- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Estrogen: The necessary evil for human health, and ways to tame it
- medicinapropraxi.cz - Phytoestrogens. Marie Vrzáňová, MD, Jana Heresová, MD, CSc.
- medicalnewstoday.com - Everything you need to know about estrogen. Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D.
What is the hormone estrogen and how does it affect the female body?

Estrogen is nicknamed the "female hormone" because it has a significant effect on the female body throughout life. It is the main sex hormone in women, but it is also found to a small extent in men. What is its role and importance?
Article content
The name is derived from the estrous cycle (female period) in which they play a significant role.
Estrogens are formed mainly in the ovaries and during pregnancy in the placenta. To a lesser extent, they are formed by the liver and adrenal glands. Three basic types of estrogens are known - estradiol, estrone and estriol.
Estradiol
Estradiol is one of the most potent estrogens from the first menstrual period until the end of menopause. Estradiol production occurs in the ovaries.
Its levels begin to increase during menstruation, which helps the egg to mature and promotes ovulation. It is produced in the corpus luteum of the egg, the adrenal glands, the liver and during pregnancy it is formed in the placenta.
Its main role is the physiological development of the female reproductive organs as well as the development of secondary sex characteristics. An important function is also the promotion and maintenance of gestation - pregnancy.
The level of estradiol is monitored in case of infertility and menstrual cycle disorders. In pregnancy, its level rises and reaches a peak just before the term of childbirth.
Estriol
Estriol is a type of estrogen produced in the ovaries and during pregnancy in the placenta. It is an important hormone of pregnancy. In women who are not pregnant, it is found at the same level as in men or as in postmenopausal women.
Estriol levels increase mainly from the eighth week of pregnancy until the time of delivery. Estriol also normalises the vaginal epithelium and thus helps to restore the physiological microflora and pH in the vagina.
It also has a beneficial effect on the pituitary gland in the brain, which is manifested by the regulation and elimination of climacteric syndrome in the female menopause.
Estron
Is a hormone produced in the subcutaneous lubricant, ovaries, adrenal glands and liver. Of the trio of estrogens, estrone is considered the weakest hormone.
It is especially important during menopause and menopause, when the ovaries are no longer active.
Functions of estrogen
The main function of estrogen is to have a beneficial effect on the development, function and activity of the reproductive organs.
It is involved in the development of female sexual characteristics and the regulation of sexual behaviour. It influences the growth and repair of the uterine lining and the maturation of the egg during the menstrual cycle.
Another function is the beneficial effect on bone growth and growth hormone. It has a positive effect on promoting bone density and the elasticity of the vascular system.
Estrogens significantly affect energy metabolism, which slows down with the onset of menopause and estrogen depletion. They reduce and regulate the amount of muscle mass and in turn increase water retention in the body.
Another effect is to support memory, learning and cognitive function.
Functions of estrogen in the female body:
- Function and activity of the sexual organs
- Supporting the renewal of the uterine lining
- Maturation of eggs
- Growth of breasts and female proportions
- Higher tone of voice
- Less body hair
- Regulation and support of the course of pregnancy
- Reduction of bone thinning
- Supporting brain activity
- Supporting the immune system
- Regulation of metabolism and body weight
Estrogen levels in the body
The level of estrogen in a woman's body depends on age, phase of menstrual cycle, medical history, drug therapy, diet and lifestyle.
Estrogen levels in women fluctuate regularly depending on the menstrual cycle. Estrogen levels are highest around the middle of the menstrual cycle at the time of ovulation and the woman's fertile window.
It is reported that the optimal estrogen level in a woman's blood is 43-180 pg/ml.
Fluctuations in estrogen levels are not good for health, the hormonal system, and proper body function. Depleted or excess estrogen levels should be investigated, a doctor consulted, and then the appropriate form of treatment determined.
Estrogen depletion
Estrogen levels naturally decline, primarily due to the decline in ovarian function associated with older age and a woman's menopausal period.
There is a decrease in bone density, collagen formation, skin elasticity, and decreased libido. Conversely, the risk of anxiety, depression, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis increases.
The process of menopause is a natural time-limited hormonal imbalance. However, with the help of pharmacotherapy and natural treatments, it is possible to eliminate the symptoms of menopause.
Other non-physiological causes of the decline in estrogen levels can be improper dietary and exercise habits, stress, lack of sleep, thyroid disorder, pituitary disorder, hormone therapy, drug therapy, breast cancer and other gynecological organic disorders.
Women who exercise for long periods of time with high intensity and excessive physical exertion may stop producing sufficient amounts of estrogen.
With malnutrition, anorexia and low body weight, when the body does not get enough of the necessary nutrients, the female body cannot produce sufficient amounts of estrogen.
How can estrogen deficiency manifest itself?
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- loss of menstruation
- vaginal dryness
- decreased libido
- frequent urinary tract infections
- moodiness, anxiety
- excessive unusual body hair
- deterioration of skin and hair
- breast reduction
- lack of energy
- problem getting pregnant
How to supplement estrogen?
Hormonal treatment
First of all, it is necessary to find out and correctly diagnose the cause of estrogen depletion, and then determine the appropriate treatment.
Currently, hormone replacement therapy is available, which is indicated by a doctor. The most common drug complex of estrogen supplementation is in oral form (tablets) and injectable form.
There is also topical treatment in the form of vaginal creams containing estrogens and progesterones.
Prescription drugs and preparations are indicated after examination and determination of the cause of reduced estrogen levels.
Hormonal treatment is often chosen for the risks of cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, hormonal balance disorders, pituitary, thyroid and other organic gynecological diagnoses.
Natural treatments
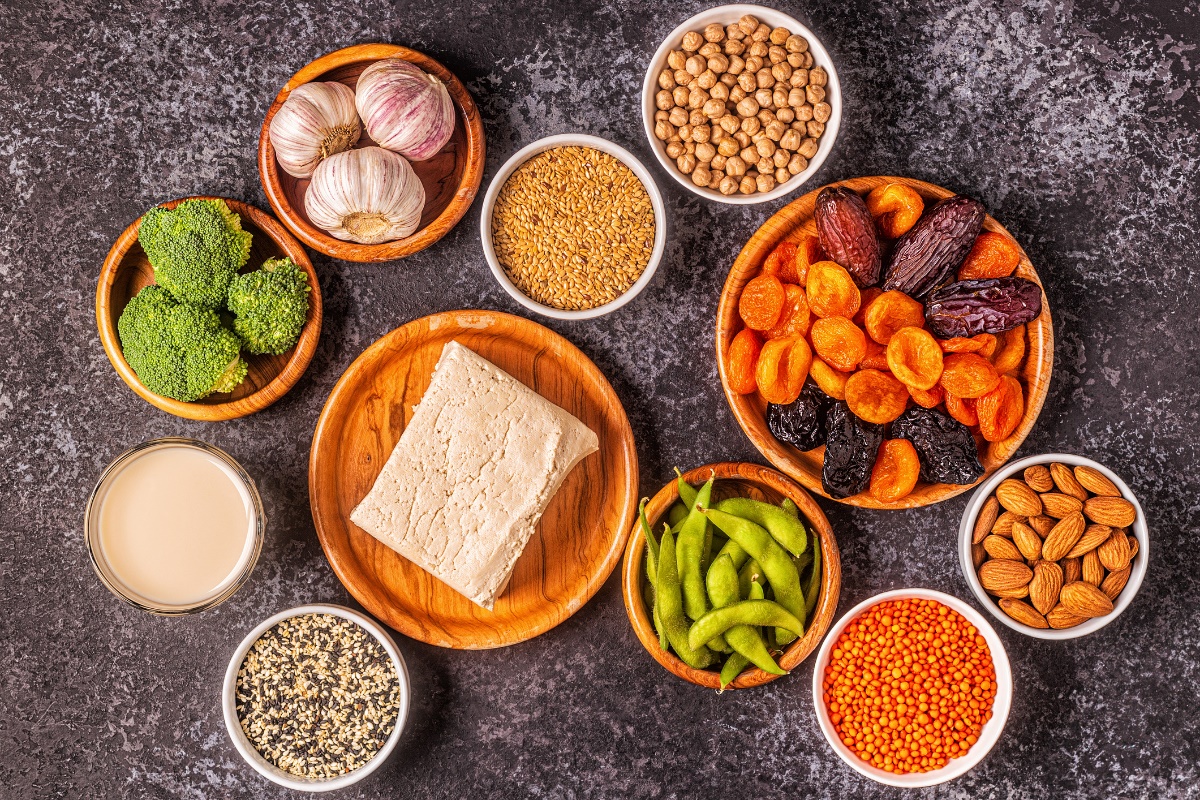
Natural treatment of elevated estrogen levels is based on modifying exercise habits, a complete balanced diet containing phytoestrogens and with the help of the action of herbs.
A phytoestrogen is a natural substance similar in its properties to estrogen.
The group of medicinal herbs containing natural estrogen includes herbs such as grape thistle, common drumstick, clary sage, red clover and flax.
Phytoestrogens are mainly found in plant foods such as soy, soy milk products, tofu, beans and peas. Fruits containing phytoestrogens include strawberries, figs, plums and apricots. Vegetables containing phytoestrogens include broccoli and lettuce. Various nuts and seeds are also suitable.
Nowadays, many dietary supplements are available in the form of tablets and creams, which with their natural composition help to increase the level of estrogen in the female body.
Over-the-counter estrogen creams harness the power of natural estrogens when used externally.
The primary effect is to moisten the vagina and support the physiological state of the vaginal mucosa. They are available in the form of creams or special estrogen capsules.
Natural complex tablets also contribute to the optimal level of female hormones in the body, which, in addition to supporting hormonal balance, also help with symptoms of fatigue, weakened immunity and support the overall vitality and energy of the body.

Excess estrogen
When there is an elevated level and excess of the hormone estrogen in a woman's body, the body sends out warning signals.
Excessively painful menstruation, heavy menstrual bleeding, PMS symptoms, irregular menstrual cycles, decreased sex drive, excessive water retention, breast pain, sleep problems, increased body weight, moodiness, hypersensitivity and migraines.
The presence of PCS, ovarian cysts and endometriosis is possible. If a woman ignores these symptoms for a long time, she may dangerously increase her risk of developing breast cancer.
Elevated estrogen levels can be naturally alleviated by lifestyle changes: avoiding alcohol, caffeine and phytoestrogens in the diet, reducing fat stores, regular rest, sufficient physical activity and limiting long-term stress.
It is advisable to consult a doctor to determine the cause of estrogen dominance and to determine the course of treatment (hormonal treatment, drug therapy, natural treatment, lifestyle changes).
Estrogen and pregnancy
If fertilization of the egg does not occur, the corpus luteum of the follicle disappears and estrogen production works as usual.
Once the pregnancy is successful, the corpus luteum produces female hormones (progesterone and estrogen) that are important for the maintenance and proper course of the pregnancy. Its function is taken over by the placenta in the following months.
Estrogens promote the development and elasticity of the muscle fibres of the uterus and pelvis. They allow the uterus to increase in volume for the growth of the baby. They promote the production of breast milk, increase blood circulation and blood volume.
High levels of estrogens can cause bleeding from the nose or gums. The hormonal balance of a woman in pregnancy should be continuously and preventively monitored by a doctor.
Estrogen and hormonal contraception
Combined two-component hormonal contraceptives contain synthetic forms of the hormones estrogen and gestagen. This type of contraceptive is the most commonly prescribed and is considered the most effective against pregnancy.
The main effect of combined contraceptives is to stop ovulation. The uterine lining is rearranged, making it impossible for the egg to nest.
The main risk of using combined contraception is a higher risk of blood clots, thrombosis, embolism, heart attack or stroke.
There is an increased synthesis of clotting factors in the blood, thereby increasing the clotting capacity of the blood itself. Careful consultation with a gynaecologist is necessary when choosing and indicating hormonal contraceptives.

Estrogen in men
Estrogen is not exclusively a female hormone. It is also found in small amounts in the male body. The main role of estrogen in the male body is its role in sperm maturation and libido regulation.
Its role is sensitivity and activation of the adenosine receptor, regulation of the lipid profile, and support of immune and anti-inflammatory processes. Estrogens in men are produced in the liver, adrenal glands, adipose tissue, and breasts.
Blood levels of estrogens in men should be in the range of 10 to 25 pg/ml.
Manifestations of excess estrogens and testosterone depletion in men can be gynecomastia (breast enlargement), decreased libido, decreased body hair, weight gain, moodiness, and possible fertility problems.
Functions of estrogen in the male body:
- Effect on glucose uptake and utilization
- Effect on lipid profile
- Support for bone density
- Immune function
- Sperm development
- Regulation of libido
Interesting resources










