- nemocnicakomarno.agel.sk - Removal of tonsils - tonsillectomy
- solen.sk - Tonsilotomy in childhood
- orl-lfuk.sk - Chronic inflammation of the palatine tonsils
- wikiskripta.eu -Tonsilla palatina
- solen.sk - How paratonsillar abscess manifests itself
Tonsils: Is it time to remove them? (Tonsillectomy in adults and children)

Do you suffer from recurrent tonsillitis? Do you have a sore throat? You may need to have your tonsils removed.
Article content
They prevent infections from descending into the lower structures of our body, such as the bronchi and lungs.
Removing them does not have a negative effect on the immune system because their function is taken over by other components of the immune system.
The cervical or palatine tonsils (Tonsillae palatinae) are a paired organ located at the back of the throat, between the two arches. The tissue bunches together to form what are called crypts. They should be clearly visible when the mouth is opened. Under physiological conditions, they are pink in colour.
Sore throat, lack of appetite, fatigue, difficulty swallowing, bad breath or repeated upper respiratory tract infections?
These symptoms can also mean you have a problem with your tonsils.
What are some known tonsillitis-related diseases?
- A paratonsillar abscess is a circumscribed purulent sac around the tonsils.
- Acute mononucleosis is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus - infectious mononucleosis.
- Tonsil enlargement (hypertrophy) - Tonsils are thickened and cause decreased airway patency. They can cause snoring and sleep apnea.
- Strep throat - The tonsils and throat are infected with bacteria of the genus Streptococcus, which cause high fevers and considerable pain.
- Tonsilloliths (tonsil stones) - Tonsils form lumps on the tonsils that harden over time and may fall out spontaneously. They cause a distinctive bad breath.
Acute tonsillitis can be caused by bacteria and viruses. It is one of the most common diseases affecting the tonsils.
Interesting information in the article.
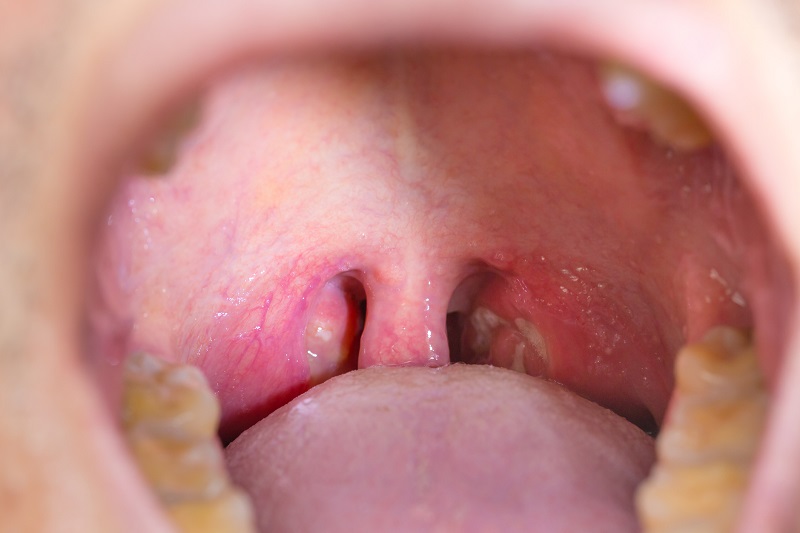
The most common indications for tonsil removal are chronic diseases
Chronic tonsillitis is most commonly found in people after repeated inflammation of the tonsils.
After repeated inflammation, scars form on the tonsils. They are a suitable breeding ground for the proliferation of microorganisms and thus the persistence of inflammation. The body's defensive cells are unable to penetrate the scar tissue, so the possibility of defense is minimized.
As a result of the change in tissue structure, the tonsils lose their protective function and become a source of possible infection.
The manifestations of the disease can be divided into:
- local manifestations
- systemic
- general discomfort
Table of manifestations of chronic tonsil disease
| Local manifestations | Systemic | Overall |
| Recurrent tonsillitis | Cardiac - pericarditis | Fatigue |
| Throat scratching, pain | Obliterative - glomerulonephritis | Increased temperature |
| Excessive formation of purulent plugs | Cutaneous - eczema | Nausea |
| Cough (other cause excluded) | Articular - inflammation, arthritis | Malaise |
| Mucus leakage (other cause excluded) | ||
| Impaired swallowing | ||
| Bad breath | ||
Diagnostics
Tonsil disease is not to be taken lightly. Diagnosis and subsequent treatment is extremely important.
Doctor:
- Takes a thorough medical history - Mention to the doctor about the condition and the course of the current illness. Do not forget about previous ones, such as frequently recurring tonsillitis.
- Performs a visual examination - After opening the mouth, the doctor will examine the oral cavity, the intensity of redness, the amount of plugs and the size of the tonsils.
- Conduct a listening examination - He or she will check for cysticity, breathing rate, regularity and any changes in heart rhythm.
- Collection of laboratory results - After blood is drawn, the doctor sends the sample to a laboratory to check for inflammatory parameters in the blood, most commonly CRP - C-reactive protein, FW (Fareus Westergren) - blood sedimentation rate, ASLO (antistreptolysin antibodies) - used as evidence of ongoing infection and recent streptococcal infection.
- Examination by an ENT specialist (otorhinolaryngologist) - Often not only for ongoing difficulties, but also to rule out a focal infection. An inflammatory lesion can cause inflammation in other parts of the body that show no symptoms - in this case the tonsils.
Treatment
Medical treatment - Antibiotics are mainly used for acute inflammatory diseases of the tonsils. For chronic tonsil disease, this treatment is ineffective.
So-called regimen measures are implemented, which include:
- Increased oral hygiene.
- Regular rinses
- Gargling
- After a visit to an immunologist, immuno-supportive treatment (which may only be temporary) may be started
Surgical treatment - Surgical removal of tonsils (tonsillectomy)
Surgical removal of tonsils by laser is a modern gentle technique.
You often ask:
When is it time for tonsil removal?
Answer:
There are not many reasons why you should have your tonsils removed. An important indication for tonsil removal is when our tonsils become our enemy, so to speak, and do more harm than good. When they threaten other organs and are a breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms.
The indications for surgical removal of tonsils (tonsillectomy) are as follows:
- Frequently recurring tonsillitis (tonsillitis 4 or more times a year is considered a frequently recurring condition).
- If repeated treatment with antibiotics does not lead to stabilisation of chronic tonsillitis
- Late complications of the heart, kidneys, joints
- When enlargement of the tonsils or lymphatic tissue causes constricted breathing
Surgical removal of tonsils (tonsillectomy)
This procedure should be carefully considered and consulted with your doctor.
The doctor numbs the tissue around the tonsils with an injection and then performs the procedure.
Or...
Under general anesthesia, where the patient is numbed in the presence of an anesthesiologist. Then the doctor performs the actual procedure.
ATTENTION!
Tonsillectomy is contraindicated in women during menstruation!
After surgery:
- Immediately after surgery, nose or mouth bleeding may occur. The attending physician or staff should be contacted immediately.
- Pain may occur in the post-operative period, which can be controlled with analgesics (painkillers).
- However, take them after consulting your doctor!
- A change in voice, bad breath or change in taste may occur.
What then?
14 days after surgery you should not:
- Do strenuous physical activity
- Bathe in hot water
- Wash your hair
- Drink alcoholic beverages, black coffee and smoke
- Socialize with different people (more susceptible to infections)
- Eating solid food (porridge, ground food is recommended)
In case of nosebleeds, mouth bleeds and increased body temperature, contact a doctor immediately!
When is tonsil removal not recommended?
Contraindications for tonsil removal can be divided into:
Absolute - Diseases that adversely affect the blood clotting system.
Relative - Currently prevent any planned procedure from being performed. The procedure can be performed once the medical condition has improved.
Table of absolute and relative contraindications to tonsillectomy
| Absolute contraindications | Relative contraindications |
| Haemophilia | Conditions following acute infectious diseases |
| Leukemia | Menstruation |
| Agranulocytosis | Pregnancy (especially 1st and 3rd trimester) |
| Severe anaemia | Mild anaemia |
| Scurvy | Organic diseases of the nervous system (after consultation with a neurologist) |
| Osler's disease | Acute mental illness (after consultation with a psychiatrist) |
| Advanced atherosclerosis | |
| Severe hyperasotemia | |
| Cardiovascular decompensation | |
| Acute liver failure |
Surgical laser removal of the tonsils
Thanks to advances in medicine and modern technology, laser surgery is now an option in addition to conventional surgical removal of the tonsils.
Instead of a metal scalpel, a laser beam is used to cut through the tonsils.
The laser is a source of direct current radiation of the same wavelength.
This wave acts on the tissue.
Tonsillectomy takes advantage of the destructive effects of the beam.
Laser surgery results in immediate haemostasis (stopping of bleeding), thanks to the effect of the laser beam.
Types of laser tonsil removal:
- Radical tonsillectomy - complete removal of the tonsils
- Laser ablation - removal of superficial tissue
The type of blade is chosen according to the type of surgery and the condition of the tonsils:
- Optical laser - Used for extensive inflammatory involvement.
- Infrared laser - With this laser, the tissue can not only be separated but also fixed.
- Holmium laser - Removes deposits inside the tonsils, but the surrounding tissue remains intact.
- Carbon laser - Reduces the volume of the tonsils and infected areas through the effect of tissue evaporation.
Indications and contraindications are the same as for surgical removal of tonsils.
But...
Laser surgery is not recommended for children under 10 years of age and for women in all trimesters of pregnancy!
Advantages and disadvantages of laser tonsil removal
Like any intervention in the body, tonsil removal has its pitfalls and, conversely, its advantages.
Let's take a look at the advantages:
- The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia, eliminating the risk of allergies to anesthetics.
- Short duration of the procedure. The procedure takes 15-30 minutes.
- No bleeding. The risk of posthemorrhagic acute anemia is reduced.
- The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis. Recovery time is shorter. The patient usually does not have to take much time off work.
- There is no open wound. There is no need to administer antibiotics in the postoperative period.
Disadvantages include:
- Possible tissue burn and pain after the local anaesthetic wears off.
- Recurrences are possible with ablative surgery because the tissue is not completely removed.
- The procedure is more costly because some technical equipment is required.
Tonsillectomy in children
There are two common indications for tonsillectomy in children. The first is constricted breathing caused by enlargement of the tonsillar tissue, often associated with enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsils. The second indication is recurrent inflammatory diseases of the tonsils, which subsequently become chronic.
Surgical removal of the tonsils is never the first choice. It is performed only after all possible conservative procedures have been exhausted.
Surgical removal of tonsils in children
Fear or apprehension on the part of parents is quite common. However, there is no need to postpone the necessary procedure or to worry unnecessarily. All necessary and specific information should be thoroughly discussed with the paediatrician. After consideration and examination by the paediatrician, the child will undergo pre-operative examinations.
The course of surgery in children:
- The child is under the expert supervision of the anaesthetist and the operating physician throughout the procedure.
- The child is put to sleep for approximately 20 minutes and the anaesthesia is not prolonged.
- The doctor removes the tonsils through an open mouth, so no external incision is necessary.
- After the tonsils are removed, thorough haemostasis (stopping the bleeding) is performed.
- The child is then taken to the post-operative ward. His physiological functions (body temperature, pulse, respiratory rate) are monitored.
- The hospital stay is not long. Usually 12-24 hours after the operation, the child and the parent go home for care.
However, it depends on the course of the operation and the subsequent recovery in hospital. In case of complications, the child's stay may be prolonged. This is decided by the attending physician!
You ask:
How should I care for my child after tonsil surgery?
Answer:
A child who has had tonsil surgery follows similar precautions as an adult.
Recommended:
- Do not perform any strenuous physical activity.
- The child should not attend school, kindergarten.
- Do not bathe the child in too hot water. Do not wash the child's hair.
- Observe oral hygiene.
- If it is necessary to administer analgesics (painkillers), consult the paediatrician for the exact dosage!
- Take plenty of fluids (not too cold or too hot).
- Intake of porridge to liquid food (soups, broths, puddings...).
- During the entire period of convalescence at home, it is necessary to monitor the general state of the diet, changes in body temperature and any bleeding. In case of bleeding, do not hesitate to contact the doctor.
How to help yourself at home?
Taking various herbs, teas and gargles can help you recover faster at home.
Recommended:
- Herbal teas - elderflower tea, rosehip tea, dried lime blossom tea, ginger tea
- Gargles - salt water, echinacea tincture (diluted 1:1)
Herbs and gargles are used only as a supportive agent in primary treatment in adults
Interesting resources
Related










