- wikipedia.org - information on Wikipedia
- psoriasis.org - About Psoriasis
- mayoclinic.org - Psoriasis
- nhs.uk - Psoriasis
Psoriasis: Non-infectious, but long-term disease, what are its symptoms?
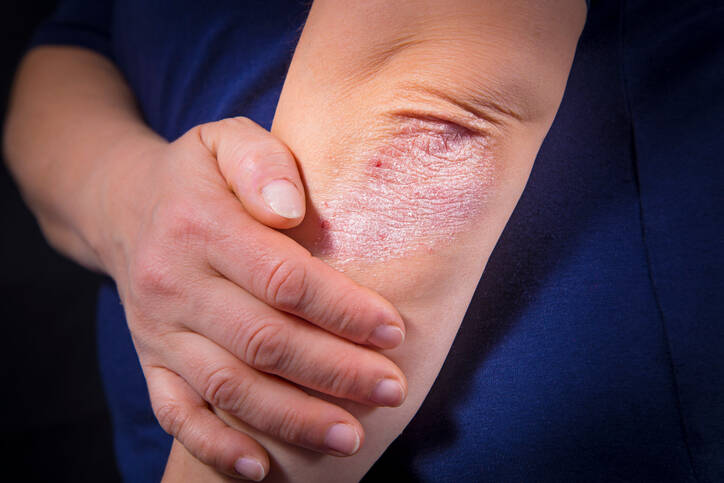
Psoriasis, also known as psoriasis, is one of the most common skin diseases and affects about 3 percent of the population.
Most common symptoms
- Joint Pain
- Skin pain
- Deformed nails
- Hyperpigmentation
- Rash
- Wetting of the skin
- Strokes on the nails
- Blisters
- White patches on the skin
- Buds
- Dry skin
- Itchy skin
- Itchy scalp
- Fatigue
- Reddened skin
Characteristics
However, in addition to the skin, psoriasis also affects the nails and joints. At the same time, there are regressions and relapses during life.
Psoriasis is a non-infectious, non-communicable, inflammatory autoimmune skin disease. It is chronic, which means that its duration is lengthy. In many cases, it lasts a lifetime and in some, it disappears.
The term psoriasis is from the word psora, ie peeling, scratching. In Latin, psoriasis vulgaris.
During life, periods of remission and acute exacerbations of the disease alternate. It may have a rapid onset and more intense symptoms. The chronic form is milder. The naming of psoriasis is derived from the formation of scales. These are formed mainly at typical, so-called predilection sites.
Periods of alternation are also called remission, ie retreat and recurrence, ie return, repetition.
The disease affects various parts of the skin, which are usually exposed to more pressure or strain. For example, it concerns the elbows, knees and also affects the skin on the feet, small joints on the hands, but also nails, specifically nail beds. Sometimes the manifestations are not very pronounced and one hardly even notices them.
In some cases, when the joints are affected and only the skin is affected, psoriatic arthritis is also mentioned. In total, according to external manifestations, there are several forms and types of psoriasis.
Sometimes there are symptoms and only local difficulties, on the palms and legs. At other times, psoriasis only affects the joints. The fewest cases are in the form of generalized, ie whole-body psoriasis. This can result in inflammation of the skin all over the body.
Causes
Worldwide, psoriasis can affect up to 5% of the population. However, the highest percentage of those affected is white, less common in Asians and least in blacks.
The autoimmune process also has an effect, as the chance of psoriasis also increases as a result of another autoimmune disease. Sometimes, some infections from the outside environment or other external influences such as medication or injuries can trigger psoriasis.
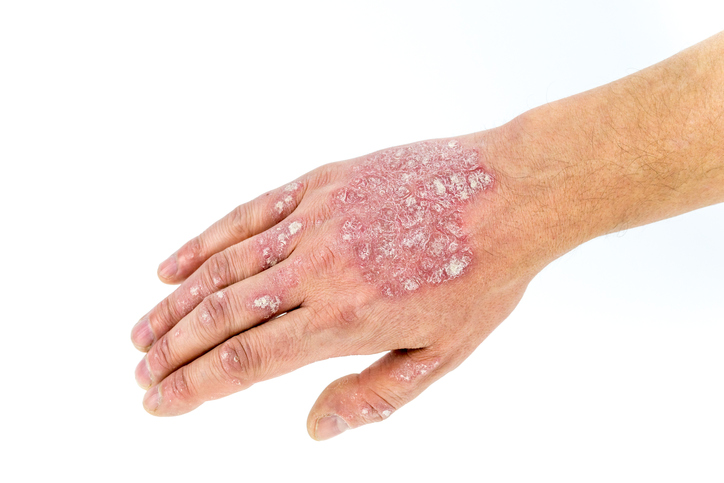
Among the risk factors for the development of psoriasis include:
- heredity - to some extent it is hereditary and family occurrence has a significant impact on the risk of origin
- hormonal changes, such as puberty, menopause, postpartum
- infection (upper respiratory tract, tonsillitis, tooth infection)
- diabetes
- liver disease
- obesity
- DNA
- sunbathing
- stress and mental strain
- drugs such as beta-blockers, antimalarials
- smoking
- alcohol
- lack of sleep
- refined sugar
- overloading the skin with physical influences (sudden and sudden changes in temperature, friction, pressure)
- chemicals (burns)
You often ask :
Is psoriasis contagious?
How is psoriasis transmitted?
Well, it's not.
As you have read, it is an autoimmune disease, not an infectious one.
Thus, there is no transmission of the disease from person to person.
Symptoms
However, psoriasis is most often a form of focal and local disease. Then psoriasis manifests itself in red scaly deposits on the skin, which takes peel off. There are sowing pimples red color with whitish flakes.
If psoriasis affects the nails, a yellow spot appears under the nail. At the same time, the affected nail is deformed and dull. Inflammatory deposits with solid scales, which can be found in various parts of the body, are typical of the chronic form of the disease.
On the upper and lower extremities are characteristically formed small tubes filled with pus usually. In severe forms of the whole-body disease, reddened deposits of scales cover the skin of almost the entire body. Intense itching is also very common.
However, psoriasis takes various forms. It manifests itself accordingly.
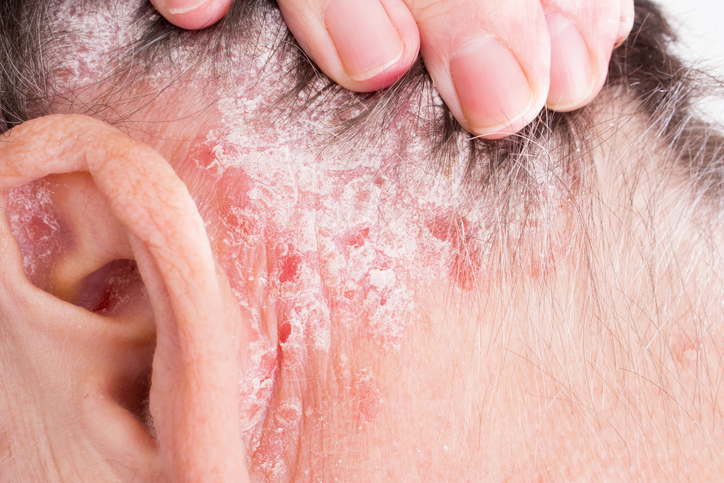
We know these forms of psoriasis:
- psoriasis punctata, which is manifested by the sowing of small pimples
- psoriasis guttate, ie the sowing of rashes in the size of a droplet, also called droplet, droplet-like
- psoriasis nummularis, rashes are up to 1 cm in size
- psoriasis pustulosa, especially in adults, with blistering, inflammation (palms, feet, or elsewhere on the body)
- psoriasis arthropatica, if small joints are also affected, psoriatic arthritis
- psoriasis flexuralis, which affects areas such as the armpits, under the breasts, groin, and navel, especially in old age, is possibly referred to as inverse psoriasis
- acute exantemic form, manifests itself mainly in young people, preceded by difficulties such as angina or virosis
- erythrodermal form, manifested by extensive redness and peeling of the skin, can occur throughout the body, with fever and joint pain
- chronic stationary form manifests at predilection sites such as:
- elbows
- knees
- back, trunk, and sacrum area
- form a barber when located on the palm area, especially in middle-aged women
- zumbusch is a severe form of generalized psoriasis
- nail involvement, various nail deformations, in 20 to 50% of those affected
Of course, the sowing itself, whether it is psoriasis in the hair (hair), on the head, or psoriasis on the elbows or elsewhere on the hands and feet, is accompanied by itching. Pain is associated if cracks form in the skin.
Diagnostics
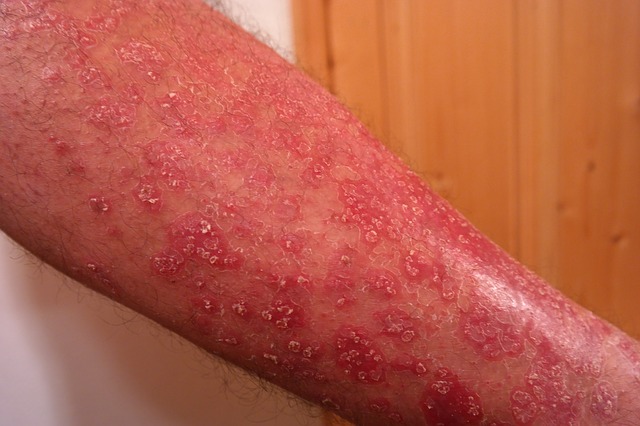
Psoriasis can also be determined by looking. Based on the anamnesis and physiological examination, the dermatologist can diagnose her at the first visit to the outpatient clinic. Clinical signs, including subjective difficulties, help determine psoriasis.
In addition, histological sampling helps to determine the diagnosis. A sample is taken from the surface of the skin at the affected area or the scales. On the basis of laboratory examinations, the form and type of psoriasis can then be determined.
Histological examination is also important to distinguish other diagnoses in connection with skin diseases. Blood sampling for blood counts, immunological parameters, or the level of vitamins, especially B12, as well as elements, ie iron.
Course
This process is common, especially in young people. Skin changes heal faster than the chronic type. In chronic psoriasis, there is a recurrence, ie recurrence of these symptoms. Subsequently, periods of rest, or remission, begin.
In psoriatic arthritis, joint pain occurs first and then on the skin. At the same time, local psoriasis has a less intense course than generalized. Exudative psoriasis has another form of course. It forms bearings with seeped yellow scales. The deposits are deep red and bordered.
After healing, the pigmentation of the skin at the site of the previous lesion increases. In other cases, on the contrary, pigmentation is reduced, and local skin discoloration is present. The resolution of the symptoms is usually spontaneous or even after effective treatment.
Psoriasis in children
Psoriasis also occurs in childhood. Also, even in this period significantly reduces the quality of life. And not just for aesthetic aspects. Her speeches are also unpleasant.
Sickness at this age can trigger angina as well as other diseases. Thus, the trigger can be of various causes. Of course, it also affects lifestyle, hormonal changes, physical or chemical influences.
It is different in children than in adults. It can manifest itself already in the diaper period. According to him, it was also called diaper psoriasis. Redness and inflammation of the skin with scales can result in the formation of blisters. Blisters can have purulent contents.
The acute course of psoriasis is typical for the age of 6 years. From the age of 12, it is rather significant for its chronic form. Skin manifestations vary. And in the form of stripes anywhere on the head or body. From psoriasis on the forehead, around the eyes, chest, through the palms to the feet.
How it is treated: Psoriasis
Treatment of psoriasis - medications and biological treatment
Show morePsoriasis- interesting video
Psoriasis is treated by
Interesting resources
Related










