- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Stretch Marks; Amanda M. Oakley; Bhupendra C. Patel
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - A novel 1565 nm non-ablative fractional device for stretch marks: A preliminary report; Matteo Tretti Clementoni and Rosalia Lavagno
What are stretch marks? A little big problem: Why do they form and how to remove them?
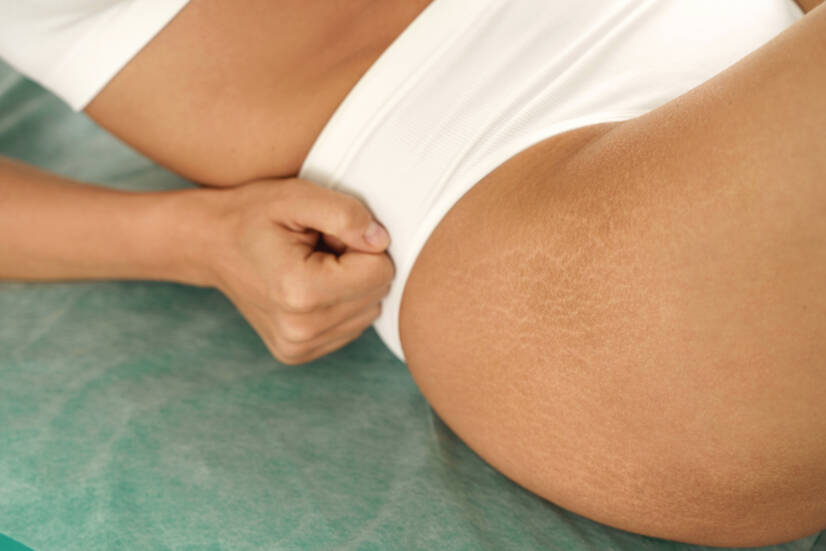

Stretch marks are small scars on the skin. Most of us have them. And those of us who don't have them have probably at least heard of them.
Article content
But what are stretch marks?
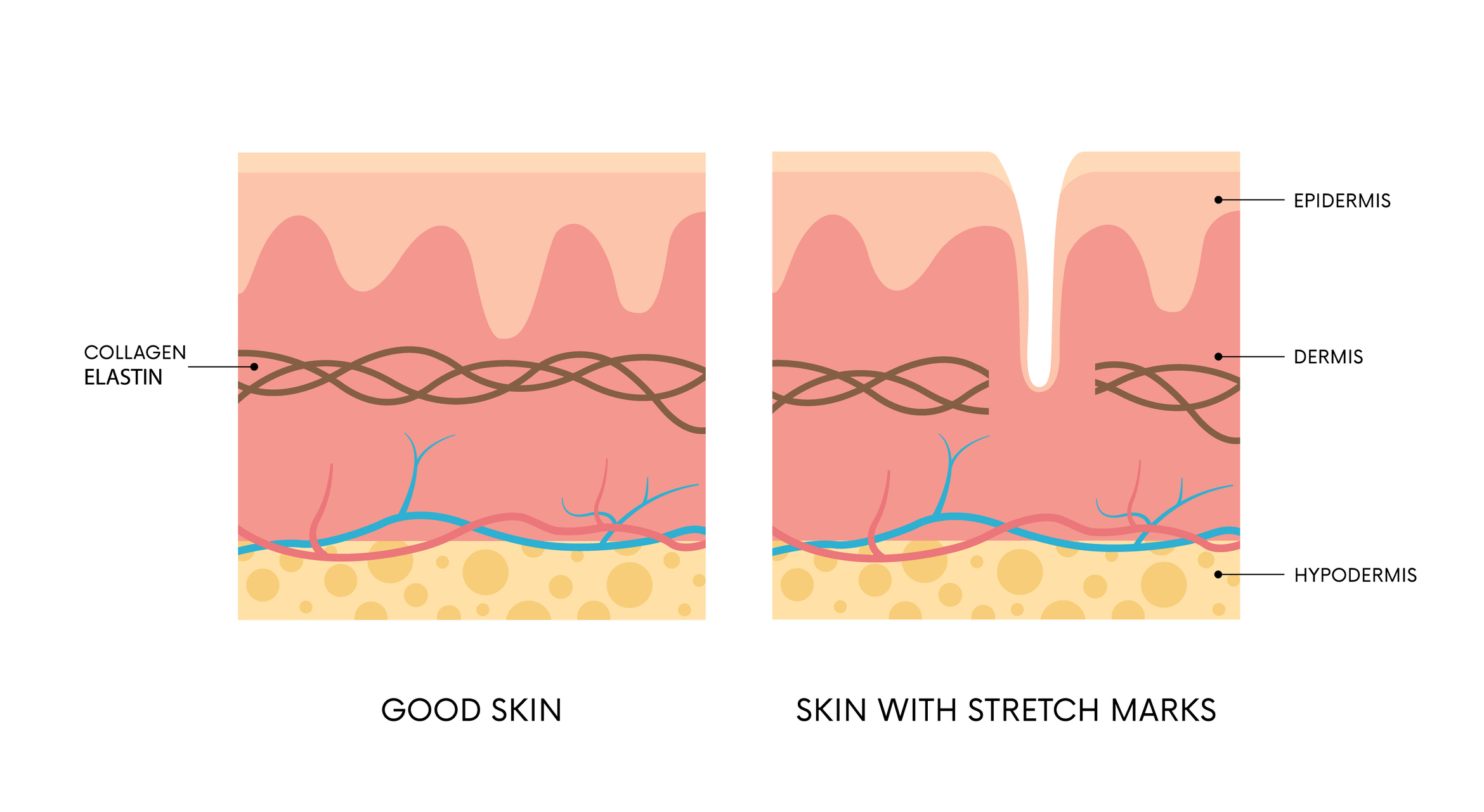
Stretch marks are scars. They are a group of so-called dermal scars. They are most often caused by stretching of the skin - when the elasticity of the skin is no longer sufficient and the skin cracks.
In addition, there is a second factor of formation, namely structural changes in collagen and elastic tissue at the same time.
Stretch marks most commonly affect the skin:
- Abdominal
- buttocks
- and thighs
In addition to the above mentioned areas, they can very often appear on:
- breasts
- back
- but also in the armpits
- or in the groin
Stretch marks fall into several categories.
Stretch marks are known as:
- atrophic - they arise at the site of thinning of the skin
- pregnancy stretch marks - occur mainly during pregnancy, but can also appear after pregnancy
- distension - caused by stretching of the skin
Stretch marks are also divided into several categories based on their colouration.
At the beginning of their formation, stretch marks are pigmented. Over time, this pigmentation fades and stretch marks fade. From this so-called colour point of view, they can be divided into:
- red striae - striae rubra
- black stretch marks - striae nigra
- dark blue or dark purple striae - striae caerulea
- white striae - striae alba
In addition to their appearance, stretch marks can sometimes be manifested by itching of the skin, especially just before and during their appearance.
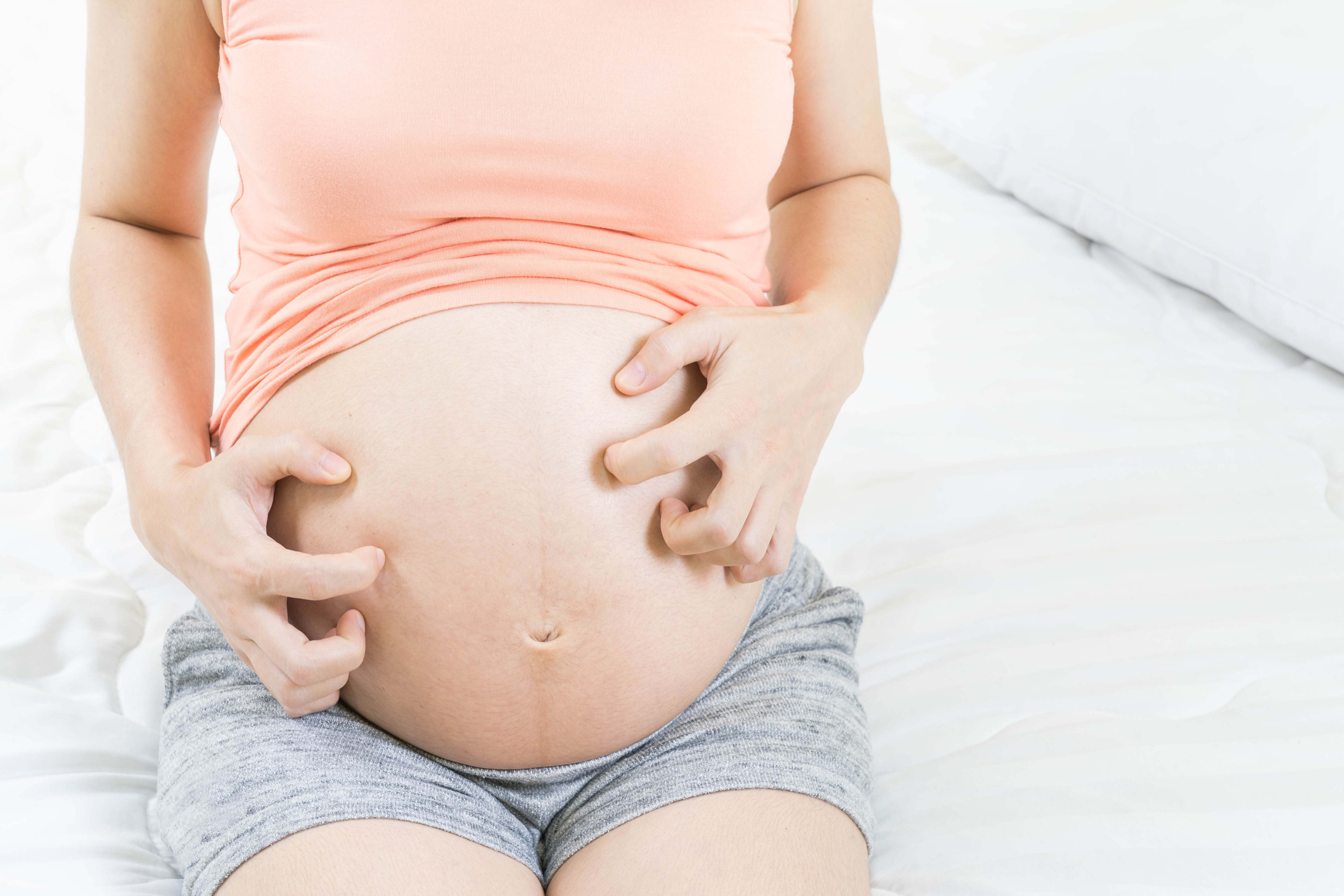

Stretch marks on the skin occur especially with rapid weight change. However, they can also be caused by endogenous or exogenous corticosteroids.
As we have already mentioned, stretch marks distensae are formed when the skin is stretched.
Thus, they usually arise:
- during pregnancy - 43% to 88% of stretch marks
- during puberty - 6% to 86% of stretch marks
- obesity - 43% of stretch marks
Read also: Stretch marks in pregnancy not only on the abdomen?

Atrophic stretch marks are usually caused by a disease - for example, Cushing's syndrome or Cushing's disease.
This can be systemic, when the medication is taken internally. It can also be exogenous, in the form of preparations applied to the skin.
However, their cause may be different, for example, they may also arise in:
- anorexia nervosa
- various febrile illnesses
- or chronic liver disease
In addition to corticosteroids, other medications can also affect the appearance of stretch marks. These include:
- Chemotherapy
- long-term treatment with antibiotics
- contraceptives
- or even treatment with neuroleptics
Stretch marks are more common in women than in men.
Their occurrence is also influenced by genetics. In the case of the black race, their occurrence is more frequent. Family history is also a significant factor - that is, their occurrence in our parents and grandparents.
Even one study reported a higher incidence of stretch marks in smokers than in non-smokers.
Treatment of stretch marks - How to remove them?
Although stretch marks are only an aesthetic defect, for many people they are primarily a major psychological problem. And that's why many of them are looking for a way to treat them.
The most ideal case, of course, is to prevent their formation altogether. Sometimes, however, they cannot be avoided completely.
Let's take a look at how and if there are even methods and procedures that can remove stretch marks.
In the case of red stretch marks, the key point is treatment:
- relieve the redness
- reduce swelling
- and remove irritation
In the case of white stretch marks, the key is:
- increase collagen production
- increase the production of elastic fibres
- improve skin hydration
- reduce inflammation
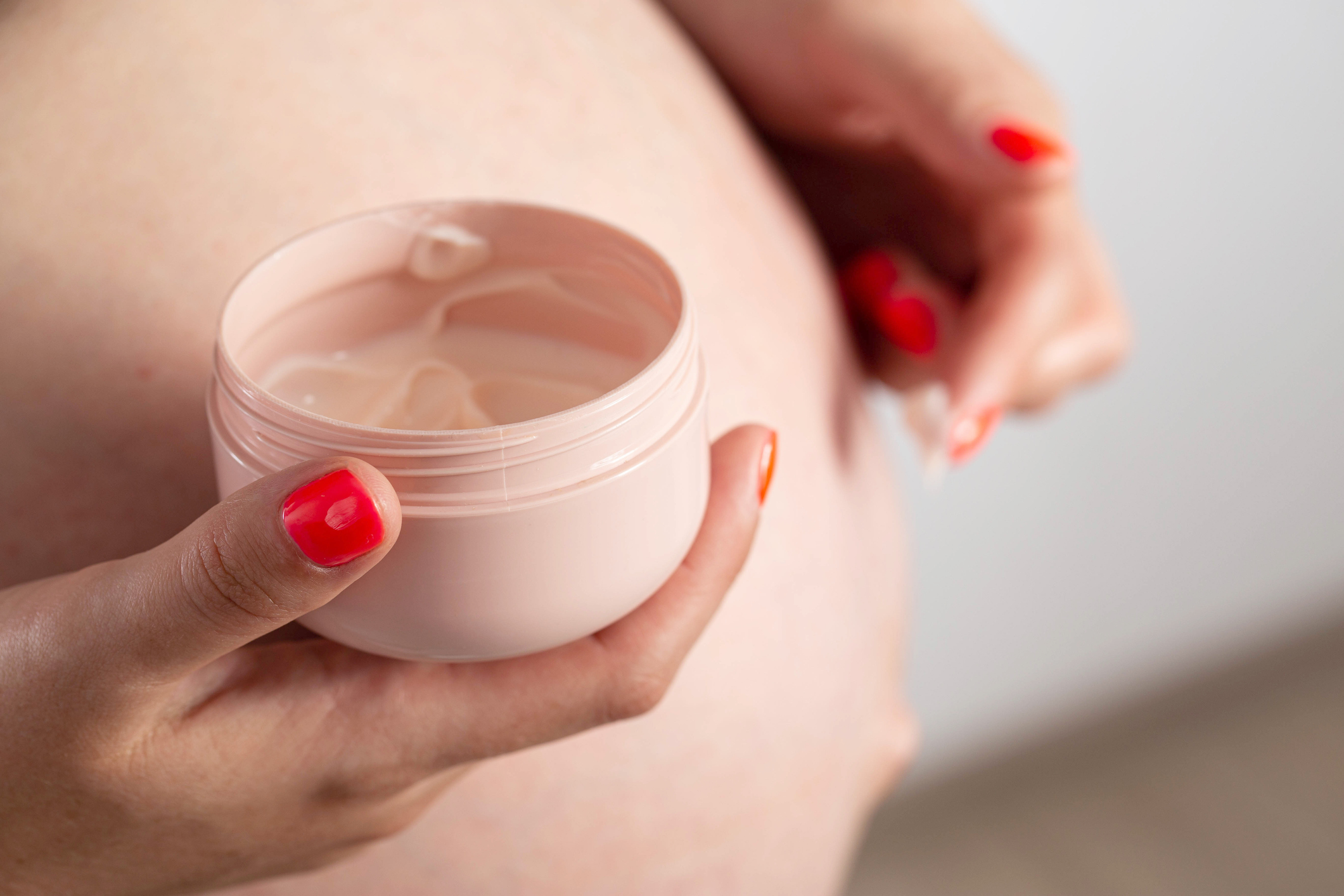
Topical gel or cream for stretch marks + skin massage
The most common and probably the most affordable way to prevent and treat stretch marks are various topical products. These are mainly creams and oils that are rubbed into the skin.
Most of these products are designed and used primarily by pregnant women. This is mainly to prevent them from forming or at least to reduce their quantity or severity.
However, none of these products have significantly positive effects. Although the price is in many cases quite high. The reason for the lack of evidence of effectiveness is mainly due to the low number of people involved.
Some publications mention the use of silicone gels for the treatment of atrophic scars. These silicone gels are recommended especially for stretch marks distensae.
Another study describes the positive effects of topical preparations containing tretinoin. These results were observed when used for red stretch marks compared to placebo. The application lasted for six months.
However, caution should be exercised especially during pregnancy. Preparations containing tretinoin should not be used during this period.
Sometimes you may also come across chemical peel-based products that are designed to remove stretch marks. These usually contain various acids. However, their effectiveness is also not reliably proven.
In the case of application of products to the skin, massage is also recommended. This should be part of the therapy, whether in the case of stretch marks or scars.
Ultraviolet light treatment can cause repigmentation in white stretch marks. However, the effect of this treatment is only temporary. Within a few months, the pigment is lost again.
Laser treatment as the most effective form?
Laser stretch mark removal shows the best and probably most promising results so far.
It has been shown that the appearance of stretch marks improves after this treatment. On the other hand, it is not yet clear exactly which type of treatment and at which stage (white or red stretch marks) is most suitable.
The pulsed laser targets the vascular structures in red stretch marks. This reduces the redness and swelling of the stretch marks. Therefore, it seems to be more appropriate at this stage.
On the other hand, fractional lasers stimulate skin components (called fibroblasts) to produce collagen and elastin fibres. This can provide repigmentation in striae alba (white stretch marks).
Of course, like everything else, laser (or light) treatment has its negative effects. Short-term and temporary swelling may occur after its application. Redness of the skin may also occur.
Especially for darker skin types, it is better to avoid this treatment, as this skin type is at a much higher risk of side effects such as oedema (swelling) and erythema (redness).
However, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can also occur - even if only temporarily. However, this can be replaced by long-term hypopigmentation. As far as the type of laser is concerned, non-ablative devices (e.g. ResurFX) are safer than ablative ones.
Ablative and non-ablative lasers have relatively the same efficacy. Ablative types, however, have:
- more painful treatment course
- higher incidence of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- longer lasting redness
ResurFX
Twelve Caucasian patients participated in a study using the 1565 nm ResurFX non-ablative fractional laser. The study yielded relatively favorable results.
These volunteers had striae distensae in various stages. They underwent three treatments with the non-ablative laser. Each of these treatments was performed with the laser at two different settings:
- dense impact - the base of the atrophic scar needs higher collagen production - this is achieved by delivering more energy to one spot
- diffuse deep impact - used primarily to smooth the edges of stretch marks
The results were evaluated after three months. In all patients an improvement in volume but also in the colour of the stretch marks was observed.
Immediately after the procedure, severe swelling and transient redness appeared. However, no long-term and severe side effects were observed. Soreness during the treatment was described as acceptable.
The study concluded that such treatment resulted in improvement:
- pigmentation
- volume
- and appearance of stretch marks
However, it is very difficult to assess or evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. Different types of lasers may have different parameters:
- pulse smoothness
- pulse duration
- spot size
- frequency
They may also require different amounts of sessions - treatments. Also, the combination of multiple treatments is not proven or researched.
Other forms of treatment
Another popular method is the use of radiofrequency energy devices. These devices use high-frequency alternating electric current. This generates skin heat through its action.
Recently, the method of delivering radiofrequency energy to a depth of 3.5 mm has been used. This is done by multiple needle delivery.
By delivering the energy deeper into our skin, it ensures that stretch marks are shut down in all directions. This ultimately leads to an improvement in their overall appearance.
This type of treatment is also used for:
- Wrinkle reduction
- skin tightening
- improving the appearance and condition of cellulite
The above treatment has a supportive effect on:
- collagen renewal - so-called neocollagenesis
- elastin formation - neoelastogenesis
At the same time, the amount of molecules with a protein core (called proteoglycans), which form the basic component of connective tissues, increases. However, they are also found on the surface of cells.
All these processes should work together to improve the appearance of stretch marks.
In addition to the above treatments, the following treatments, for example, are used to remove or improve the appearance of stretch marks:
- microdermabrasion
- galvanopuncture
- pulsed magnetic field treatments
- but also ultrasound devices
The use of platelet-rich plasma in the form of injections is also being investigated.
The reason for the lack of evidence of the different treatment methods is the lack of photo documentation.
Ideally, these methods should have standardised photographs before and after a series of treatments. However, equally important are the results at six and twelve months after treatment.
Based on these data, it would be possible to evaluate the effectiveness of individual treatments.
Stretch marks change their appearance over time. The positive news is that many will improve over time. The most ideal time for treatment is when stretch marks are stable and no longer change over the long term.
Many of the creams and oils that are promoted these days have very little evidence of their effects.
Laser or radiofrequency treatments appear to be the most promising. They cause changes in vascularity, collagen and elastin, but the risk of hyperpigmentation cannot be underestimated.
In general, stretch marks remain a major challenge in terms of their treatment. The fact that patients' expectations are always very high plays a major role. Therefore, any therapy, as well as its possible side effects, should always be carefully discussed before the procedure itself.
Interesting resources










