- "Anaphylaxis". National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. April 23, 2015.
- Caterino, Jeffrey M.; Kahan, Scott (2003). In a Page: Emergency medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 132. ISBN 9781405103572.
- Simons, FE; Ardusso, LR; Bilò, MB; El-Gamal, YM; Ledford, DK; Ring, J; Sanchez-Borges, M; Senna, GE; Sheikh, A; Thong, BY; World Allergy, Organization. (February 2011). "World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis". The World Allergy Organization Journal. 4 (2): 13–37.
- Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, et al. (February 2006). "Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report—Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 117 (2): 391–7.
- Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. pp. 177–182. ISBN 978-0-07-148480-0.
- NHS (29 November 2019). "Overview - Anaphylaxis". NHS (National Health Service). United Kingdom: British government. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- Khan, BQ; Kemp, SF (August 2011). "Pathophysiology of anaphylaxis". Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 11 (4): 319–25.
- The EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines Group (August 2014). "Anaphylaxis: guidelines from the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology". Allergy. 69 (8): 1026–45.
- Lee, JK; Vadas, P (July 2011). "Anaphylaxis: mechanisms and management". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 41 (7): 923–38.
- Ma, L; Danoff, TM; Borish, L (April 2014). "Case fatality and population mortality associated with anaphylaxis in the United States". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 133 (4): 1075–83.
- Gylys, Barbara (2012). Medical Terminology Systems: A Body Systems Approach. F.A. Davis. p. 269. ISBN 9780803639133. Archived from the original on 2016-02-05
- Oswalt ML, Kemp SF (May 2007). "Anaphylaxis: office management and prevention". Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 27 (2): 177–91, vi.
- Marx, John (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice 7th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. pp. 1511–1528. ISBN 978-0-323-05472-0.
- Simons FE (October 2009). "Anaphylaxis: Recent advances in assessment and treatment". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 124 (4): 625–36, quiz 637–8. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.08.025. PMID 19815109.
- Limsuwan, T; Demoly, P (July 2010). "Acute symptoms of drug hypersensitivity (urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock)" (PDF). The Medical Clinics of North America. 94 (4): 691–710, x. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2010.03.007. PMID 20609858. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2011-12-09.
- Brown, SG; Mullins, RJ; Gold, MS (Sep 4, 2006). "Anaphylaxis: diagnosis and management". The Medical Journal of Australia. 185 (5): 283–9.
Anaphylactic shock: Anaphylaxis as an exaggerated, severe allergic reaction?
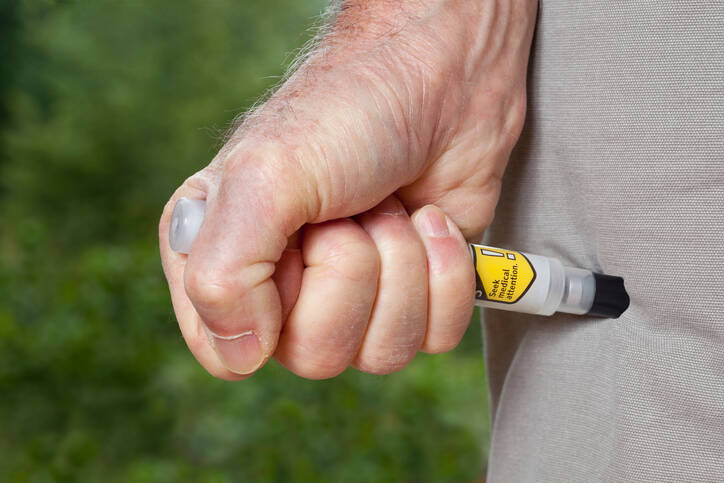
Photo source: Getty images
Most common symptoms
- Malaise
- Apathy
- Headache
- Hoarseness
- Cramps in the abdomen
- Spirituality
- Diarrhoea
- Rash
- Flatulence - bloating
- Nausea
- Low blood pressure
- Lung Island
- Swelling of the limbs
- The Island
- Swollen fingers
- Swollen eyelid
- Full nose
- Disorders of consciousness
- Buds
- Itchy skin
- Head spinning
- Tremor
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Reddened skin
- Decreased body temperature
- Accelerated heart rate
Show more symptoms ᐯ
• Treatment of anaphylactic reaction and first aid + EpiPen injection in allergic patients
Show moreAnaphylactic shock is treated by
Anaphylactic shock is examined by
Other names
Anaphylactoid, anaphylactic shock