- fnnitra.sk - How to keep joints healthy
- wikiskripta.eu - Joints of the lower limbs
- mayoclinic.org - Swollen knee
Water in the knee and swelling: what are the main causes? What will help in the treatment?

Are you suffering from water in the knee or knee pain? What are the most common causes?
Article content
One of the many symptoms of knee joint disease is an excessive amount of water.
Accumulated excessive water in the knee causes swelling of the structures of the knee itself and is one of the significant symptoms of knee joint damage.
The knee joint, along with the hip joint, is one of the most stressed joints in our body. These joints bear the entire weight of the body and provide the movement itself.
The knee is the most complex joint. It can perform a variety of motor functions that allow walking on a level or incline.
The knee joint (articulatio genus) consists of 3 parts:
- the femur.
- the tibia
- patella (kneecap)
The femur, which is the largest bone in the body, connects to the tibia by the patellar ligament and capsule. The patella is located on the front of the knee and helps with extension (stretching) and flexion (bending) of the leg.
The knee also has the ability to rotate (pivot) slightly.
Inside the knee joint there are contact surfaces that are covered with cartilage. This cartilage has a protective function for the knee, helping it to move smoothly and protecting it from premature wear and tear.
On both inner sides of the knee there is a special cartilage called the meniscus. The meniscus absorbs shock and stabilises the knee joint.
The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments of the knee act as the main stabilizers.
In order for our knee to perform its function and not collapse, it needs a lubricant called synovial fluid to function. This fluid is found in small amounts between the bones of the knee joint that rub together.
Water in the knee and its symptoms
The water in the knee, technically called synovial fluid, has an important function in the joint space. It ensures pain-free movement, preventing the parts of the joint from rubbing against each other.
It also has a nourishing function for the soft parts of the joint - cartilage and tendons.
If the fluid begins to form excessively for various reasons, it presses on the structures of the knee and causes deterioration of the movement functions.
Other symptoms of water accumulation in the knee may include:
- Pain - especially when moving, especially when walking
- Swelling - pain is usually accompanied by swelling of the affected knee
- Redness and heat differential - the knee feels hot to the touch
- Itching - the affected knee often itches (caused by excessive blood flow)
- Feeling of stiffness - prevents freedom of movement and limits walking itself
- Feeling of a heavy knee - in some cases up to the whole leg
Causes of water in the knee
Why does water accumulate in the knee, you ask?
There are many causes for the accumulation and increased formation of water in the knee.
Most commonly, it is a disparity between the production and absorption of synovial fluid due to inflammation of the knee joint structures. The body defends itself and uses water as a protective agent.
The plasma contains white blood cells and these try to suppress the inflammation. The manifestation of all this is a change in the colour and consistency of the synovial fluid.
All the more damaging.
If the amount of water increases significantly, it begins to press on the surrounding structures. Pain comes and swelling develops.
Swelling has various causes. The most common is overloading of the joint or repetitive trauma, most often in athletes.
Overweight people are also at risk.
Water in the knee can also form after fractures and surgery.
Swelling in older people is mainly caused by systemic diseases.
These include arthritis, gout, rheumatoid arthritis and infections.
You can read more about these diseases here:
What is arthritis, what are its causes, symptoms and stages? How to stop it?
Gout: What is gout disease, why does it occur, what causes attacks and what is the treatment?
Rheumatoid arthritis: the first signs of rheumatism are not nodules, what is the treatment?
Diagnosis
Significant swelling, pain and reduced mobility are the most common factors that prompt us to see a doctor.
What to expect at the doctor?
The first step is to take a thorough medical history.
And what to remember to tell the doctor?
- Recent injuries
- Excessive sports
- Cracking or breaking in the knee
- Pre-illness, i.e. whether you have already been diagnosed with inflammatory joint disease
The doctor will use special tests to determine the condition and function of your mobility.
Imaging methods such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound (USG) are used to get a better view and clarification.
In systemic and inflammatory diseases, blood tests are also used to determine inflammatory parameters in the blood CRP - C-reactive protein and other specific laboratory tests.
Diagnostic and therapeutic tests include arthroscopy of the knee (AS).
This is a form of minimally invasive surgery.
A small camera is inserted into the joint (usually under spinal anaesthesia).
It is used to make an accurate diagnosis.
If necessary, doctors will immediately perform the necessary procedure.
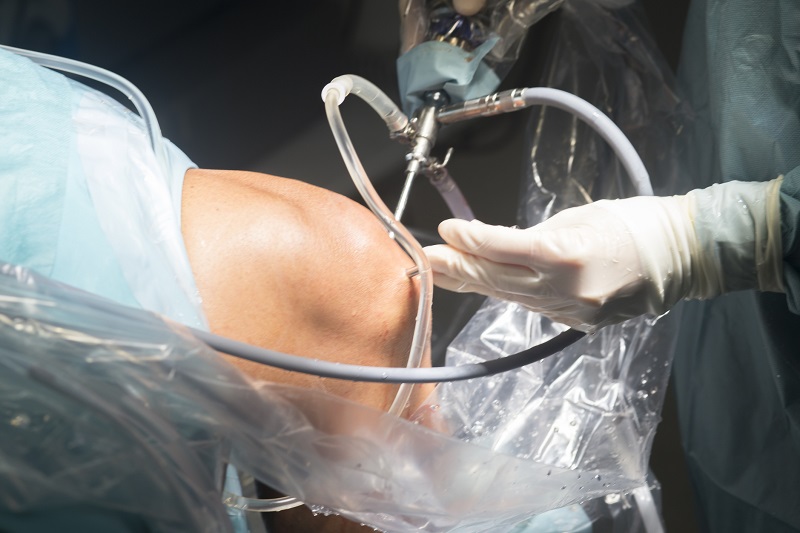
What is the treatment?
Treatment of water in the knee is a long haul. After a professional assessment, a specialist doctor will determine the treatment as required.
- Puncture - A thin needle is inserted into the knee and the doctor pulls out the water. This relieves the pressure and the fluid is sent to a laboratory to determine its contents (presence of bacteria, blood, proteins, etc.). Then the doctor proceeds with the treatment.
- Medication treatment - Painkillers (analgesics), anti-inflammatory drugs (corticosteroids), which can be applied locally (directly into the knee) or in the form of tablets. If the presence of bacteria in the puncture is detected, the doctor prescribes antibiotic treatment.
- Surgical treatment - Most often used for verified damage to the joint structures of the knee after injuries, this is the aforementioned arthroscopy of the knee joint.
The high success rate of treatment is up to us.
Therefore, it is essential:
Rest - Do not load the affected limb, lighten the limb or keep it in an elevated position with a pillow, load it gradually according to the doctor's instructions.
Icing - Cool the affected area with ice or devices specially developed for this purpose (gel packs).
CAUTION:
Never apply ice immediately and directly to the affected area.
It is recommended to cover the ice or aid with a cloth, preferably wrapped in a towel.
Knee brace - Used to stabilize the affected knee joint.
Injury or damage to the knee is not only very painful for all of us, but it also represents a significant limitation to our quality of life. Therefore, prevention and care of our joints is extremely important.
And what does knee care involve?
After knee problems have been alleviated or resolved, follow-up care is important.
Rehabilitation - After treatment, your doctor may recommend follow-up rehabilitation or spa treatment.
But...
Even after the doctor ordered treatment is complete, the following should not be forgotten:
- sufficient relaxation and sparing of the limbs
- the opportunity to see a physiotherapist who will recommend and show you various exercises to strengthen the muscles around the joint, which you can then do at home
- wearing suitable quality or orthopaedic footwear
If...
- play sports, you should prefer sports that put as little stress as possible on the knee joints, such as swimming and cycling.
- you are overweight, it is advisable to reduce your weight.
- some physical activities are demanding for you, avoid them.
- If problems recur, do not hesitate to see a doctor.
Frequently asked:
Can you help yourself at home?
Home treatment should be supportive, but has a role in treatment and prevention.
Herbs that are suitable for treating joint pain and swelling:
- Stinging nettle
- Elderberry
- White willow
- Narrow-leaved lavender
Wraps are often recommended.
You can prepare them at home.
Try:
- Yolk
- 1/2 teaspoon salt
- plastic wrap
- bandage and leucoplast
Procedure:
- Mix egg yolk with salt and rub this mixture on the knee.
- Cover with plastic wrap and secure with a bandage.
- replace the bandage with a new one every 2 hours
Interesting resources










