What are the treatment options for female infertility?
Unfortunately, in some cases treatment is not possible, especially if it is congenital infertility, which is characterised, for example, by the lack of function of some important sex glands. Or treatment is not successful and another alternative must be chosen after the desire for a child.
In other cases, it is possible to treat first the causes that caused the infertility, and thus this undesirable condition should be corrected. This is for example hormone replacement therapy, or the cure of a gynaecological inflammation, or the cure of a gynaecological disease such as endometriosis.
If a woman's infertility condition is caused by a problem with the fertilisation of the egg or a mechanical problem in the fallopian tubes, the solution is usually artificial insemination, where fertilisation occurs under laboratory conditions. This solution has been steadily improving and advancing over time, and covers a number of different causes where infertility in women can be resolved in this way.
Other types of treatment
Treatment for ovulation disorders
In the treatment of ovulation disorders, a therapeutic method with weight adjustment and treatment of disorders of other systems is used.
Clomiphene citrate is the drug of first choice to promote ovulation, by direct action on the pituitary gland. It is given for problems with ovulation, or for PCOS - polycystic ovary syndrome.
Gonadotropins are given in treatment where ovulation is absent. These drugs act directly on the ovaries and promote ovulation. They are administered by injection.
Stimulating hormone on follicles supporting the process of ovulation. It is usually administered by injection. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone support is used for irregular ovulation.
Metformin is a medication for normal ovulation especially in insulin resistance or PCOS. This medication lowers the levels of male hormones in women and helps to ovulate.
Bromocriptine is given at high prolactin levels to promote ovulation.
All medications given for ovulation increase the possibility of having multiple pregnancies.
Surgical treatment
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are performed for adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes, for disorders of the lining of the uterus to eliminate the causes of infertility.
Methods of assisted reproduction
Intrauterine insemination is one of the least invasive methods of assisted reproduction. In the laboratory, the most motile sperm are selected and then introduced through a catheter directly into the uterus during ovulation. By injecting the sperm directly, their journey to the egg is shortened and the likelihood of conception is increased.
In vitro fertilization, or IVF, is a method by which fertilization of an egg with the sperm of a partner or donor is carried out outside the woman's body. The fertilized eggs develop in an incubator for 3 to 5 days before being inserted into the woman's uterus. Which means the highest possibility of smooth fertilization of the egg with subsequent insertion into the uterus and implantation into the uterine lining.
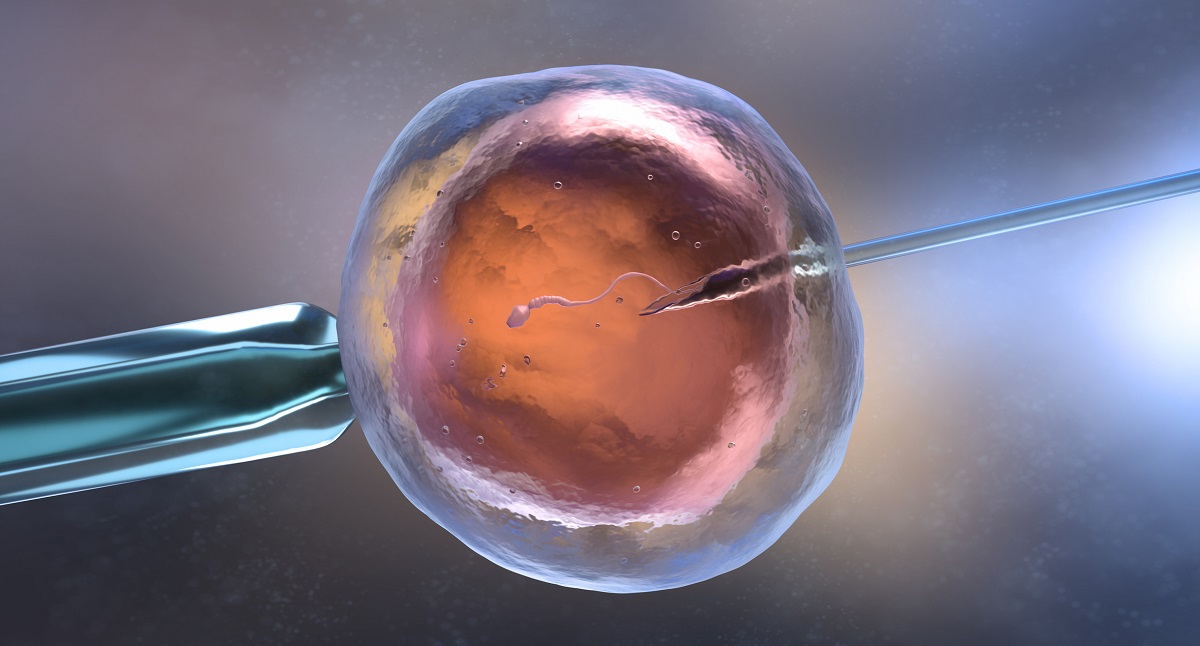
Oocyte donation, also known as egg donation, is the only option for some women to become a mother. Without egg donation, they would never get the chance to become a mother.
Embryo donation is a procedure in which donated eggs are fertilised with sperm from a donor. Once the egg is fertilised, it is followed by its development to a certain stage of development where they are frozen. They are then inserted into the woman's uterus under certain conditions, where the embryo develops after it is conceived and the woman has the opportunity to bear the desired child.










