- internimedicina.cz - Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome
- solen.sk - SLEEP BREATHING DISORDERS
- mayoclinic.org - Sleep apnea
- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Sleep apnea syndrome: what is it, what causes and symptoms? Diagnosis

Sleep apnoea is a disorder classified as a sleep-wake disorder, a sleep-disordered breathing disorder. It is a condition in which breathing repeatedly stops during sleep and starts again after a brief awakening.
Characteristics
Sleep apnoea mainly affects people who snore in their sleep.
This disease is dangerous because of daytime fatigue and the development of serious lung and heart diseases.
Sleep apnea is a civilization disease that is classified as a sleep-disordered breathing disorder within sleep-wake disorders.
The term "sleep apnoea" refers to a condition in which breathing stops for more than 10 seconds and is repeated more than 5 times per hour. The term "hypopnoea" refers to a condition in which the tidal volume is reduced by more than half for at least 10 seconds. In these situations, desaturation, or reduced oxygen saturation of the blood (haemoglobin), occurs.
The main types of sleep apnea include:
- Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common form of the disease and is caused by airway obstruction.
- Central sleep apnoea occurs when signals from the brain's respiratory centre to the muscles that control breathing are attenuated.
- Complex sleep apnoea syndrome is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnoea, for example when treated with certain drugs.
In developed countries, it is a common disease with a prevalence of 5-8% of the population. The actual numbers may be even higher, as it is a significantly under-diagnosed disease.
Males are more often affected, at a ratio of 2:1 to females, but after the menopause the incidence of sleep apnoea increases in females. The highest incidence is between the ages of 40 and 50.
Causes
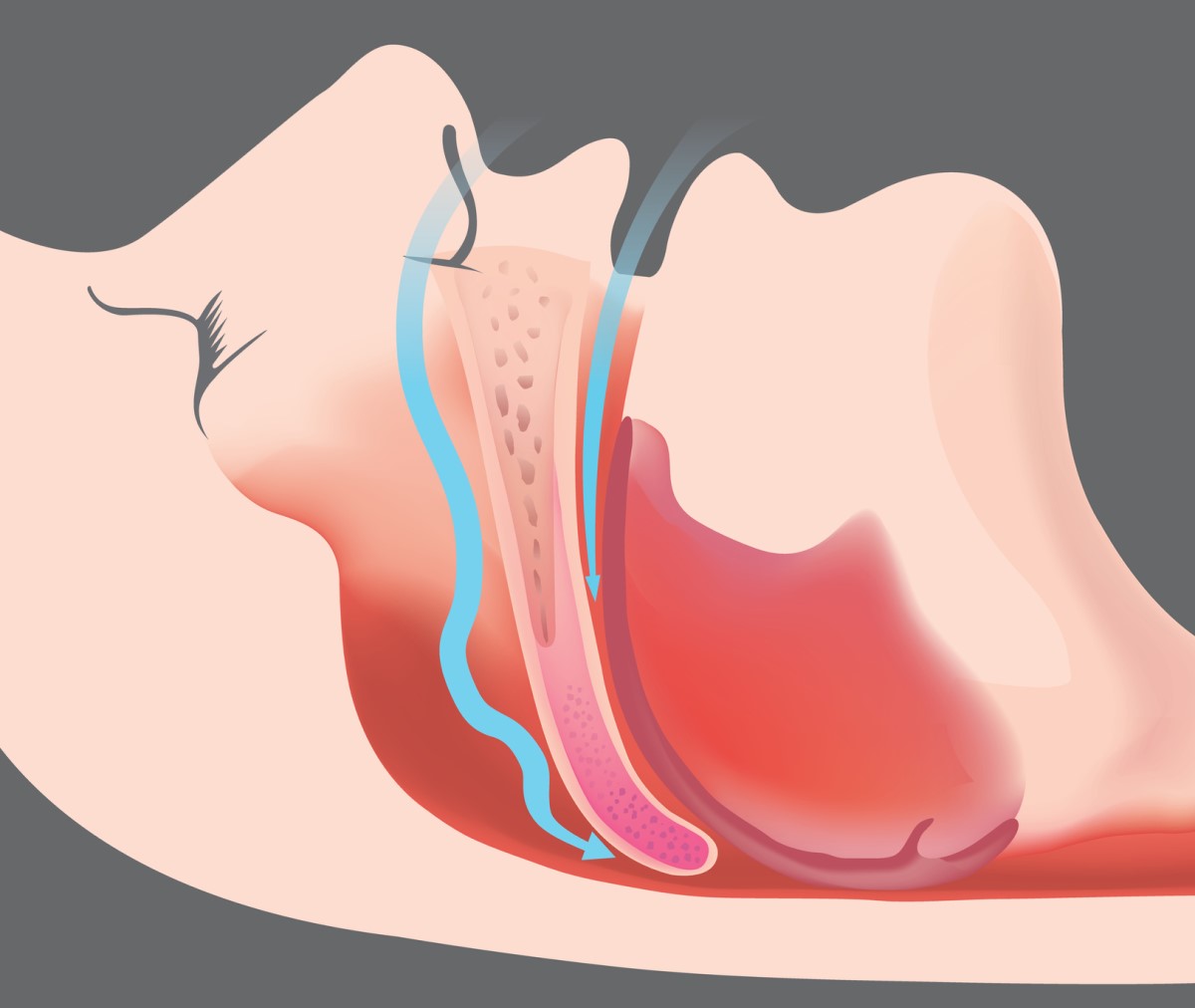
The cause of airway closure during sleep is an imbalance between the force of the muscles that keep the breathing muscles open and the force that closes them.
During sleep, muscle tone decreases. The forces of the surrounding tissue that close the airway begin to predominate.
Such tissue may be fat deposited around the throat in obese individuals, enlarged tonsils, an elongated long palate, an enlarged tongue, abnormalities of the temples and jaws, tumors in the oral cavity and throat region, and so on.
The airways collapse under such a force, become flaccid, their lumen narrows until they are completely obstructed by the clenched walls of the pharynx. By interrupting the air supply to the lungs, the oxygen saturation of the blood decreases and the proportion ofCO2 rises, the heart rate and blood pressure increase.
The chemoreceptors, located in the aorta and carotid arteries, are very sensitive to changes in blood gas concentration.
Activation of the chemoreceptors leads to involvement of the respiratory muscles and reflex induction of breathing, followed by micro-awakening.
The result of adrenaline washout is an increase in blood pressure and constriction of blood vessels in the systemic and pulmonary circulation.
This cycle is repeated several times during sleep and is accompanied by snoring.
If the cycle repeats 5-15 times per hour, it is a mild disorder;
15-30 apneic pauses per hour is classified as a moderate disorder.
More than 30 episodes of apnea are present in a severe disorder with many health consequences.
Central sleep apnoea is a less common cause of apnoeic pauses during sleep. Breathing is a spontaneous activity controlled by the breathing centre in the brain.
Thanks to this centre, we do not need to control our breathing. It takes place even during sleep when we are not conscious. Central sleep apnoea occurs when the breathing centre in the brain is unable to transmit signals to the breathing muscles.
In practice, this means that the person stops breathing for a short period of time because the brain does not "force" them to do so.
Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea:
- Overweight and obesity significantly increase the risk of sleep apnoea. Accumulated fatty tissue in the neck and under the chin can press on the airway and obstruct breathing
- A wide and bulky neck
- Narrowed airways due to enlarged cervical or nasal tonsils, especially in children
- Male gender and female gender after menopause
- Age 40 years and above
- Family history
- Drinking alcohol, taking sedatives. These substances relax the neck muscles, which cannot keep the airway open
- Nicotinism. Smokers are 3 times more likely to suffer from sleep apnoea
- Chronically blocked nose, such as nasal polyps, crooked nasal septum or mucosal swelling in allergies
- Chronic diseases such as heart failure, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, Parkinson's disease, polycystic ovary syndrome, hormonal disorders, sudden stroke or asthma increase the risk of sleep apnoea
Risk factors for central sleep apnoea include:
- Older age
- male gender
- heart disease, e.g. congestive heart failure
- use of opioid painkillers
- use of painkillers
Symptoms
Symptoms of sleep apnea vary depending on the severity of the disease.
The most typical symptom is loud snoring, which varies in intensity during sleep and is punctuated by silence - an apnoeic pause without breathing.
During the day, patients suffer considerable fatigue caused by numerous interruptions of sleep during the night.
The fatigue is so pronounced that microsleep occurs during the day. This can be potentially very dangerous if one is in a profession where one must be alert and attentive, e.g. professional drivers.
It is reported that patients with sleep apnoea are up to 7 times more likely to have a car accident.
Other common symptoms include:
- waking up in the morning with a dry mouth.
- sleep headache
- difficulty falling asleep (insomnia)
- unbearable daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- difficulty in maintaining attention and concentration
- nervousness

Watch out for complications
One of the serious health complications of sleep apnea is an increase in blood pressure to pathological levels and the development of heart disease.
The sudden drops in blood oxygen concentration that occur in sleep apnea are responsible for the increase in blood pressure. Too high blood pressure puts a strain on the cardiovascular system and mechanically damages blood vessels.
Untreated high blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack, sudden stroke and arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation.
Sleep apnoea also increases the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
The combination of several metabolic disorders, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high blood sugar and obesity, is called metabolic syndrome and is directly related to the development of heart disease.
In addition, obstructive sleep apnoea can be a complication of general anaesthesia.
Patients with sleep apnoea have an increased risk of developing complications during major surgery. They are prone to breathing difficulties, especially if they are sedated and lying supine, which is common during surgery.
Diagnostics
The first step to diagnosis is anamnestic data. Usually obtained with the help of a partner who sleeps in the same room.
Information about smoking, alcohol use and the use of various hypnotics (sleeping pills), which can aggravate apnoea, is important. Patients complete various questionnaires, on the basis of which the doctor will make a diagnosis or consider the need for further investigations.
Specialists from a number of disciplines are usually called in for further diagnosis, such as a neurologist, pulmonologist, otorhinolaryngologist (ENT) or psychiatrist. As this is a sleep disorder, most investigations will take place in specialist sleep disorder centres.
The examination consists of a sleep assessment and includes nightly monitoring of breathing and other bodily functions during sleep in a sleep centre:
- Nocturnal polysomnography is an examination in which the patient is connected to a machine that monitors heart rate, breathing activity, brain activity, hand and foot movements, and blood oxygen concentration during sleep.
- Home sleep tests are simplified tests for home use. They also monitor heart rate, blood oxygen concentration and breathing activity.
In addition to sleep tests, you should have an examination by an ENT specialist to rule out the presence of nasal obstructions such as polyps or crooked nasal septums.
A neurologist will investigate the cause of central sleep apnea. A cardiologist will assess the state of the cardiovascular system and the extent of damage to it in long-term sleep apnea.
Course
Patients often do not notice the onset of the disease immediately.
The apnoeic pauses are short and imperceptible even to the partner. In addition, the partner is usually asleep and the loud deep breaths after an apnoeic pause may not wake him/her up.
The partner is usually alerted when frequent pauses in breathing or snoring are followed by panting. The situation is accompanied by daytime fatigue, lack of concentration, nervousness and a drop in performance.
This is when people first see a doctor. They usually assume other causes for their exhaustion.
In addition to sleep apnoea, there is an associated condition called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The combination of these two diagnoses is known as an overlap syndrome.
It is a combination of two types of airway obstruction. COPD results in dynamic lower airway obstruction, which makes it difficult to breathe out. At the same time, upper airway collapse occurs due to sleep apnoea, which in turn makes it difficult to breathe in.
In these patients, severe hypoxaemia or chronic oxygen deficiency in the tissues occurs.
This combination of conditions leads to other serious diagnoses such as chronic pulmonary heart disease, polycythemia (increased blood cell count), heart rhythm disturbances and congestive heart failure. These diagnoses are associated with high mortality rates.
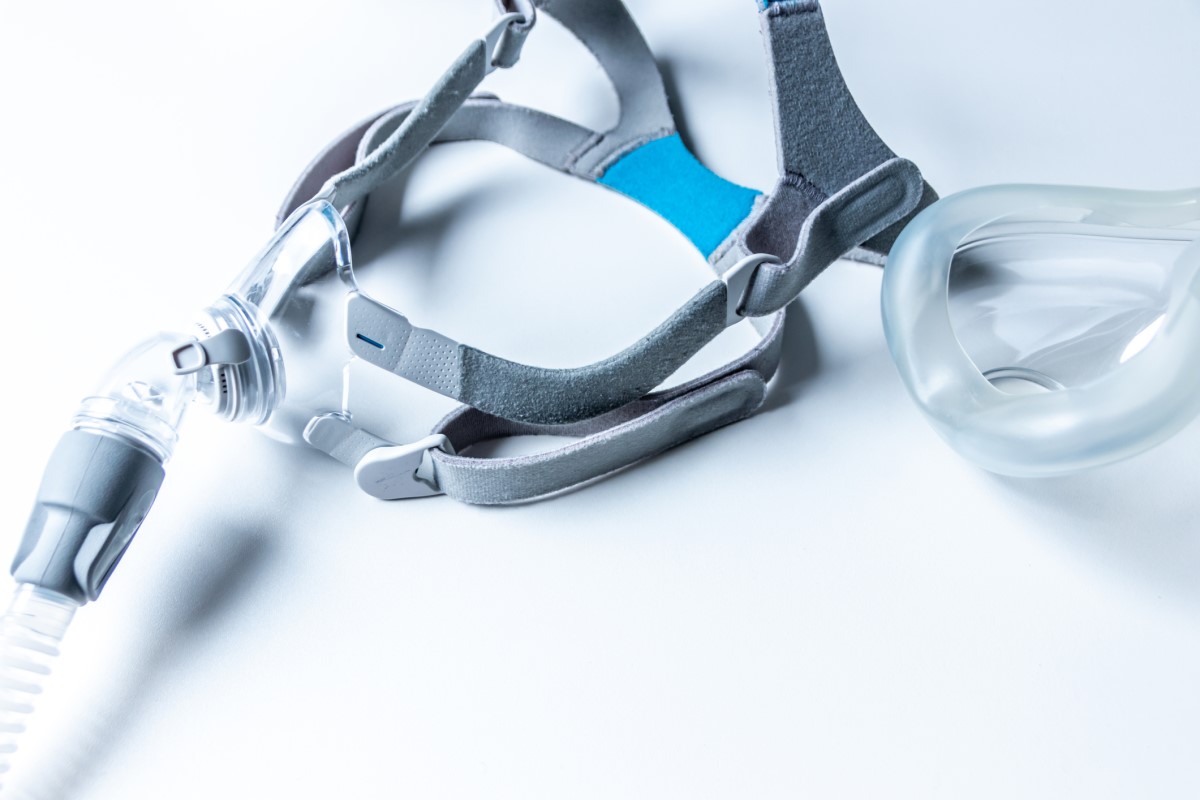

How it is treated: Sleep apnoea syndrome
Treatment of sleep apnea syndrome: drugs, weight and devices
Show moreSleep apnoea syndrome is treated by
Sleep apnoea syndrome is examined by
Other names
Interesting resources
Related










