can spread rapidly to other teeth. This is why, if this disease is suspected, specialist treatment by a dentist should be started as soon as possible.
Periodontal atrophy
It occurs naturally in old age, usually after the age of 60. The disease is non-inflammatory and relatively the same on all teeth. There is a loss of tissue in the suspension apparatus and also tissue in the jaw and a loss of cementum.
But if it occurs earlier and other problems are associated with it, a professional examination is needed. Of course, the treatment suggested by the dentist is also necessary.
Video and information about the cause of tooth problems
Diseases with symptom "Teeth wiggling"
Interesting resources
Related










