Pathological fracture: what is the cause of excessive bone fragility?
A pathological fracture is a fracture that is caused by minimal force. It can occur during normal activity, but also while sitting. Vitamin D deficiency, calcium deficiency, structural disruption, as well as the action of a tumor process are involved in increased bone fragility.
It may be a fracture as a result of a slight trauma, blow or other injury. A fracture will not occur in a person with healthy bones due to the minor nature of the action.
However, in the case of people suffering from pathological fractures, the situation is different. The bones are more sensitive to impact or trauma, but also to normal loading. This is caused by altered, broken bone structure, decalcification, tumour disruption or other causes.
Diseases that cause pathological fractures
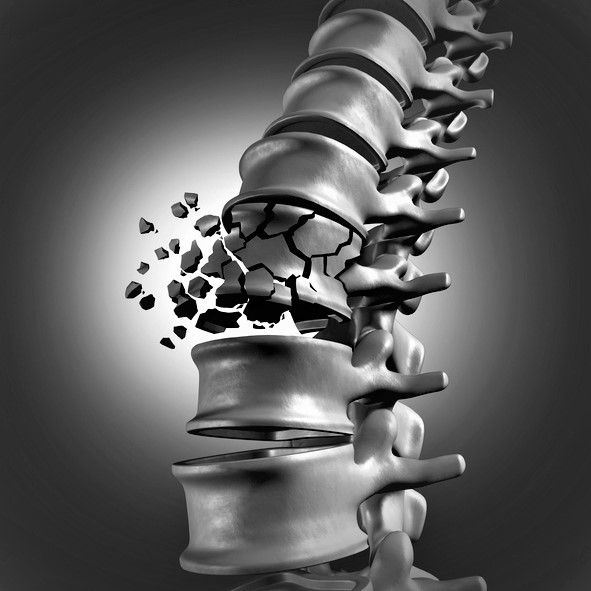
In mild fractures, i.e. pathological fractures, a disturbed structure is involved in their occurrence. This disturbance can result in increased brittleness of the bones during normal tasks. In the most severe forms, for example, a vertebral fracture can occur during ordinary sitting.
Increased bone fragility can be caused by a deficiency of vitamin D. In children, a deficiency of this vitamin causes rickets. The deposition of calcium in the bones is impaired and they become deformed. In older age, it is a cause of osteoporosis.
Paget's disease
However, pathological fractures are most common in people who have musculoskeletal problems. For example, in Paget's disease, bones lose their strength and original shape. This affects, for example, the skull, spine, pelvis or large and long bones. These are more susceptible to various injuries caused by pressure or impact.
Osteoporosis
The development of pathological fractures is also related to the strength and quantity of bone mass in the bone. Osteoporosis is a metabolic disease of the bone that causes a reduction in the overall quality of the bone and also a reduction in the strength of the bone.
For this reason, bone breakage is common in people affected by osteoporosis, even with minimal impact or minor injury. Bones are less resilient, their elasticity decreases and their strength is lost. It is also a problem of calcium and vitamin D deficiency.
Cancer
Bone cancer also causes pain in the limbs and sometimes swelling and weight loss. Firstly, cancer can be primary, where tumours develop directly from bone or cartilage cells.
Second, secondary. This is cancer in which the tumour has developed in another part of the body but has metastasised to the bone. Metastasis is the transfer of a tumour, which is transmitted by blood or lymph, but also by contact.
In bone cancer, pathological fracture is also common, due to weakening of the strength of the affected bone. In most cases, surgical removal of the tumour is required as part of the treatment.
Bone tumours do not arise directly from bone or cartilage tissue. They arise elsewhere and then metastasize directly to the bone via the bloodstream or lymphatic pathways.
If they are malignant, they can metastasise to surrounding tissues such as bone. This is a very serious disease and usually at this stage the success rate of treatment is already quite low.
Diseases of the blood
Some blood diseases can also affect the bones. An example is multiple myeloma. This is a cancer of plasma cells and their accumulation in the bone marrow.
The disease affects the bone marrow, where osteolytic deposits are formed that destroy the bone material itself. These deposits thus destroy the structure of the bone and weaken it. And this can be the cause of mild and pathological fractures. This disease also belongs in the hands of professional treatment based on examination and diagnosis by a doctor.
Other causes of increased bone fragility
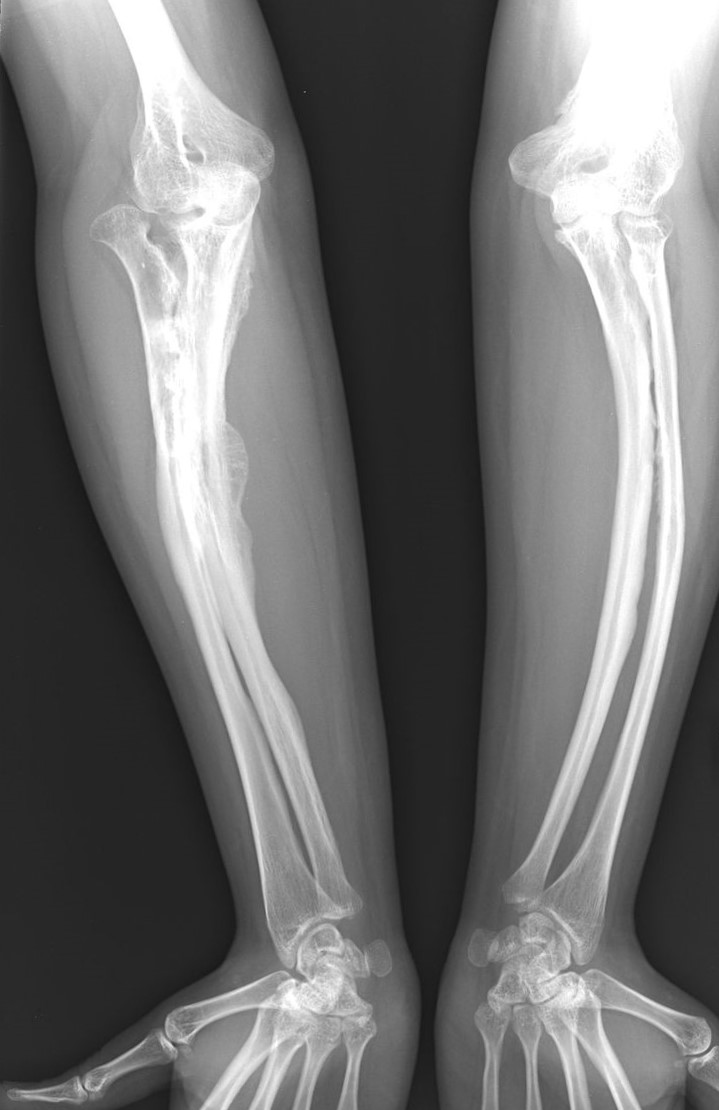
In addition to the disruption of the bone by cancer, a bone cyst can also contribute to a pathological fracture. Another cause is various benign tumors. This type of fracture also occurs with diseases that cause increased function of the parathyroid glands.
The most common cause is a parathyroid tumour, which causes increased bone calcification. This promotes the formation of pathological fractures. Another example is Cushing's syndrome.
There is also a congenital hereditary disease that results in brittle bones. Osteogenesis imperfecta, otherwise known as fragility ossium, Brittle Bone Disease or Lobstein's syndrome:
- fragility and brittleness of long bones
- bone deformities
- brittle teeth
- blue sclerae, or whites of the eyes
- hearing impairment or loss
Diseases with symptom "Pathological fractures"
Interesting resources










