- solen.cz - Fibre
- solen.cz - Prebiotics and postbiotics in the 21st century
- prolekare.cz - Optimization of inulin isolation from chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) and its some applications in social practice
- medicalnewstoday.com - What to know about inulin, a healthful prebiotic
- researchgate.net - Inulin Effect on Weight Loss and Associated Parameters with the Development of Cardiovascular Disease in Obese Dyslipidemic Subjects
- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Beneficial health properties of psyllium and approaches to improve its functionitie
- medicalnewstoday.com - 7 benefits of psyllium
- prolekare.cz - News in obesity pharmacotherapy
What is fibre: what effect does it have on weight loss + where is it found

Fiber is essential for the proper functioning of our body. Does it really have an effect on weight loss?
Article content
- What are prebiotics?
- What prebiotics are found in infant formula?
- What are the properties of fibre?
- Fibre and its effect on the small intestine
- Fibre and its action in the large intestine
- What are the sources of fiber?
- What are the benefits of foods that contain fibre?
- Fibre in food supplements
- Does fibre help with weight loss?
Fibre must not be absent from our diet. It has many health benefits, for example, it softens stools and speeds up the passage of food residues through the digestive tract. This reduces the risk of colon cancer or diverticulosis.

By fibre we can think of edible plant parts that are not broken down and digested in the small intestine. These plant parts are processed in the large intestine.
The action of intestinal bacteria produces short fatty acids (acetic, propionic, butyric) and gases (carbon dioxide, methane). This processing of dietary fibre is called fermentation.
The main benefit to the human body is the formation of short fatty acids. These are used for energy in the portal transfer of blood to the liver. In addition, they provide fuel for the cells of the intestinal epithelium.
Butyric acid has a protective effect for the colonic epithelial cells (colonocytes).
Short fatty acids create an acidic environment in the intestine. As a result of their action, the growth of putrefactive bacteria is inhibited and the growth of fermentative bacteria is promoted.
By this mechanism of action, they reduce oncogenic activity in the intestine and also reduce the risk of civilisation diseases.
Dietary fibre binds certain vitamins, trace elements, calcium and cholesterol, thereby affecting their absorption. In addition to these substances, it has the ability to bind certain toxins, thereby protecting the intestinal mucosa from their action.
Due to its positive effect on the intestinal microflora, fibre is referred to as a prebiotic.
What are prebiotics?
Prebiotics are defined as indigestible substances that are part of food.
Prebiotics selectively promote the growth or activity of one bacterium or a limited number of intestinal bacteria. As a result, they positively influence the composition of the intestinal microflora of the large intestine.
In addition, they have a beneficial effect on the overall health of a person.
They are involved in the so-called bifidogenic effect, by which they promote the selective growth of bifido and lactobacteria. In addition, they help to increase the number of bacteria that process hydrogen sulphide, indoles, ammonia and bile acids.
Among their effects is the ability to increase the volume of the intestines. They thus have an anti-constipating effect.
Among the conditions for the proper action of prebiotics are:
- they cannot be hydrolysed
- they are absorbed in the upper digestive tract
- they are a selective substrate for one or more strains. probiotics
- affect the intestinal flora by selective induction or systemic action
The most important prebiotics obtained from the diet include: pectins, inulin, lactose, lactulose, lactol, sorbitol, xylitol, arabinogalactan, raffinose, betaglucan, oligofructose, alcoholic sugars, difructose anhydride, resistant starch.
Oligosaccharides of prebiotic fiber are found in the following foods: breast milk, onions, artichokes, leeks, parsley, chicory, garlic, broad beans, peas, bananas, whole grain breads and pastries, oats, cereals and cow's milk.
What prebiotics are found in infant formula?
Infant formula contains several types of prebiotic mixtures. These mixtures consist mainly of oligosaccharide derivatives (composed of 2 to 10 monosaccharide units).
The most commonly used combinations are low molecular weight galacto-oligosaccharides and high molecular weight fructo-oligosaccharides.
What are the properties of fibre?
Fibre has many positive effects on the human body. The properties of fibre include:
- resistance to hydrolysis by digestive enzymes
- ability to pass unchanged from the small intestine to the large intestine
- the ability to influence certain functions of the digestive tract

Fibre and its effect on the small intestine
Fibre in the small intestine increases the content of the food eaten. As a result of its action, the passage of the contents of the small intestine is accelerated. At the same time, it reduces the absorption of nutrients, thereby reducing the activity of pancreatic and intestinal enzymes.
By reducing the absorption of nutrients, glycaemia is reduced. Fibre has the ability to bind bile acids to itself. In this way, it acts to lower blood cholesterol levels and reduces the absorption of fats from the diet.
Fibre and its action in the large intestine
The colon is considered to be the main site of action of fibre. Most soluble fibre undergoes a fermentation process in the colon. Difficult to dissolve fibre will increase its volume and frequency of stool.
Fiber protects the lining of the colon from the action of toxic substances.
Fibre is divided into 2 groups:
- Soluble fiber (fermented) - Can be fermented to varying degrees. These include pectins, gum Arabic, inulin, fructooligosaccharides.
- Insoluble fibre - Cannot be fermented. This group includes cellulose, wheat and corn bran, resistant starches.
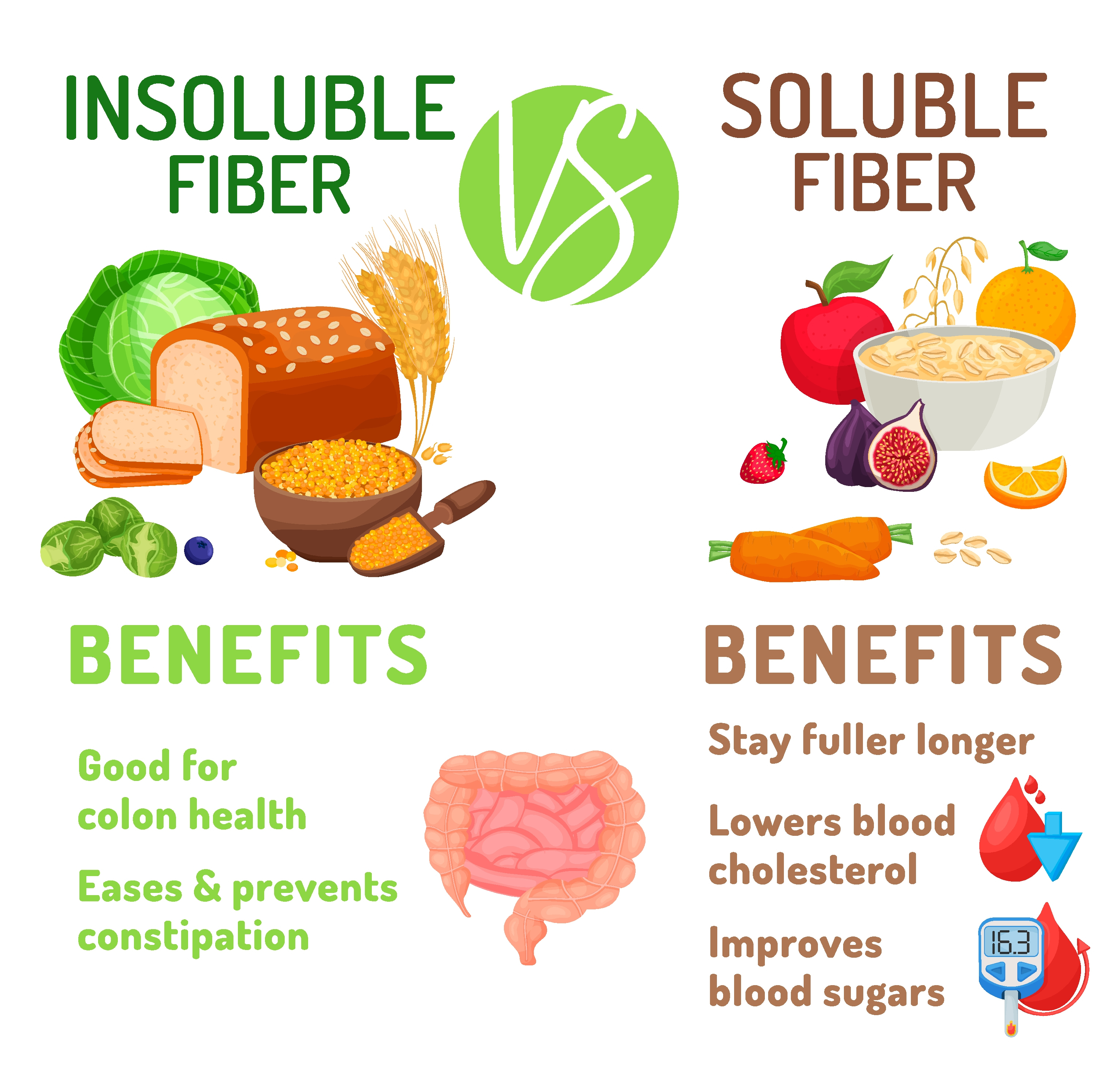
What are the sources of fiber?
Soluble fiber is found mainly in fruits (apples, citrus fruits), vegetables and legumes (beans, lentils, peas). Nuts and seeds are also sources of fiber.
The highest content is in flaxseeds.
Sources of insoluble fibre are wholemeal flour products (wholemeal bread, pasta, couscous) and wholemeal cereals (paddy rice, bulgur, barley).
Both types of fibre are present in different amounts and proportions in foods. For this reason, it is very important to eat more foods that contain fibre.
Adults should take care to increase their fibre intake.
The average consumption is approximately 15 g/day. Experts recommend an intake of 30 g of fibre/day.
This means that an adult should eat approximately 400 to 500 g of fruit per day. Many of you cannot imagine.
The fruits that contain the most fibre include:
- raspberries
- plums
- blackberries
- gooseberries
- currants
Vegetables should be part of our diet. Every meal we eat in a day should contain either raw or prepared vegetables.
Vegetables contain the most fibre:
- beans
- broccoli
- cauliflower
- peppers
- tomatoes
- lettuce
- white cabbage
What are the benefits of foods that contain fibre?
Foods that contain more fibre are usually difficult to chew. Therefore, it takes a long time to eat such foods. As a result, you feel full and reduce overconsumption of food.
Fibre in food supplements
Dietary supplements contain mainly inulin and psyllium.
- Inulin
Inulin is a polysaccharide. It is formed in the leaves of plants. Like starch, it is also stored in the seeds and underground parts of plants (root, tuber). Inulin is found in approximately 30 000 plant species.
In our conditions, the most well-known plant species include: oman, sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, dandelion, burdock, burdock, thistle, black root, dahlia, onion and garlic.
What are the effects of inulin?
In medicine and pharmacy, inulin is considered a therapeutic diagnostic. It is used as a reference substance in the determination of kidney function. Inulin is a marker in the determination of the total size of the extracellular spaces.
It is also added as a major or minor ingredient in commercially produced tea mixtures. These are used to treat both severe and milder forms of diabetes.
Inulin has a positive effect on the microflora in the colon. It also has a beneficial effect on bifidobacteria and other beneficial bacteria found in the digestive tract. Overall, it has a positive effect on the health of the human body.
In the cosmetics industry, inulin-type fructosans are an important ingredient in skin creams. They have very good moisturising properties. They are particularly popular because they are non-sticky and non-greasy.
- Psyllium
Psyllium is a natural source of concentrated fibre. It is obtained from the purified seed coats of the plantain.
It has many beneficial effects on human health:
- lowers total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol - promotes bile and fat excretion
- has a positive effect on glucose metabolism
- antidiarrhoeal effect - has the ability to absorb water in the intestines
- anti-constipation - increases the volume and adjusts the consistency of stools
- lowers blood pressure
Does fibre help with weight loss?
Some types of fiber are used in achieving weight loss goals. In general, fiber is known to reduce appetite.
The mechanism of action is that fiber has the ability to absorb water in the intestines and slow down the absorption of nutrients. As a result of this action, the person feels fuller and therefore reduces calorie intake.
The effects depend on the type of fibre. Some types have no effect on weight loss. Others have a significant effect. An example is the plant polysaccharide glucomannan.
Glucomannan is found in the root of the plant Amorphophallus konjac. Glucomannan is a natural fibre. In combination with a low-calorie diet, it is very effective for weight loss.
The following properties apply when trying to lose weight:
- it contains few calories
- binds water
- promotes satiety
- reduces fat absorption
- helps maintain normal cholesterol levels
How should we use fibre for weight loss?
Fibre should be taken before meals (15 to 60 minutes). It is recommended to take it with at least 250 ml of water.
Can glucomannan have side effects?
Yes, it can. Side effects include feeling bloated, passing loose stools, feeling gassy and diarrhea.
Interesting resources
Related










