Treatment of shingles: Pain medication and antivirals
The purpose of treatment is to prevent the virus from multiplying. Therefore, antivirals are administered. However, they do not completely destroy the virus, but suppress it, reduce the severity of the symptoms, the occurrence of complications and shorten the overall duration of treatment.
Aciclovir, famciclovir, amantadine are just some of them.
Analgesic treatment relieves pain. Opiates for severe pain that are not covered by common analgesics.
Corticosteroids help relieve pain and shorten the duration of treatment. They must be combined with an antiviral. Neuralgia may need to be treated later.
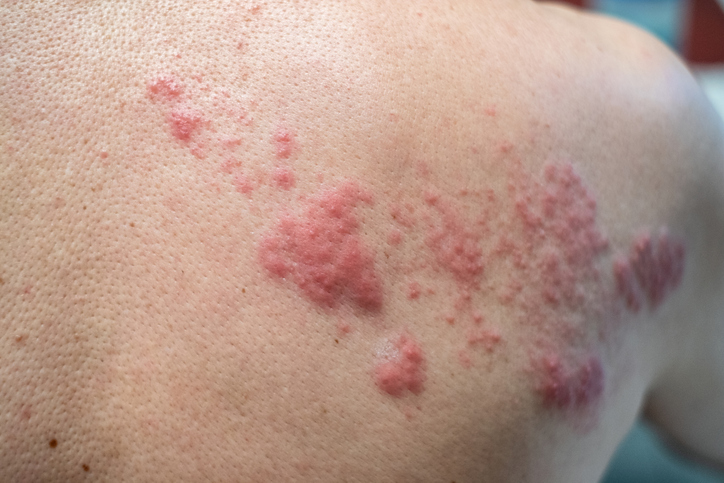
It is important to treat herpes defects and to prevent their secondary infection by bacteria. The wound must be clean and covered. Various ointments, creams, gels or patches are used. Their effect is that of pain relief, healing and a local antiseptic.
It is recommended to increase the intake of vitamins or start an enzyme therapy with immunomodulatory solutions.
Tricyclic antidepressants are also used for long-term treatment. They alleviate long-term neuralgia or depression. Depending on the occurrence of complications, special treatment is chosen.
Herpes Zoster Vaccination
Vaccination has been around for a long time. It helps to reduce the incidence of the disease and reduce the rate of consequences and complications, as in the case of postherpetic neuralgia.
An attenuated (with reduced virulence) vaccine, such as Zostavax, is safe to use. It is especially recommended for people over 50 years of age.










