- mandibularka.sk - World of dentistry
- skzl.sk - Dental caries
- procare.sk - Milk teeth should last in children for years
Sealing teeth in children: does it have its meaning and what is it sealed with?

One of the latest trends in dental care is tooth sealing, which is a procedure that aims to protect the tooth from decay and is therefore intended to serve as a preventive measure. It is particularly preferred in paediatric dentistry.
Article content
Preventing tooth decay should therefore be on the mind of every responsible parent. Do you know what you can do to prevent, or at least minimize, your child's painful experience at the dentist?
One of the options is to seal the teeth. However, it is only done under certain conditions.
How do baby teeth grow and how are they different from adult, permanent teeth?
The baby teeth play an important role. The importance of their care is often underestimated. These teeth hold the space for the permanent teeth and are important for the growth of the jaw. They are also needed for proper speaking or pronunciation.
If the baby teeth are decayed or otherwise damaged, there are consequences for the permanent ones as well.
Milk teeth are particularly prone to decay due to their lack of mineralisation and the prominent pits and fissures on their crowns. Plaque easily forms and bacteria multiply in these areas.

Milk teeth are the first teeth to appear in a child's mouth. An exception is the so-called prelactal teeth, which may already be present at birth. However, this is an isolated phenomenon.
Such teeth are undesirable and should be removed.
Usually around the sixth month, the first milk teeth begin to erupt. This period, which is also called the period of milk teeth, lasts until about the age of three. At this age, the milk teeth should be complete.
At about the age of six, the first permanent teeth, the sixes, erupt. These do not have a milk precursor and erupt in a row behind the milk fives. This is why many parents do not notice them. They usually expect the units to fall out and erupt, but these usually follow the eruption of the adult sixes.
They are often not given as much attention, and this is also the reason for their frequent malformation.
Read also the article.
Approximate teething times
| Milk teeth (20 teeth): | |
| 4-7 months | lower teeth - incisors |
| 8-12 months | upper teeth - incisors |
| 9-16 months | upper and lower deuces - second incisors |
| 12-19 months | upper and lower first molars |
| 16-33 months | upper and lower triplets - eye teeth lower and then upper - second molars |
| permanent teeth (28 teeth): | |
| 6 years | permanent sixes are cut through - first molars the milk units - incisors are replaced by permanent teeth |
| 7-8 years | replacement of lower and upper bicuspids - second incisors |
| 9 years | replacement of lower triplets |
| 10 years | upper and lower fours - molars |
| 11 years | replacement of upper, then lower molars - molars later upper triplets - ocular |
| 12-13 years | eruption of sevens - second molars |
| 17-21 years | Eights - third molars (wisdom teeth), many do not erupt throughout life |
The eruption of milk and permanent teeth is individual for each individual. The figures in the table are only indicative. However, if in doubt, do not hesitate to contact your dentist.
Read more about teeth or tooth care in the article.
What is tooth sealing?
The oral cavity is the first part of the digestive system. Here, food is bitten, chewed or mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that are important for processing food.
The teeth are an important part of the entire digestive system. However, their surface contains various grooves or crevices where food debris can accumulate. This provides an ideal environment for bacteria to multiply. These form acid after the sugars from the food are added.
This corrodes tooth enamel, resulting in tooth decay.
These parts of the tooth surface can be difficult to clean. The crevices, especially in children's teeth, can be so small that the bristles of the toothbrush are too large to clean them. The chewing surfaces of the teeth, which are not yet sufficiently mineralised, are particularly susceptible to decay. These are the so-called sixes and sevens.
Even children who brush their teeth thoroughly can easily develop cavities.
However, it must be done on healthy and undamaged teeth. It is actually a kind of sealing of these gaps and irregularities with something like a sealant. Such a tooth has a smooth surface and cleaning is easier and more effective.
This does not mean that the tooth in question no longer needs to be cared for. It is just about making it easier to clean the unevenness and crevices on the chewing surfaces of the tooth. This is how proper and regular cleaning effectively prevents tooth decay.
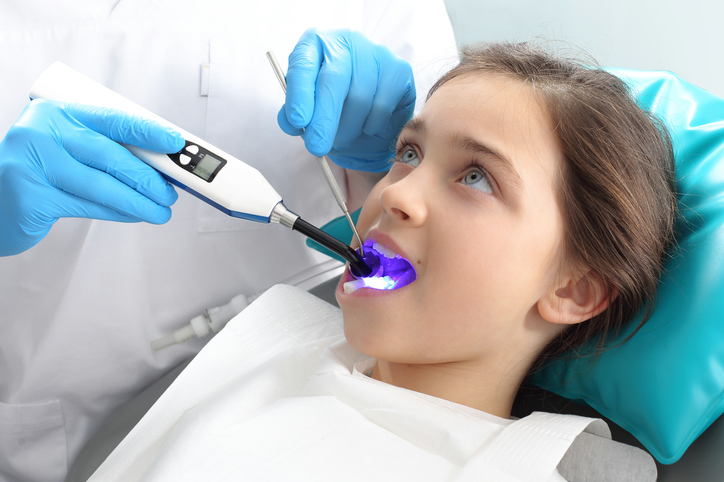
For whom and on which teeth are sealants performed?
Dentists usually recommend sealants for children, as soon as possible after the eruption of the first permanent teeth. There are cases when sealants can also be performed on baby teeth. These are especially children who have high tooth decay.
However, the cooperation of the child is also important.
The procedure is carried out mainly on the molars, on the so-called chewing surfaces. These surfaces are the most in contact with food and the most grooves are found here. The site of the seal can also be the lateral wall of the tooth, where the sockets are located.
These are the most common locations of the lateral surfaces of the lower hexes and the palatal surfaces of the upper hexes.
Most often, only the upper, chewing part of the tooth is sealed. It is thus possible to have a child seal a tooth that is not yet completely all the way out.
It is also possible to seal a filled tooth and an adult tooth. However, it depends on the doctor's assessment. In no case, however, should a tooth be sealed that has decay.
How is the sealing, "filling" and with what are the teeth sealed?
Only a healthy tooth without decay can be sealed.
This is why the first step is always a check-up. This can also be done with the help of X-rays of the bite (bitewing) or with a laser examination using a device called a diagnodent.
The tooth needs to be thoroughly cleaned. Doctors use an airflow rotary brush (sandblasting) or what is known as airpolishing, which in simple terms is a cleaning or polishing process using water, air and a special powder. The tooth is then sterilised with ozone. This destroys the micro-organisms present on the tooth.
A small amount of phosphoric acid is applied to the surface.
+
This ensures that the bonding compound adheres to the surface of the tooth.
+
Using a fine brush or small syringe, the sealant itself is applied.
+
A probe is used to check that no unwanted bubbles have formed under the sealant.
Finally, the area is irradiated with UV light, which causes the sealant to harden and become fluoridated. The procedure takes about 5 minutes and after the procedure, you can eat and drink almost immediately.

What is tooth fluoridation?
Fluoridation is actually another alternative to prevent tooth decay. It can be done alone, but is also preferred when teeth are sealed. It involves the application of fluoride, which increases the teeth's resistance to the acids that bacteria in plaque create.
Fluoridation can be systemic or topical. Systemic fluoridation is done by adding fluoride to the diet such as milk, water or by taking fluoride tablets.
Topical fluoridation is more commonly used. In this method, fluoride-containing substances are applied topically to the teeth.
What sealants are used?
There are different sealants. There are white or translucent ones, but also in different shades. So there is a wide range to choose from. So they can be adapted to the colour of the teeth. For children, white ones are used more often, for easier control.
For adults, shades as close as possible to the colour of their teeth are preferred for aesthetics.
Resin-based sealants are among the more aesthetically pleasing and permanent ones. However, they are only used on well-cooperative patients, as working with this sealant requires as dry an environment as possible.
Less demanding of a dry oral environment are sealants based on glass ionomer cements. These are used especially in children because of their low maintenance. However, they are less aesthetic.
Inspection of the sealed tooth
Teeth treated with sealants should be checked twice a year. Routine preventive check-ups should be carried out just as often.
The integrity of the sealants, which are contrasting, can easily be checked with the naked eye. Even so, an inspection by a dentist is of course necessary. Translucent sealants are inspected with a probe. If necessary, the sealant can be refilled or completely removed and replaced with a new one.
How long do dental sealants last?
Generally, a tooth seal will last for about three to five years. This depends on many factors. These are mainly external influences such as food consumption or adherence to oral hygiene. It also depends on the position of the teeth in the tooth order.
The fact that children's teeth are developing until around the age of 12 or 13 also has an impact on the durability of sealed teeth.
Disadvantages and risks of sealing
Many parents rely on the fact that children are not at risk of developing any decay after having their teeth sealed. It happens that they neglect oral hygiene or good eating habits. However, the tooth is only sealed on certain, most often biting parts. Thus, the whole tooth or other teeth are not protected in any case.
It is still important for the child to brush his or her teeth regularly and thoroughly. Of course, it is also important to minimise the consumption of sugary foods or drinks. These create an acidic environment in the oral cavity which, together with plaque, is ideal for bacteria and the development of tooth decay.
It is also important to use an interdental toothbrush or floss.
Interesting information can also be found in the article How to choose a toothbrush
Another risk that can occur is if tooth decay is overlooked before sealing. This can increase unnoticeably under the sealant.
Ukážka pečatenia zubov
Interesting resources
Related










