Symptoms associated with the ears, nose and oral cavity
Scratching in the throat
Most of the time, the origin of scratching in the throat is a cold, flu or other seasonal illness. Allergies and oesophageal diseases represent non-infectious causes. In case of prolonged scratching, an examination is recommended for a possible oncological process.

Cracked lips
Dry and chapped lips can be distressing, especially when the chapping is accompanied by inflammation. Chapping is a common symptom of dehydration. Unsuitable cosmetics also have a negative effect, as does the weather. In some cases, chapped lips can indicate another disease.
Dry mouth
What is xerostomia and why do I have dry mouth? Several diseases can be the cause. Beware of unpleasant complications.

Pricking in the ear
Pain in the ear is a symptom of disease in the ear itself, but this is not always the case. Sometimes it originates elsewhere and only radiates to the ear. However, the highest percentage of these pains originate in the ear. The earache is just a symptom.

Raspberry tongue
Tongue discoloration can indicate a problem going on in our body. And a raspberry tongue is an example of this. In addition to signaling a B vitamin deficiency, it can be a sign of other diseases. For example, even scarlet fever.

Nosebleeds - Epistaxis
A nosebleed is a scary sight for many people, coupled with concerns about their own health. The good news, however, is that most of the time, nosebleeds are not a serious problem.

Thickening of the voice
Vocal dryness can be the cause of vocal cord thickening. It occurs mainly during the heating season, but also during the summer. Often the cause is congestion in the vocal cords. But it can also be caused by respiratory diseases. In milder cases, inflammation, in worse cases, a tumour. Other causes can also be behind vocal cord thickening, such as hormonal changes.

Tinnitus
Tinnitus can be so unpleasant that it does not allow a person to concentrate on normal activities. Why does it arise, what are its main causes?

Acetone Breath
Acetone breath, or acetone halitosis, is a major manifestation of excessive blood sugar elevation in diabetics. However, it can have other causes. Do you smell acetone from your child's mouth?
White tongue
White tongue is a common harmless phenomenon, especially in the morning after waking up. In other cases, a yeast infection or other disease conditions may be behind the condition.

Increased saliva production
It occurs reflexively, i.e. when the senses are stimulated. For example, when we look at food or smell it. It can also be triggered by chewing. In pregnancy, it occurs mainly in the first trimester. And in some cases, it is a symptom of various diseases.

Loss of sense of smell
The sense of smell is one of the senses. It is important for the perception of smells and odours. Its importance in smelling perfume, food or flowers is clear. But its most important function is to detect odours in the environment. It can alert us to dangerous substances whose inhalation could be fatal to life.

Teeth wiggling
Milk teeth in children loosen naturally to be replaced by adult, permanent teeth. But in an adult, this is a phenomenon that indicates a disease. Neglect can mean serious complications.
Bleeding gums
Bleeding is a problem that indicates inflammation or other diseases of the gums. For example, gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontitis. Its cause is also insufficient and improper oral hygiene. The risk is higher in diabetics, smokers and women due to hormonal changes.

Deafness
Hearing is a sensation we use every day. It is necessary for verbal communication. It also informs us about what is happening around us. For example, it warns us of danger. Its disorder can be congenital or acquired. It is caused by several diseases.
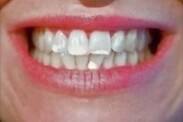
White Spots on Teeth
Tooth stains form for a number of reasons. For example, food stains the teeth. Excess fluoride will also show stains. In children, they are an early sign of tooth decay. Poor hygiene and excess plaque tend to be the cause of these stains.

Lingering in the ears
Hearing is an important part of our perception of our surroundings. It informs us about what is happening in our surroundings. Sometimes it is disturbed. One of them is the hearing loss. It can be short-term and long-term. It can be caused by inflammation, but it can also have other causes.

Discharge from the ear
It is important for the self-cleaning ability of the ear. It helps dirt to travel out of the ear. But if there is an increase in its production, inflammation may be the cause. Bloody discharge is common, for example, in severe head injuries.

Aphthae
Aphthae are among the most common inflammations of the oral mucosa. They affect approximately 20% of the population, both children and adults. Some people develop them only once and others develop them repeatedly throughout their lives. The cause is not yet fully understood.
The ears, nose and oral cavity are part of the head and most of the sensory receptors are located here, while at the same time the oral cavity is an important input to both the respiratory and digestive systems. Diseases and disorders of the ears, nose and throat are dealt with by a medical specialty called ENT, which stands for ear-nose-throat medicine, but several symptoms occurring in the oral cavity are also dealt with. In addition, due to the function of the oral cavity, other symptoms are also manifested in this area.
The nose functions within the upper airway and is mainly used to inhale oxygen into the lungs. Problems with the nose usually arise mainly from respiratory diseases or injury, for example in the form of nosebleeds, or there may be a malfunction of the olfactory receptors, which are located in the nasal cavity and help the brain to identify smells and odours. Most often, however, nasal congestion occurs due to mucus production in infections and inflammation.
The ears not only serve as an auditory receptor to perceive stimuli from the environment, but also have a connection to the balance system, which ensures the coordination of a person's posture. Very often the ears are affected by inflammation and most of the symptoms are related to inflammatory diseases of the outer, middle and inner part of the ears. Hearing impairment can sometimes have nerve causes and is typical in the elderly. A serious symptom is already bleeding from the ears, which is usually related to a life-threatening condition or injury.
Symptoms associated with the nose and ears
It happens quite often, especially to young children, that blood starts to flow from their nose. This is the result of either an injury or damage to a small blood vessel in the nasal cavity, and it doesn't have to be anything serious. However, in the case of major or frequent bleeding, it may be a symptom of dried mucous membranes or leukaemia. The loss of the nose, unless it is caused by nasal congestion and blockage due to respiratory disease, is very often due to hormone fluctuations, or is a primary symptom of a neurological disease.
There are many more problematic phenomena associated with the ears. For example, with pricking in the ear, it is very often a symptom of inflammation, either in the ear canal or directly in the middle ear. Sometimes it can also be a symptom of a skin infection in the outer part of the ear. Pressure in the ears is natural, for example, when climbing altitude, but it is also one of the symptoms of inflammation of the nasopharynx, rhinitis or otitis media. Sometimes, the drooping also accompanies hay fever, which is an allergic disease.
Tinnitus also accompanies ear infections, most commonly otitis media, but also occurs as a symptom in Meniere's disease, where it is very intense and associated with vertigo. Sometimes it can also be related to atherosclerosis. Otitis media is also associated with discharge from the ear, especially in the chronic form. Sometimes the discharge may also be caused by inflammation of the external ear canal and is accompanied by hearing problems and a sensation of lying in the ear.
In acute otitis media, there is also a temporary hearing impairment, which subsides as the inflammation heals. However, it is worse in the case of Meniere's disease or presbyacusis, for example, when the deterioration is permanent. Complete deafness is quite common, especially in the elderly, also due to old age and damage to the hearing system. Deafness also occurs when the eardrum ruptures as a result of trauma. Untreated otitis media is also dangerous, where deafness can also occur sporadically.
Diseases of the teeth and gums
In the oral cavity, problems occur very often, especially with the gums and teeth. Purulent discharge from the gums usually indicates an advanced infection or inflammation, for example as a result of acute periodontitis, in abscesses or in periodontitis. Similarly, in periodontitis or even in periodontitis, bleeding gums can occur, which is also an inflammatory disease of the area around the tooth bed. Bleeding gums are also common in gingivitis, which is already an infection formed not only on the gums but also on the teeth.
Very often periodontal disease is accompanied by the formation of so-called periodontal chobots, which form around the affected tooth and cause it to loosen in the tooth bed. This is a typical symptom of both periodontopathy and periodontitis. Similarly, problems with the dental apparatus and gums are also manifested by loose teeth and this is due to the inflammatory process in the gum, which weakens the structure of the gum itself and also the tooth. Tooth wobbling is also very common as a result of untreated decay.
Damage to the gum and tooth can also be caused by a condition called sensitive teeth, where a person feels pain on the tooth enamel as a result of, for example, too hot or cold food in the oral cavity. At the same time, this is also one of the early signs of incipient tooth decay. Periodontal problems can also cause overall poor tooth development, although this also occurs with calcium disorders, for example it is part of the symptoms for Lobstein's syndrome, Marfan's syndrome or phenylketonuria.
When it comes to teeth, many people notice discolouration as one of the symptoms. This can either be a genetic predisposition, which over time affects the colour of the teeth, but also, for example, the removal of calcium from the teeth. Sometimes the darkening of the tooth is also directly related to the death of the tooth, i.e. no nutrition is flowing into the tooth through the dead root. The appearance of white stains is usually related to demineralisation of the teeth, or it may be a problem of using overly fluoridated toothpastes.
Disruption of the tooth structure is also a very serious symptom. Breaking off part of a tooth may be accompanied by the appearance of tooth decay that has been left untreated for a long time, or it may be a symptom of a calcium deficiency in the body. Direct tooth decay is most often related to tooth decay and problems of the fixation apparatus. The frequent occurrence of tooth decay can in turn indicate a lot about either poor dental hygiene or oral cavity disorders such as overacidity. However, with increasing age this is a natural process.
Tongue, palate and lips
A white film on the tongue is a typical symptom of strep throat or scarlet fever, or of infection with the yeast Candida albicans. Yellow or greenish plaque is a symptom of metabolic disorders. Overall, tongue discolouration is considered a very good indicator of the health of the body. A raspberry or strawberry tongue can be a sign of vitamin B deficiency, or sometimes it is an atypical symptom of infectious scarlet fever or Kawasaki disease.
A smooth tongue arises as a result of atrophic changes on its surface usually occurs in problems with hormone levels, for example, in hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. It is also a symptom of an inflammatory disease called glostitis, or it may also occur in anaemia, or anaemia. An enlarged tongue may in turn indicate the presence of a tumour on the tongue, or it may be a disease called acromegaly, which is caused by the overproduction of the hormone STH. It may also be a symptom of amyloidosis.
The occurrence of ulcers on the tongue but also on the lining of the oral cavity is typical of stomatitis, which is an inflammation of the inner mucous membranes of the oral cavity. It may also be a typical manifestation of a disease called scurvy, which is almost completely absent in our country. If there is redness of the tongue and also of the palate, there may be several causes. Either it is part of the symptoms of tonsillitis, or it is an immune disorder accompanied by aphthae, or it is an inflammation of the tongue or oral mucosa called glostitis.
In the oral cavity, aphthae occur on the tongue, but usually more on the palate. These are small whitish boils that can signal an allergy to food, toothpaste or dental instruments. Sometimes aphthae can also be a symptom of tonsillitis or chickenpox. The problem on the lips is quite often cracking, which occurs, for example, when there is a lack of iron or vitamin B, or may be natural in winter. Both chapped lips and a red tongue are symptoms of Kawasaki disease.
Other symptoms associated with the oral cavity
During various infectious diseases, it is also possible to observe changes and symptoms on the tonsils. For example, typically during tonsillitis, so-called pins, which are smaller white lumps and bump-like plaques, appear on the tonsils. Sometimes they also occur in scarlet fever. In addition to scarlet fever and tonsillitis, swelling of the tonsils is also associated with diphtheria or infectious mononucleosis, which is also manifested by enlarged lymph nodes in the throat and also by sore throat and neck.
A feeling of pressure on the tonsils usually also accompanies several infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract, typically tonsillitis or influenza. Similarly, such sensations can also occur with scarlet fever, and this is because the role of the tonsils is to trap infections still in the upper respiratory system. Infections of this type are usually associated, for example, with a scratchy throat, which is also common with the common cold, but can sometimes be associated with laryngitis, which is a more serious inflammation of the larynx.
Excessive salivation in the oral cavity can occur, for example, in intoxication and poisoning, but also as a symptom of staphylococcal enterotoxicosis or Huntington's disease. Increased salivary secretion is also typical of Parkinson's disease, and in some diseases it is also accompanied by salivary leakage from the oral cavity. This may be the case in nervous problems with a drooping corner of the mouth, or when swallowing saliva is not possible, for example in epiglottitis.
The opposite of excessive salivation is dry mouth. This accompanies several diarrhoeal diseases, for example salmonellosis, but also salivary gland disorders. Dry mouth is typical in poisoning, for example, but it is also a symptom of botulism or diabetes. The salivary glands also include the parotid gland, which can swell in some diseases. This is, for example, typically in angina or laryngitis, but sometimes also as a result of the formation of a tumour in this area, possibly in parotitis.
Both sinusitis and hay fever are associated with hoarseness. This symptom usually occurs even with a congested nose and occurs in diseases with high mucus secretion. However, it can also be a manifestation of epiglottitis, which is a life-threatening condition. People who are heavy smokers or who have a tumour or inflammatory disease of the larynx are also troubled by thickening of the voice. In thyroid diseases, when there is a drop in hormone levels, this symptom can also sometimes be present.
From the mouth it is sometimes possible to catch a bad smell as a disease symptom. In the case of the smell of acetone, it may be a symptom of intoxication, or it may also be a symptom of diabetes that has been untreated for a long time. This is the case in type I diabetes, i.e. congenital diabetes. At other times, other odours such as digestive problems, kidney failure or alcohol abuse are manifested by bad breath. In some cases, halitosis is one of the symptoms of tonsillitis.
In bleeding disorders, not only nosebleeds often occur, but also bleeding from the oral cavity. Sometimes blood can come from the gums or the oesophagus, so a medical examination is definitely needed. Less common symptoms related to the oral cavity include spasms of the masticatory muscles, which can occur during an epileptic seizure, but also during a tetanus infection or an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. They sometimes occur in younger children even during febrile seizures.









