- Silva V, Grande AJ, Peccin MS (April 2019). "Physical activity for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic obstruction". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD012044. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012044.pub2. PMC 6450803. PMID 30953341.
- Chang RT, Kirby R, Challacombe BJ (April 2012). "Is there a link between BPH and prostate cancer?". The Practitioner. 256 (1750): 13–6, 2. PMID 22792684.
- Lower urinary tract symptoms in men: management, NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence)
- "Urge incontinence". MedlinePlus. US National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 6 October 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- White JR, O'Brien III DP, Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW (1990). "Incontinence and Stream Abnormalities". Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations (3rd ed.). Boston: Butterworths. PMID 21250138.
- Robinson J (11 February 2008). "Post-micturition dribble in men: causes and treatment". Nursing Standard. 22 (30): 43–6. doi:10.7748/ns2008.04.22.30.43.c6440. PMID 18459613.
- Sarma AV, Wei JT (July 2012). "Clinical practice. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms". The New England Journal of Medicine. 367 (3): 248–57. doi:10.1056/nejmcp1106637. PMID 22808960.
- "Urination – difficulty with flow". MedlinePlus. US National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 6 October 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- "Urination – painful". MedlinePlus. US National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 6 October 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- "Bladder outlet obstruction". MedlinePlus. US National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 6 October 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- "Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 5 July 2021.
- Truzzi JC, Almeida FM, Nunes EC, Sadi MV (July 2008). "Residual urinary volume and urinary tract infection--when are they linked?". The Journal of Urology. 180 (1): 182–5. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2008.03.044. PMID 18499191.
- Wu CP, Gu FL (1991). "The prostate in eunuchs". Progress in Clinical and Biological Research. 370: 249–55. PMID 1924456.
- ^ Testosterone and Aging: Clinical Research Directions". NCBI Bookshelf. Archived from the original on 5 November 2017. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- "Proscar (finisteride) Prescribing Information" (PDF). FDA – Drug Documents. Merck and Company. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- Bartsch G, Rittmaster RS, Klocker H (April 2002). "Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia". World Journal of Urology. 19 (6): 413–25. doi:10.1007/s00345-002-0248-5. PMID 12022710. S2CID 3257666.
- Feldman BJ, Feldman D (October 2001). "The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 1 (1): 34–45.
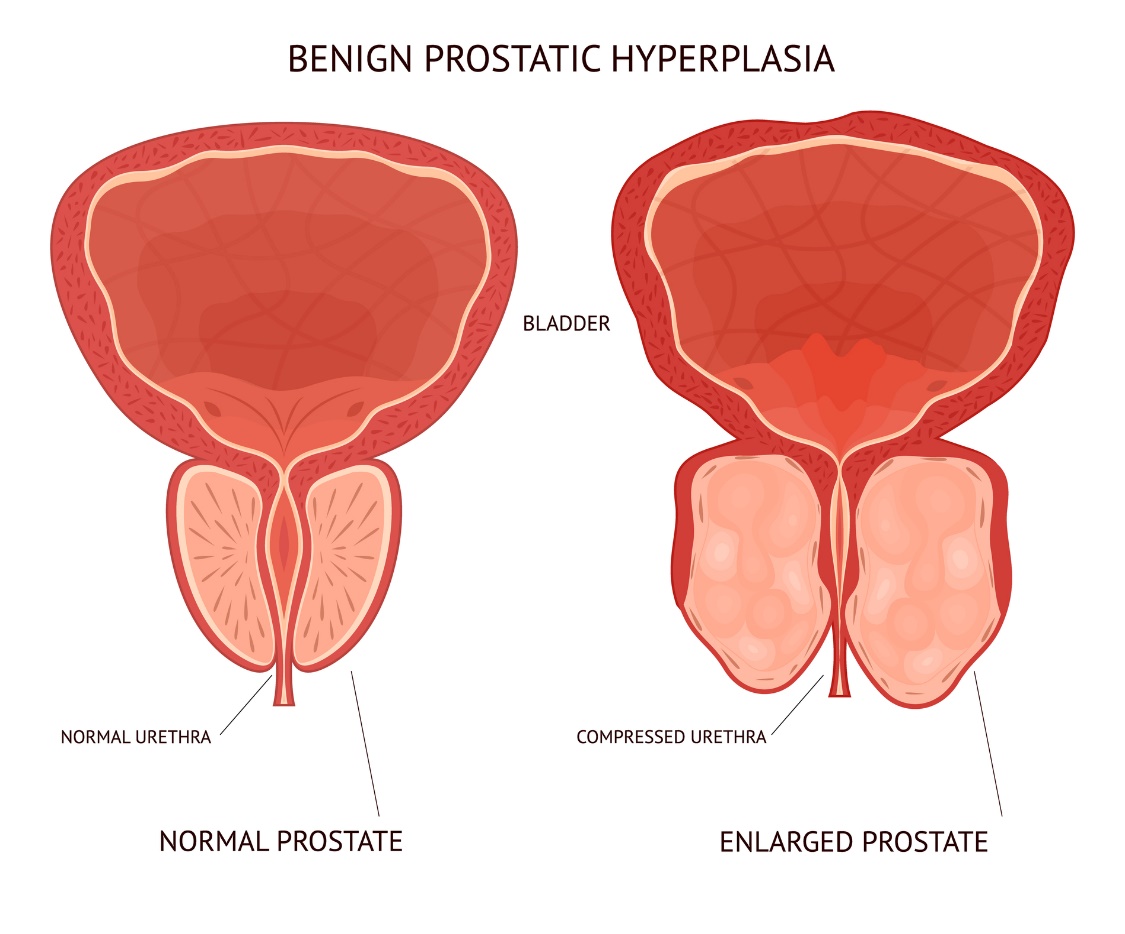
Enlarged Prostate: Causes, Symptoms, Risks

Photo source: Getty images
Most common symptoms
- Urethral pain
- Lower Abdominal Pain
- Painful urination
- Frequent urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Erectile dysfunction
- Urinary retention - anuria/retentiveness
Show more symptoms ᐯ
Prostate enlargement treatment: monitoring, medications and surgery
Show moreEnlarged Prostate is treated by
Other names
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH