- ortopedienohy.cz - Foot orthopaedics - anatomy
- wikiskripta.eu - Hallux valgus
- fyzioklinika.cz - Hallux Valgus - Kinesiotaping
How does hallux valgus occur: bunions? The influence of shoes + treatment and splints

Ladies, look out! Do you love high heels? They're beautiful and they make a woman's feet look sexy. But only temporarily. If worn for long periods of time, they distort the arch of the foot and can cause toe deformity. Hallux valgus doesn't look so nice. Take care of your feet so you don't have to hide them from the world.
Article content
You also ask: Does footwear have an effect? What is the treatment?
Do tapes and splint correctors or other braces help?
Everyone wants to have beautiful feet, but beautiful means healthy. Bunions are one of the foot deformities that are on the rise in the global population. They are becoming more common, especially in women.
It is caused by a combination of factors. In most cases, this pathological process can be prevented.
"The human foot is a machine of masterly design and a work of art" (Leonardo Da Vinci).
Anatomical proportions of the foot
The foot (Latin: pes) is anatomically made up of a large number of bones, up to 26 in total. It is also made up of joints, muscles, tendons, blood vessels and nerves. The joints are reinforced with stiffer ligaments, especially in the areas where the foot is most stressed. They also limit unwanted movement.
All these interconnected structures enable the body to maintain stability, posture and walking itself.
The basic compartments of the foot:
- The hindfoot (regio tarsalis) is made up of seven bones (talus, calcaneus, os naviculare, os cuboideum, os cuneiforme laterale, os cuneiforme intermedium, os cuneiforme mediale), whose connection is not very mobile. This part is important for the transfer of body weight.
- After the forefoot, the inflammation continues to the instep, which consists of five metatarsals (one elongated bone for each toe). The instep (regio metatarsalis) is a flexible part of the foot that plays an important role in shock absorption during gait.
- The toes (digiti pedis) maintain the overall stability of the foot during gait. Their links are connected to the metatarsals. Each toe has 3 links, except the big toe, which has only two. Despite the deficit of one link, the big toe is crucial in moving the foot away from a firm base.
Interesting:
The foot originally evolved from flippers. However, significant changes have occurred over the course of evolution. In our ancestors, it was initially adapted to climbing and the big toe to grasping objects. It was shaped into its present form by their need to cover ever greater distances in search of food.
The arch of the foot - development from childhood to adulthood

The shape and connection of the bones of the foot is anatomically determined. Together they form the so-called foot vault, and this needs to be maintained.
However, the bracing and the arch are gradually shaped with age, with the loading of the foot.
The arch is made up of a system of bones, articulations, muscles and tough ligaments.
The muscles involved in maintaining the longitudinal arch are the m. flexor digitorum longus, m. flexor hallucis longus and m. tibialis posterior.
The transverse vault is the responsibility of m. tibialis anterior, m. peroneus longus and, above all, the ligaments.
The first aspect in shaping and maintaining the arch of the leg is to load it when the child is learning to stand upright on two legs. Walking gradually strengthens it. Walking also prevents the muscles and ligaments in this area from weakening.
You may not have known.
What causes a distortion of the transverse arch of the foot?
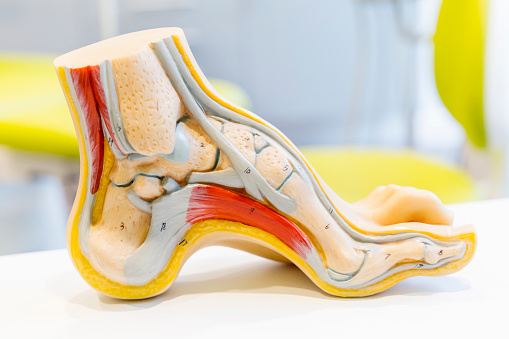
Disruption of the physiological foot arch in the plus (high arch) or minus (flat foot, pes planovalgus) direction always has its consequences.
As far as bunions are concerned, the plantar arch is of paramount importance.
On the basis of a violation of the transverse and longitudinal vault, a hallux valgus can arise. Also, it happens the other way around - in hallux valgus, there is a decrease in it.
The examination method dealing with the arch of the foot is called plantography. A plantogram is a result that is obtained using pressure mats, pressure pads and special platforms.
However, an assessment can also be made based on a coloured impression of the foot on paper. Newer methods use more modern digital equipment which can be used to determine the weight distribution on the foot.
Interesting fact: Footprints are a lot like fingerprints. No two feet are the same in the world. Even within the same individual, their feet are not identical. This often makes it difficult to buy shoes. One fits like a glove, and the other squeezes.
Foot arch categories - flatness index, in table
| Foot arch type | Flatness index |
| Extremely high foot arch | > 3.1 cm |
| moderately high foot vault | 1.6-3 cm |
| moderately high foot vault | 0.1-1.5 cm |
| physiological foot arch | 0.0-45.0 cm |
| slightly flat foot arch | 45,1-50 cm |
| flat foot arch | 50,1-60 cm |
| severely flat foot arch | 60,1-100 cm |
Hallux valgus - bunion
Hallux valgus, or so-called bunion, is the most common three-dimensional deformity of the forefoot. It involves lateral deviation of the big toe from its central axis (subluxation), with pronation (inward movement).
The arch of the foot is distorted in the sense of its subsidence and extension, as a result of prolonged changes in the metatarsophalangeal joint or in the fan-shaped position of the first and second metatarsals.
The deformity of the thumb may be so pronounced that it causes overlapping of the second finger, or the thumb to slide under the second finger. This position of the thumb is also called valgus position.
It causes stiffness of the thumb joint and the formation of a bony growth (exostosis).
In the area of exostosis, there is significant mechanical pressure or friction against the shoe. This results in local painful reddening of the skin (bursitis).
How does lateral bunion occur?
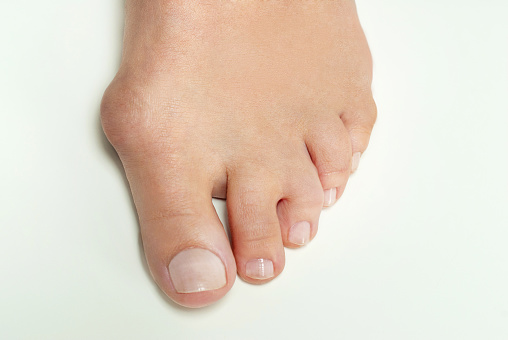
Lateral bunions occur due to a variety of causes. Not all of them are clear and certain. Also, a combination of several mechanisms is involved in its occurrence at the same time.
The anatomy and physiology of the big toe itself is also a cause. The deformity is due to its robustness and high flexibility compared to other parts of the foot.
In general, it is well known that women are affected 3 times more often than men. Wearing inappropriate footwear as a common cause (mostly in women) is only one of many.
However, we should also be on the lookout for certain chronic conditions.
The table lists possible causes
| Genetic predispositions | Mechanical causes | Other diseases |
|
|
|
What problems can you encounter?

The first changes in the joint do not manifest themselves outwardly in any way. As is usually the case, it is only the pain that prevents them from carrying out their daily activities that forces patients to seek medical attention.
However, by that time it is already fixed in a pathological position, and so conservative treatment may not be possible.
In the early stages of the disease, pain in the metacarpal joint is encountered.
The pain usually occurs when the affected limb is loaded and later during normal walking. The pain increases when the foot is in shoes.
The metacarpal joint may become swollen and swollen. The swollen area is red and painful to the touch.
Later, the deformity is more pronounced, the big toe is visibly off axis and sometimes under the second toe. Bursitis develops. The longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot are significantly distorted.
What is the best way to prevent bunions?
Not all causes of hallux valgus can be influenced. One of them is, for example, genetics or diseases that ultimately cause various deformities of the joints and therefore of the big toe.
Wear only high-quality and anatomically shaped shoes

Footwear must meet certain criteria for the anatomical and physiological needs of the feet. If it does not meet these criteria, there is a risk of not only bunions but also other deformities, flat feet, foot pain or blisters.
The back of the heel area must be stiff, the front flexible.
The inside of the shoe should be anatomically shaped to maintain the arch of the foot. The shoe should be lightweight and comfortable when worn. It must not press on or cut the soft parts of the foot.
Cheap shoes usually do not meet these criteria.
Therefore, if you want to maintain beautiful feet, it is better to get one expensive but good quality shoe than ten poor quality and cheap ones.
Regular loading of the foot maintains the physiological arch of the foot

Laziness and lack of exercise over time affects the entire human body. Long-term inactivity preferentially affects the musculoskeletal system. Not only the feet suffer, but also the spine, knees and other joints and bones.
Muscles weaken and atrophy (loss of muscle mass), ligaments weaken, joints are destroyed, various deformities and bone growths develop. Movement is restricted and pain sets in.
The same process also occurs in the joints of the foot and toes of the lower limb.
The ligaments weaken, the muscles weaken, the arch of the foot falls and widens. If the arch is not strengthened by regular activity, lateral buckling of the big toe occurs.
Regular movement keeps the bones, joints and muscles in shape, strong and more resistant. This reduces the risk of bone deformities. Of course, walking should be done in a neutral position.
Supination or pronation of the foot, for example when running, could cause deformation of the ankle joint, malalignment of the arch as well as bunions. Loading while standing and walking targets the musculus abductor hallucis. It is also used in physiotherapy as part of the treatment of hallux valgus.
Foot massage focusing on the muscles that control the functionality of the foot

The metacarpal joint and one of the muscles of the big toe, the musculus abductor hallucis, play the most important role in bunions.
It is the weakening of this muscle through lack of activity that can have serious consequences, such as the development of hallux valgus.
To prevent weakening of the musculus abductor hallucis, regular exercise is important. Physiotherapy exercises and massages focusing on this muscle are also useful.
Do you have a bunion? What are the treatment options?
In the treatment of hallux valgus, conservative therapy is increasingly preferred to surgery. The first step is to minimize negative factors and to acquire orthopedic shoes.
Nevertheless, barefoot walking is recommended in the home environment.
Physiotherapy exercises and massages should become a regular feature. In addition to orthopaedic shoes, orthotic aids in the form of finger splints or correctors are essential to ensure the correct position of the thumb.
Various analgesic preparations can be used to relieve pain. A newer method of pain control is the so-called taping. This involves applying fixative, taping strips to the affected area.
These options for returning the thumb to its physiological position, as well as surgical solutions, are unsuccessful in some cases. In the remaining ones, we often encounter recurrences. The deformity is resolved, but the cause remains.
Kinesiotaping - a new, active method in the treatment of hallux valgus
Doctors prefer to treat with kinesiotaping. This is a relatively newer treatment method using an electric current while pulling the thumb with a kinesiotape. The aim of the therapy is to actively stimulate the muscles of the foot to participate in keeping the thumb in plane.
Interesting resources










