- healthline.com - Signs That You Have Chronic Dry Eye
- aoa.org - Dry eye
- health.uconn.edu - Dry Eye Center
- telemedicina.med.muni.cz - Tear tract diseases in children - Congenital defects
- wikiskripta.eu - Lacrimal apparatus
- pediatriepropraxi.cz - Diseases of the lacrimal system - MUDr. Barbora Bábková, MUDr. Klára Marešová, Ph.D / in pdf
Reduced tearing: what causes it and what symptoms are added to it?
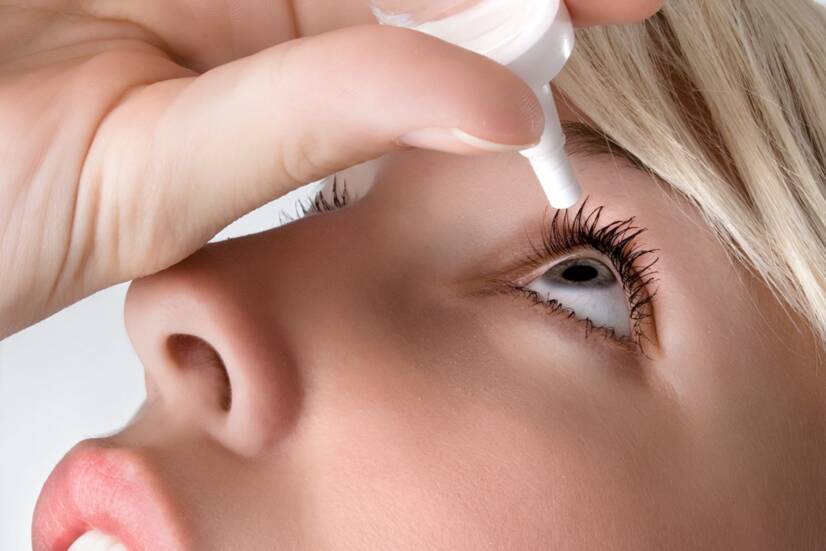
Reduced tearing and dry eye are current problems nowadays that are significantly damaging to the eye in the long term. Do you know the causes and symptoms?
Insufficient lacrimation = hypolacrimation.
Lacrimalis = relating to tears / lacrimal - lacrima = tear.
Hypo - a state of deficiency, a reduction from normal.
An eye with an impaired tear film is prone to infections. Dryness also adversely affects the nutrition of the cornea of the eye, the outer part of the eye.
The cornea, conjunctiva and the entire outer eye are exposed to the outside world, the external environment and weather conditions, dust, smog, smoke, small impurities, wind, draughts, dryness, heat, cold.
Tears wash the eye, cleanse it. Moreover, they also contain cells of the immune system, whose task is to defend against infections.
Tears are 99 per cent water. The remaining percentage is shared by salts, minerals, proteins, glucose, organic substances, immune cells, detached parts of the epithelium.
The composition of tears and tear film is of antibacterial and nutritional importance.
The tear film covers the surface of the cornea, conjunctiva. It has an irreplaceable role for the proper functioning of visual functions and vitality of the eye. Tears wash the eye and open the tear film with the help of sebaceous glands and cells from the surface of the eye.
Functions of the tear film:
- Mechanical barrier
- antibacterial protection
- cleansing from impurities
- nourishment of the eye (cornea) and oxygenation
- Optical properties and refraction - refraction of rays for precise impact of the image on the retina
Tears are one of several components of the thin film. It has three layers.
3 layers of tear film:
- mucinous - the inner mucus layer
- formed by the cells of the cornea and conjunctiva
- prevents foreign objects from sticking to the surface of the eye
- gives the film viscosity and integrity
- helps tears adhere to the eye
- aqueous - tear-producing lacrimal glands
- provides nutrients and oxygen to the outer part of the eye, the cornea
- contains minerals, electrolytes and enzymes
- washes the eye and cleanses its surface
- it is the largest part of the film
- lipoid - the outer sebaceous layer
- it is the sebum/oil/grease produced by the glands of the eyelids, eyelashes - Meibomian glands
- contains esters, fatty acids, triglycerides
- prevents rapid evaporation of tears
- stabilizes the film
- ensures a smooth surface
To ensure the effectiveness and function of this film, proper composition and sufficient blinking are important. Eyelid movement is therefore an important part of eye condition and vitality.
But what if we don't blink enough?
The tear film is not replenished to the necessary extent, sebum and tears are not spread over the surface of the eye. The aqueous layer evaporates at an increased rate, water evaporates, the cornea and conjunctiva are dry.
A problem whose name has come to be known to a large number of people, especially those who work long hours behind a monitor and watch television. Of course, several factors contribute to it.
Dry eye syndrome as the number 1 problem
Dry eye or dry eye syndrome is defined as a disorder of washing the ocular surface with associated tear film defects.
It is differentiated into qualitative and quantitative forms. In the qualitative form, the problem is in the composition and in the quantitative form, the problem is in insufficient quantity.
It is therefore an imbalance in the production and evaporation of tears or in the content of tears and tear film (simply a condition of reduced quality of tears and film).
The eye is dry, prone to infection and injury (minor corneal defects). In addition, it does not have enough nutrients and oxygen to function properly.
Multiple mechanisms are considered in the formation. Examples include a disorder of the mucinous, aqueous or fatty layer, but also eyelid defects or a disorder of the corneal epithelium.
Factors that contribute to the occurrence are:
- older age
- hormonal changes, especially in women during menopause or pregnancy
- inflammation of the eye - especially chronic and recurrent
- systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, rheumatic and autoimmune diseases, lupus, scleroderma
- Sjörgen's syndrome
- Allergies
- eye injuries and eye surgery
- certain eye drops
- wearing contact lenses and improper hygiene
- bathing in chlorinated water
- influence of the external environment
- dry environment
- air-conditioned rooms
- working in dusty environments
- draughts
- reduced blinking frequency
- prolonged work at a computer
- prolonged television viewing and mobile phone use
- long periods of reading
- driving for long periods
Any activity that requires a focused gaze, such as working at a computer or reading and driving for long periods, causes a reduced blink rate.
+
Several negative factors can aggravate the problems and symptoms, such as lack of fluids, vitamins A and omega-3 fatty acids, cold and dry environment, use of air conditioning, heating, intense lighting, stress and mental strain, frequent rubbing of the eyes, but also smoking, alcoholism...
The manifestation is unpleasant health problems that bother a person according to their severity. Especially under deteriorated environmental conditions and when spending a long time behind a monitor.
The symptoms of dry eye include:
- dry eye sensation
- feeling of a foreign body in the eye, sand in the eye
- eye pain and burning, itching, stinging, pressure in the eyes
- headache
- eye fatigue and feeling of heavy eyelids
- sensitivity to light and facial illumination
- swelling of the eyelids
- redness of the eyes, conjunctivae
- insufficient/reduced tearing
- paradoxically, increased tearing
- blurred and foggy vision, blurred image
Read more in the comprehensive article:
Dry eye syndrome: Burning and tired eyes? Can dry eye be cured by drops?
Sitting behind a computer, i.e. imaging units, for long periods of time and office work have also necessitated a new term for health problems. These are related to this monotonous workload.
In addition to eye symptoms, there are also problems throughout the body.
Have you heard the term digital eyestrain and computer vision syndrome?
Dry eye syndrome and problems with dry mucous membranes and skin are hallmarks of an autoimmune disease called Sjogren's (or also sicca, dry) syndrome.
It affects the external secretory glands, has a rheumatic basis and the inflammatory process also affects the lacrimal glands.
For more information, see the article:
What is Sjogren's (sicca, dry) syndrome? Symptoms, treatment, diet
2. Other causes
Of course, dry eye is not the only problem. There are more.
There are several conditions that occur when tearing changes. These are characterized by a disorder of tear production, i.e. the tear apparatus or also the tear ducts.
The underlying cause may be a malfunction or blockage/narrowing of the outlet of the lacrimal apparatus and lacrimal ducts. As a result, either insufficient or excessive tearing may occur.
What exactly is the reason for the lack of tears?
Frequent and recurrent inflammation of the eyelid, the small glands of the eyelids, the conjunctiva and the general area leads not only to unpleasant difficulties, but also to the syndrome mentioned above.
Conjunctivitis is common in children. This bacterial infection spreads among children and can be triggered by wiping the eyes with dirty hands.
In addition, conjunctivitis can be a complication of an upper respiratory tract infection, such as the common cold, cold or flu. This is not only in childhood, but also in adulthood.
A summary of some of the possible causes and risk factors for tear deficiency:
- Age
- Hormonal changes, especially in women after menopause or during pregnancy
- weather conditions and working environment
- air pollution
- smoking and smoke, smog
- chemicals and fumes
- inflammation of the eye
- eyelids, sebaceous glands - blepharitis/meibomitis + eyelid redness
- conjunctivitis
- corneas
- barley and wolf grain
- eye injuries and surgery
- dry eye and digital eye fatigue
- rheumatic diseases
- autoimmune diseases
- thyroid dysfunction
- diabetes
- colds and other upper respiratory tract infections
- eyelids not closing, eyelid disorders or protruding eyes
- lack of sleep
- alcoholism
Symptoms occurring together with reduced tearing
Of course, there are other difficulties that accompany reduced tearing.
Examples of symptoms include:
- irritation and redness of the eye
- eye pain, burning, cutting, stinging, itching
- feeling of a foreign object in the eye
- sensitivity to light
- sensitivity to smoke, cold, dry environments, wind and drafts
- swelling of the eyelid
- reduced acuity
- blurred vision
- in severe conditions, risk of corneal damage and visual impairment
A severe course can result in damage to the surface of the cornea and impaired quality of vision.
Diagnosis and treatment
First is the medical history followed by a specialist eye examination. The ophthalmologist observes the eye, the area around the eye, the presence of redness, inflammation + blinking function.
He examines the visual acuity, the anterior and posterior segments of the eye, or measures the intraocular pressure.
The examination is used to detect dry eye as well as determine the quality and quantity of tears and tear ducts. The use of contrast fluid and monitoring their flow is also an example.
Treatment, of course, depends on determining the cause.
The aim is to restore and maintain the quality and quantity of the tear film and the quantity of tears. This is the basis for maintaining the vitality and condition of the eye and vision.
The application of artificial tears is important. These replace the natural tears and help the film to function properly. Alternatively, preparations are given to increase tear production.
For treatment, the doctor may recommend drops, ointments, gels.
Alternatively, in some cases, the tear ducts are blocked. Small silicone or gel plugs are used for this. They can be removed as needed. They are permanently closed by surgery.
Supportive nutrition is important: vitamins, minerals, especially vitamin A or omega-3 fatty acids, eye gymnastics and regular distraction from the content of the eye, as well as a break from work.
Massaging the eyelids helps to drain sebum from the sebaceous glands. Herbal compresses should be consulted with a doctor or pharmacist at the pharmacy.
In sunny season, eye protection with glasses is also needed.
Diseases with symptom "Decreased tearing"
Interesting resources










