- orl-lfuk.sk - chronic inflammation of the palatine tonsils
- tvnoviny.sk - about tonsil stones
- stomaklinik.sk - Pins
- viapractica.sk - Chronic tonsillitis
Pins on the tonsils: what are white lumps (stone, pus)? How to remove them?
Pins on the tonsils form under normal conditions even without an ongoing disease. The other side is formed by a disease process, the basis of which is inflammation.
Sometimes, if they are larger, they can get in the way. Most of the time they release spontaneously, but sometimes this can be a problem.
You ask:
Do I have to push the pins out or wait for them to fall out on their own?
The other side is a disease process, usually caused by inflammation.
In this case, in addition to the presence of white pins on the tonsils, there is also a possible white plaque, pus or swelling of the tonsils, as well as enlargement of the nearby lymph nodes.
Of course, inflammation is also accompanied by sore throat and difficulty swallowing.
In addition to the common and frequently occurring tonsillitis, other diseases can also be behind the presence of plugs.
Do you want to know more?
What are tonsils in a nutshell?
What are the non-healthy and disease causes behind tonsils?
Read on with us.
About tonsils in a nutshell
The tonsils (also known professionally as the tonsilla) are part of the lymphatic and immune system of the human body.
A person has several tonsils (tonsil), namely:
- palatine tonsils - tonsillae palatinae
- also known as the tonsillar tonsils
- paired organ
- lingual tonsil - tonsilla lingualis
- nasopharyngeal tonsil - tonsilla pharyngea
- tonsilla tubariae - the lymphoid tissue around the Eustachian tube that connects the middle ear and nasopharynx
Tonsilla = tonsil.
These tonsils are part of the Waldeyer's lymphatic circuit, which serves as a barrier against external foreign substances, pathogens, microbes.
Tonsils have an important immune function.
The tonsils are paired tonsils, located on either side of the throat. They serve as the first sink for microorganisms from the outside world that pass through the mouth through food and air.
They are of particular importance in childhood. During this period they are often inflamed.
Inflammation of the tonsils is also known as tonsillitis.
Repeated acute inflammation can turn into chronic, i.e. long-term inflammation.
Over a long period of time and with frequent inflammation, the tonsils become infiltrated with microbes that find their refuge there. In this case, the tonsils are already a burden and must be removed.
White pins or also tonsil stones
The tonsils have their own structure and are interwoven with tunnels. The anatomical composition of the tonsils as a tissue with deep passages allows the formation of plugs.
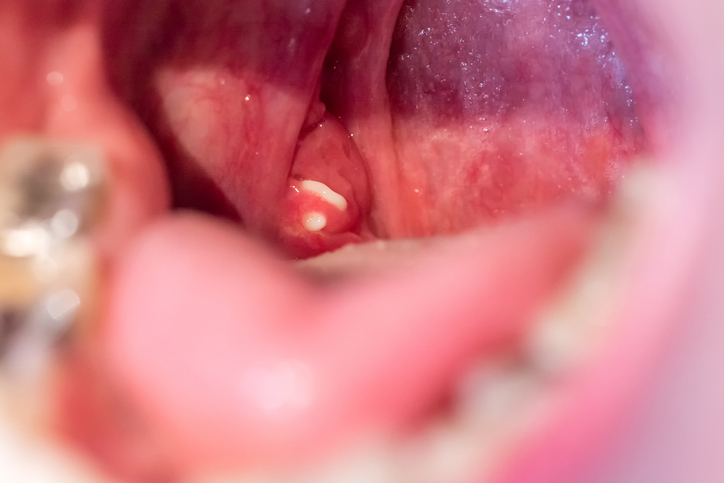
Lacunar crypts - tonsil passages.
These pins are whitish, white to yellow in color.
They are also referred to as tonsil stones. However, their consistency is not rigid and they are not hard like stone.
The stones get their name from the English name tonsil stones (stone = stone), you can also find tonsillolithis.
They contain dead tissue from the tonsils themselves and from the lining of the oral cavity, which flakes off when they are rebuilt.
Bits of food are also trapped in the area during swallowing.
+
Like the intestine, the mouth also contains a natural microflora. This is the normal, physiological colonisation of the oral cavity by bacteria.
Among them is streptococcus, which does not yet cause infection.
Except in cases where it is the cause of approximately one-third of purulent tonsillitis, but more on that later.
Back to tonsil stones.
So, in addition to the remnants of epithelial sloughing and diet, these stones also contain a certain amount of bacteria, also dead bacteria.
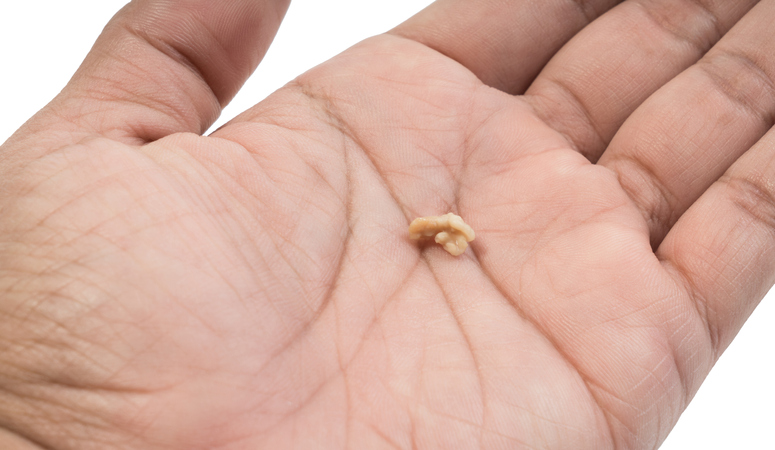
Together they form lumps.
These lumps have a soft consistency and can be crushed. They may smell strongly when crushed.
The pins or almond stones form under normal conditions, so there is no need to worry about your health.
However, they can cause an unpleasant smell, especially if their number is higher or they are larger.
Normally, they are released spontaneously during the day, can be coughed up or pass on into the digestive tract during eating and drinking fluids.
Smaller pins may not even be noticed or are only visible as small white dots on the tonsils (in the form of small balls, bullae, as if they were growths).

The lumps and plaque on almonds can also accumulate after eating certain foods, especially dairy products and other animal proteins.
By accumulating the contents, they increase in size and can even get in the way.
The accumulation of plugs is associated with the fermentation and rotting of the contents, resulting in possible unpleasant bad breath.
+ Halitosis is also affected by the composition of the normal microflora in the mouth and pharynx. But also by poor oral and dental hygiene.
It is well known that poor dental hygiene and tooth cleaning leads to tooth decay. This in itself carries the risk of spreading bacteria via the bloodstream to other parts of the body, such as the joints, kidneys or even the heart.
You ask...
Can these stones be removed mechanically? Or how else can the pins on the tonsils be removed?
Doctors do not recommend mechanical cleaning of the tonsils.
Why not mechanical cleaning?
The reason is the risk of damaging their surface.
The oral cavity is full of bacteria and microbes can enter the tonsil tissue through the disturbed surface. This causes inflammation.
An unpleasant complication of mechanical cleaning of the tonsil plugs can be their inflammation.
However, rinsing or quite ordinary gargling can serve to clean them.
There are various mouth rinse aids available, as well as mouthwashes and gargling solutions and disinfectants.
Alternatively, the doctor will recommend cleansing with certain oral medications.
We cannot forget about freely available and effective decoctions. A decoction of burdock, sage, chamomile or plantain will do for mouth rinsing and gargling.
Chewing gum, candy or gargling can alleviate bad breath.
Thorough oral hygiene and brushing of the teeth and tongue is a good preventive measure.
Can tonsils be removed because of this type of stud?
You ask:
Can tonsils be operated on because of stones?
Tonsil stones are not an indication for surgery.
Only tonsils that are chronically inflamed or cancerous, or if the acute tonsillitis complicates the course, are surgically removed.
Tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) is also performed for snoring and breathing disorders associated with tonsils.
Even tonsils with stones, as long as they are not morbidly altered, have a defensive significance in the body.
Pins and pus on the tonsils due to inflammation - often caused by tonsillitis
The most common disease condition is tonsillitis. It is a common inflammatory disease of the tonsils. It is also known as tonsillitis.
However, inflammation can have several causes.
The causes of tonsillitis are listed in the table below
| Originator | Description |
| Virus |
|
| Bacteria |
|
| Mycosis |
|
Regardless of the causative agent of tonsillitis, tonsillar plugs can occur. These are the result of an inflammatory process.
There is also visible swelling, redness and plaque, or the tonsils may have purulent plugs.
The throat is painful and the pain makes it difficult to swallow or speak.
Tonsillitis often occurs seasonally, during temperature transitions.
Often in the summer as a result of temperature shock when we indulge in ice cold in hot weather.
They often occur during a weakening of the body's immunity, but also due to excessive and unreasonable stress and prolonged mental strain and exhaustion.
Angina is divided into several forms, as shown in the table below
| Type of angina | Description |
| A. catarrhalis |
|
| A. lacunaris |
|
| A. folliccularis |
|
| A. vesiculosa |
|
| A. pseudomembranacea |
|
| A. ulceromembranacea |
|
| A. gangraenosa |
|
A specific group is tonsillitis, which arises secondary to other diseases, for example, scarlet fever.
Angina can also accompany other diseases, as shown in the table below
| Scarlet fever |
|
| Diphtheria |
|
| Infectious mononucleosis |
|
| Acute pharyngitis |
|
| Chronic pharyngitis |
|
| Syphilitic angina |
|
Read also the articles:
Angina loves heat
Proper treatment of angina in children
What do you mean by sore throat
Home treatment for sore throat
Summer colds and flu in children. Do you know how to avoid them?
Chronic tonsillitis
This is a long-term form of tonsillitis. It most often arises as a complication of frequent acute tonsillitis.
In certain forms, however, it can also break out after the first infection. Examples are mononucleosis or diphtheria, but also paratonzillar abscess.
The tonsils are damaged during inflammation.
Scars form on the surface of the tonsils as they heal.
These are a good place for bacteria to settle.
They then cause repeated inflammation.
When chronically damaged, it's the opposite. They're a source of infection.
Surgical removal is therefore recommended in this context.
The risk of recurrent streptococcal inflammation is spread to other sites in the body.
Examples are diseases such as:
- rheumatic fever - diseases of childhood
- reactive arthritis
- inflammation of the kidneys
- inflammation of the heart - endocarditis and myocarditis
- vasculitis and Kawasaki disease
- skin diseases, psoriasis, eczema
- nerve diseases
- inflammation of the eyes
- and others
Symptoms in chronic tonsillitis may be non-specific and the person may not even think about the problem.
Possible symptoms of chronic tonsillitis:
- chronic, prolonged fatigue
- exhaustion
- malaise
- recurrent increase in body temperature - especially in the morning
- in acute exacerbations, fever
- inflammation causes local manifestations that often persist for months
- sore throat, aching, scratching, cutting in the throat
- impaired swallowing and foreign body sensation in the throat
- purulent inflammation and pins and needles in the tonsils
- smelly pins and bad breath
- coughing
- phlegm in the throat
- enlarged lymph nodes
As a result of a long-standing pathological process, the tonsils are small, atrophied, atrophic, atrophying, but also pale and swollen. They are scarred on the surface, which promotes the formation of plugs.
The oily lumps are yellow to brown in colour.
You ask...
What indicates chronic tonsillitis?
- Recurrence, i.e. a relapse of the disease
- tonsillitis at least 3 times a year + at least 3 years in a row
- tonsillitis 5 times in the last 2 years
As already mentioned, chronic inflammation is an indication for surgical management. This is similar to a paratonzillar abscess, tumor or tonsil enlargement which subsequently prevents swallowing or causes snoring and sleep disturbances.
The doctor (ENT specialist) indicates the method of surgery. Either:
- tonsillectomy - complete removal
- tonsilotomy - partial removal, especially when the tonsils are enlarged and there is no chronic inflammation
- RTIFF tonsillotomy - reduction by insertion of a submucosal electrode
Summary - beware of purulent pins on the tonsils
The occurrence of purulent plugs is related to infectious inflammation in most cases.
If not only white, but also smelly or purulent plugs appear on the tonsils, a professional examination is necessary.
Purulent plugs arise because of the anatomical structure of the tonsils. They have pits, crypts, in their structure.
In these, microbes, bacteria, most often streptococci, are deposited. This form of inflammation must be treated as soon as possible with antibiotics.
Neglecting a streptococcal infection can lead to health complications and the spread of bacteria through the bloodstream to other parts of the body. Examples include damage to the joints, kidneys, heart, blood vessels or even the eyes.
Purulent pins or pus plaque on the tonsils and other problems:
- cause bad breath
- smelly lumps sometimes need to be manually removed - professionally
- can be on both sides of the tonsils, but also on one side
- adds sore throat, stinging, scratching, cutting
- impaired swallowing + worsening of pain when swallowing
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat
- irritation to cough
- fatigue, weakness and malaise
- increase in body temperature to fever
- enlargement of lymph nodes
Removal of tonsils: pros and cons
Diseases with symptom "Studs on almonds"
Interesting resources










