Cloudy urine: what are the causes of pale, white, foamy or cloudy urine?
The colour of urine depends on various factors that are not a symptom of disease, such as dehydration, fever, or after heavy exertion. However, diseases also cause cloudy urine. Examples of these are inflammation, kidney stones, or other causes.
In its normal state, urine is clear and has a golden yellow colour. This is also due to a dye called urochrome. Urine can be cloudy and change colour due to the presence of protein. Alternatively, if there is pus, blood or even faeces in the urine.
The reason for cloudy urine is not a disease
In some cases, it is possible to observe cloudy urine even without it being a symptom of a serious disease. For example, with fever, overheating of the organism or, on the contrary, when it is hypothermic.
But also when a person performs excessive physical exertion. The darker color of urine is also in dehydration. Similarly, in the morning, the color of urine is different, dark. And this is due to the fact that in the bladder there is concentrated urine from the whole night.
Tip: What are the symptoms of dehydration and dehydration in children is dangerous
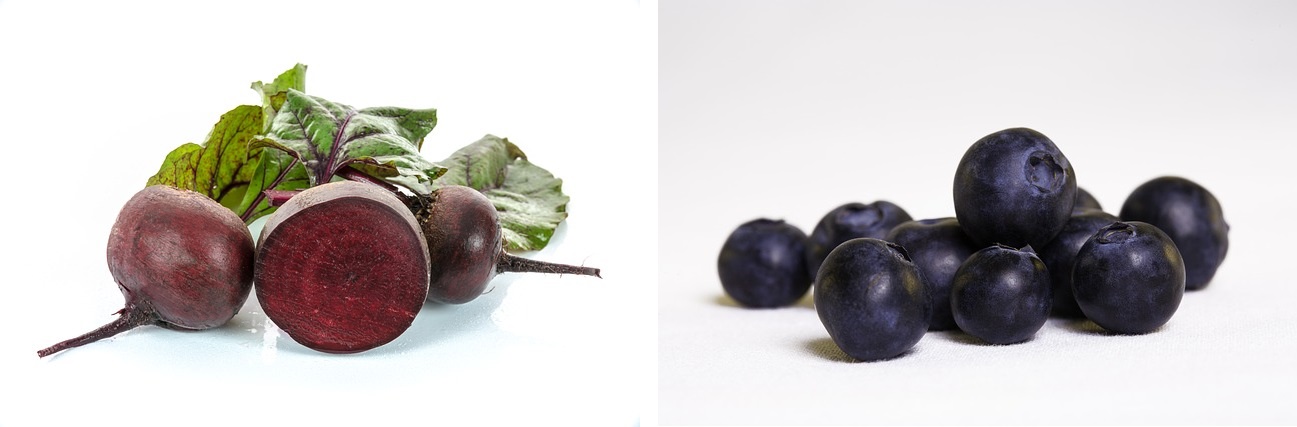

The color of urine is also influenced by food. After eating beetroot, it is natural that the urine turns pink to red. And the same is the case with blueberries, blackberries.
Diseases as a cause of cloudy urine
Turbidity of urine can be caused by various substances. In addition to diet, as we mention, urine is colored by blood, pus, the presence of proteins, insufficient fluid intake or increased exertion.
Dark colored urine is also a symptom of a problem in liver diseases. And especially in hepatitis. Dark color can also be in diseases of the gallbladder.
Cloudy urine with proteins

The presence of protein in the urine indicates that there may be a kidney disorder. Because normally protein is not found in the urine. The urine is milky cloudy, that is, white in colour.
White, pale cloudy and foamy urine = possible presence of protein.
Protein-cloudy urine can have several causes.
Protein in the urine is found on the basis of inflammation of the kidneys, in kidney stones, in excessive breakdown of red blood cells. The breakdown of muscle fibre, after an injury, can also be a cause.
Even plasma cell cancer can manifest itself in whitish urine. It is a disease of the blood when monoclonal substances penetrate directly into the urinary tract.
When is blood present in the urine?
Blood in the urine is a symptom of inflammation of the glomeruli. The glomeruli are the glands in the kidneys that are responsible for filtering the blood. For more information about this inflammation, see the article glomerulonephritis.
Blood in the urine also indicates inflammation of the urinary tract, bladder or kidneys. In most cases, it has a bacterial origin. It is typically manifested by pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urination or pain when urinating.
If urinary tract inflammation is left untreated, it can develop into kidney inflammation. This is also manifested by cloudy urine. Kidney inflammation can be either acute or chronic, in which there is a high risk of kidney failure.
Kidney failure brings with it other complications. The failure is both acute (sudden) and chronic. In acute failure, urine production may decrease or even stop. Nausea is associated with this, as well as swelling of the body and face.

Chronic renal failure is characterised by fatigue, nausea, headaches, muscle tingling and cramps. But also weight loss, scaly skin or a bad taste in the mouth.
Blood in the urine also occurs with kidney stones. These form in the kidneys or urinary tract. They occur when salts and minerals are not dissolved and combine to form concretions. The stones then travel through the urinary system and erode its walls. This irritation of the mucous membrane causes pain (colic). Blood in the urine (haematuria) may be associated.
However, blood is primarily microscopic. This means that it cannot be observed with the naked eye. It is more typical of a man's weight loss and the pallor of his skin. In some cases, it can indicate prostate cancer in men, but also inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis).
Pus in the urine
If pus is present, it is mainly an excessive amount of white blood cells in the urine. This points to some inflammatory or infectious problem. If the amount of pus is too high, the urine turns white or yellow and smells.
Urinary tract infections are common in women as well as girls. Therefore, it is possible to observe cloudy urine even in children. Also, apart from cloudy urine, it is possible to smell the odor.
The most common cause of purulent discharge from the urethra is inflammation of the kidneys or bladder. An example of an infectious disease is gonorrhoea. Urine is clouded with pus. Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease. Pain during urination is also typical in this case.
In women, infections are easily transmitted from the genital to the urinary tract. This can also be the case with vaginitis. This can be caused by chlamydia or trichomoniasis.
Faeces in the urine are a serious symptom
Cloudy urine with an admixture of faeces is a serious problem. The anatomically close positioning of the urinary and digestive systems can cause this phenomenon in some difficulties. This condition occurs as a result of diverticulosis, but also as a consequence of cancer or other pathological connection between the digestive and excretory systems.
Cloudy urine in pregnancy
In some cases, cloudy urine can also occur in pregnant women in the case of pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is a life-threatening condition, especially for the fetus, but also for the pregnant woman.

A change in urine color can occur during pregnancy for the presence of:
- blood
- white blood cells, i.e. leukocytes
- bacteria
- yeast
- proteins
- fats
- salt crystals
Diseases with symptom "Cloudy urine"
Herbs used forCloudy urine










