- Great Medical Dictionary - Martin Vokurka, Jan Hugo a kolektiv
- Chapters in Otorhinolaryngology - Patrik Štefanička
- Rinosinusitis and Mycotic Sinusitis - Ivan Hybášek
- Neurology Textbook - Michal Drobný and Collective
- Selected Chapters in Otorhinolaryngology - Vladimír Čalkovský
- Anatomy - Radomír Čihák
- wikiskripta.eu - Sinusitis
- nhs.uk - Sinusitis (sinus infection)
- webmd.com - What Is Sinusitis?
- cdc.gov - Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
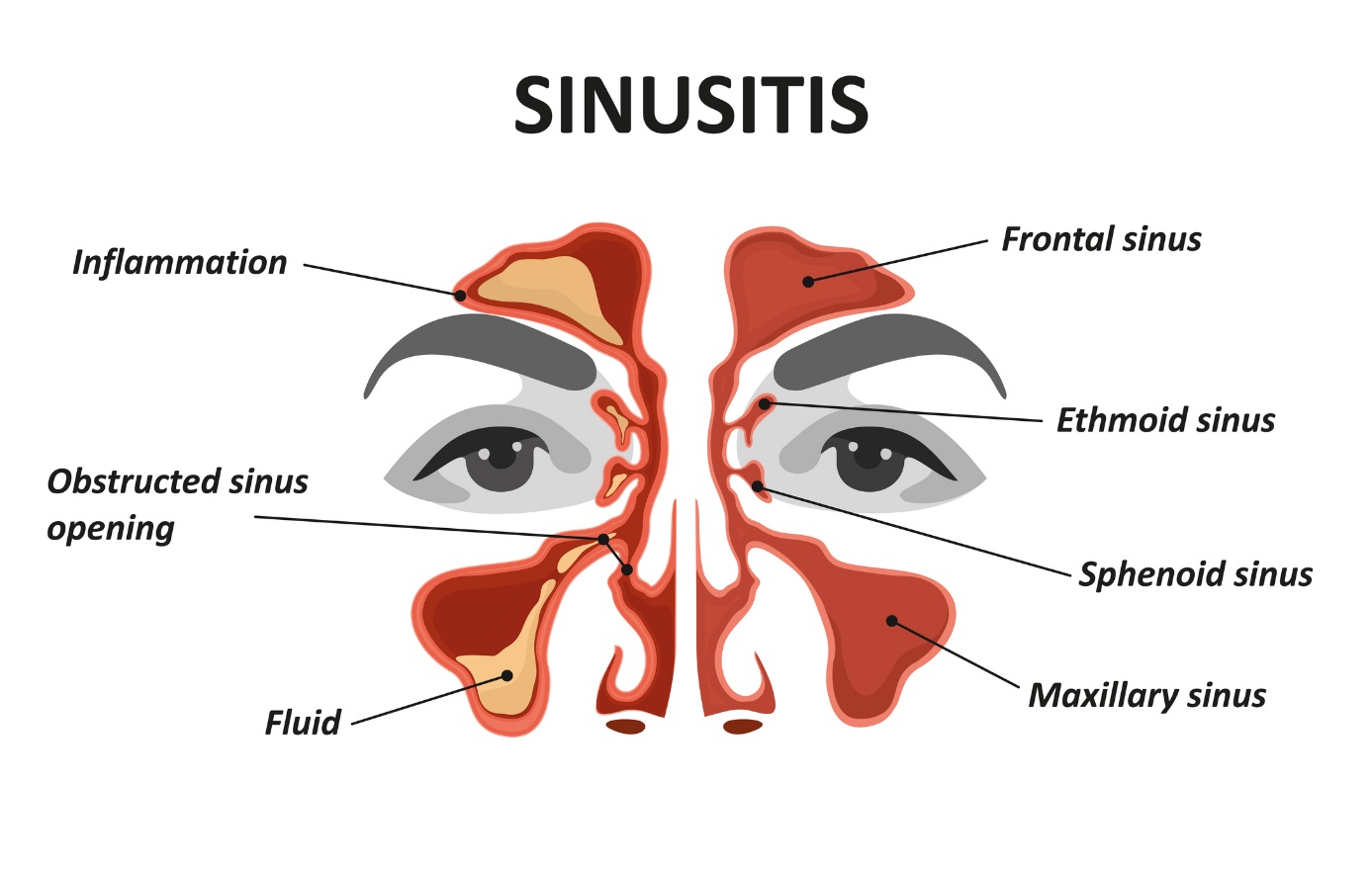
Sinusitis - sinusitis: what is it and what symptoms does it have?

Photo source: Getty images
Most common symptoms
- Malaise
- Headache
- Sore Throat
- Muscle Pain
- Ear Pain
- Tooth pain
- Hoarseness
- Fever
- Increased body temperature
- Indigestion
- The Island
- Swollen eyelid
- Full nose
- Loss of sense of smell
- Fatigue
- Damp cough
- Coughing up mucus
Show more symptoms ᐯ
How to cure sinusitis? Drugs, antibiotics and more for inflammation
Show moreSinusitis is treated by
Other names
Sinusitis, sinusitis