- solen.cz - What to expect from lymphatic drainage, MUDr. Jana Štrinclová
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov- Systematic Review of Efficacy for Manual Lymphatic Drainage Techniques, J Man Manip Ther
- theses.cz- Therapeutic significance of manual lymphatic drainage in lymphedema of the extremities. Eva Votrubová, Mgr. Petra Placatková
Lymphatic drainage: how to support the lymphatic system? What is it for?
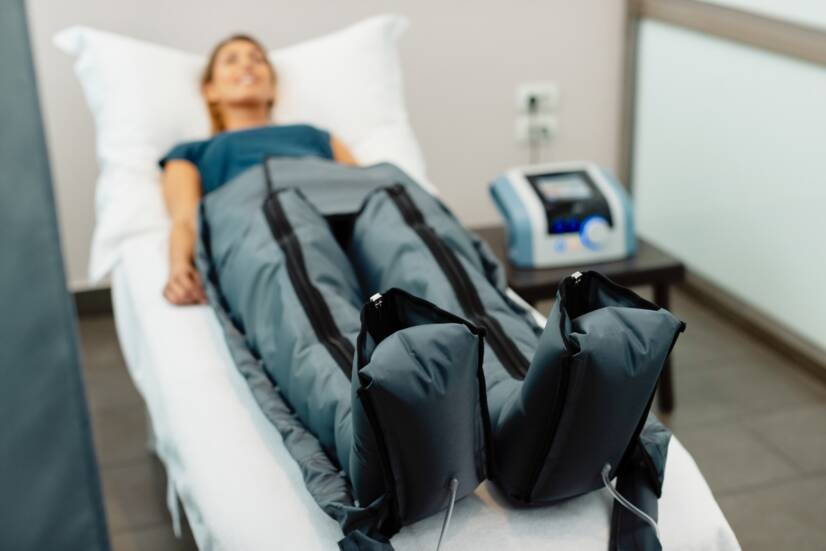
Lymphatic drainage is a specific technique primarily focused on healing the lymphatic system. It helps to reduce swelling, remove waste, stimulate metabolism and has a positive effect on the vascular system. What is important to know about the lymphatic system and lymphatic drainage?
Article content
The human lymphatic system
The human lymphatic system plays an important role as a defensive shield. From birth, it builds and improves the defenses and resistance of the immune system.
Throughout life, antibodies against dangerous and harmful substances are formed in the lymphatic organs. In the past, the lymphatic system was called "white blood vessels".
The lymphatic system consists of:
- lymph
- Lymph nodes
- Lymphatic vessels
- Lymphatic organs
Lymph
Lymph is a colourless clear fluid that is formed from tissue fluid and by filtering blood plasma. Proteins, fat-soluble vitamins, steroid hormones and some types of metals are filtered into it.
The main function of lymph is the collection, transport and removal of waste substances. An important function is its filtration and purification in the lymph nodes.
The movement of lymph is provided by the movements of the smooth muscle of the blood vessels, contractions of the surrounding muscles, respiratory movements, peristalsis of the blood vessels and suction pressure of the right atrium.
Every day, 2 litres of lymphatic fluid are exchanged in the human circulation.
Lymph nodes
The lymph nodes are specifically located in the lymph gland. They are mainly located at the points where lymph flows from a particular part of the body. The lymph nodes are entered by the supply lymph vessels and the lymph vessels exit from the lymph nodes.
The main function of the lymph nodes is to filter and purify the lymph. They are called biological filters. They filter out bacteria, viruses, fungi and other harmful waste substances. The lymph passing through the lymph nodes is thus purified.
Lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic capillaries join together to form blood vessels. They contain specific valves that prevent the backflow of lymph in the body. Their function is to mediate the flow of lymph to the lymph nodes and organs. They are distributed almost all over the human body and resemble a riverbed.
Lymphatic organs
Lymphatic organs are divided into primary and secondary organs according to their function. The primary organ is the red bone marrow and the thymus.
The red bone marrow is responsible for the production of T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, whose function is to defend the body (immune cells).
The thymus plays a role especially from birth to the end of puberty. Lymphocytes mature and differentiate into specific T-lymphocytes. It helps to recognize harmful and foreign substances. After puberty, it changes into a specific connective tissue structure.
The secondary organ is the spleen and lymph nodes.
The basic functions of the spleen include filtration and purification of the blood. It loses old erythrocytes (red blood cells). Another function is the production of white blood cells. It produces lymphocytes, which are specified into different types.
Functions of the lymphatic system:
- Production of lymphocytes (immune cells)
- Increasing the body's defenses
- Recognition of harmful substances
- Filtration of harmful and waste substances
- Filtration and purification of the blood
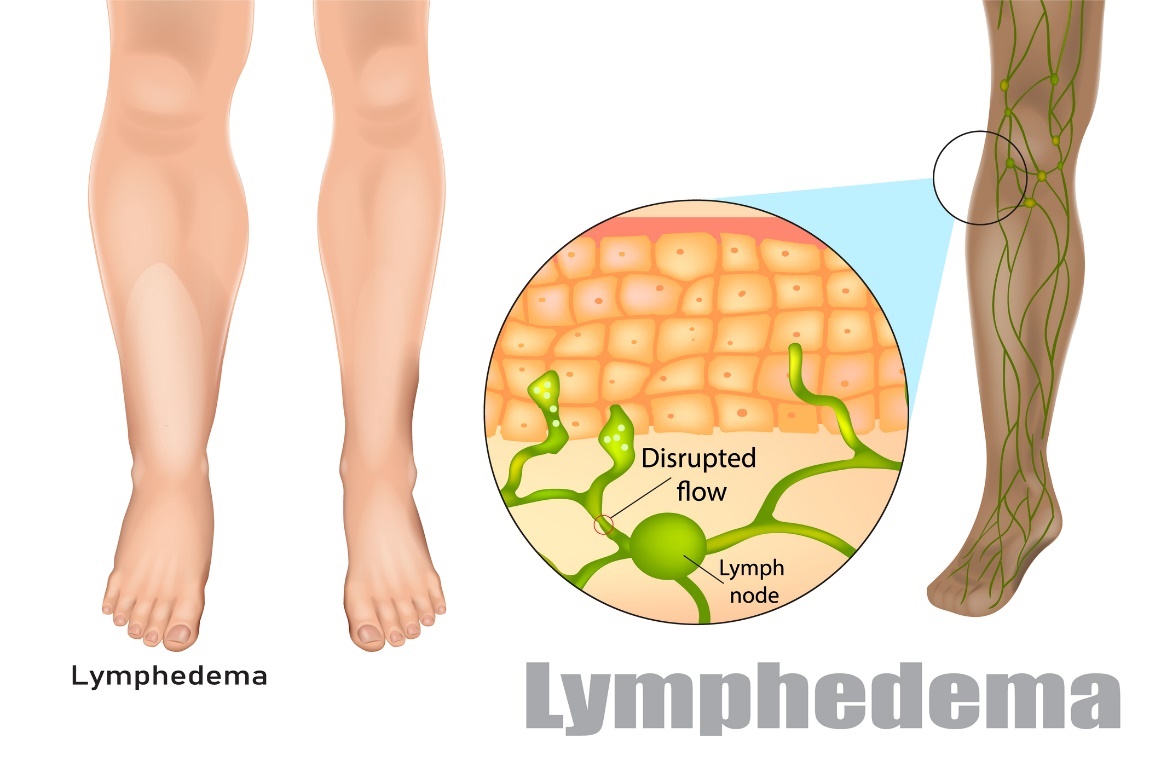
Lymphedema
Lymphoedema or lymphoedema occurs when metabolic products are not adequately drained by the lymphatic system.
It is a pathological phenomenon caused by insufficiency of the lymphatic system. Lymph accumulates and is not drained sufficiently.
Swelling can occur in any segment of the body. However, most often it affects the upper and lower extremities.
As a result of excessive accumulation of proteins or lymph, an inflammatory process occurs in the body. Collagen fibers proliferate. This leads to fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, thereby reducing the mobility of the concavity.
The most common symptoms of lymphoedema include visible swelling, a heavy feeling in the legs, pressure under the skin, numbness in the affected area and difficulty bending the limbs at the joints.
Lymphoedema is divided into primary and secondary lymphoedema according to the etiology.
Primary lymphoedema arises as a result of congenital disease (aplasia, hypoplasia of blood vessels, etc.). Initially, it manifests itself in the lower limbs and spreads towards the heart.
It can also occur during pregnancy, infection or trauma, when the lymphatic system cannot cope with the increased pressure.
Secondary lymphoedema can arise as a result of damage to the lymphatic system. It occurs at any age. The causes of damage are mainly injuries, tumours, operations, obesity, inflammation, immobilisation of the limbs and others.
As part of the diagnosis and therapy of lymphatic problems, a consultation with a doctor is necessary to determine the cause and choose the treatment.
A detailed history, examination by aspiration and palpation, and the results of vascular and cardiac examination and lymphoscintigraphy are appropriate.
The aim of treatment is to improve the patient's quality of life, relieve pain, reduce swelling, promote activation of the lymphatic system and prevent possible complications.
Lymphatic drainage
Lymphatic drainage is a special treatment technique aimed at supporting the lymphatic and vascular systems.
It is a specific massage of the soft structures of the body that increases the transport and outflow of lymph.
In the past, this method was mainly used for immune disorders and for the treatment of enlarged lymph nodes. It was an evolution of a method consisting of rhythmic gentle movements to stimulate the outflow of lymph.
Effects of lymphatic drainage:
- Promoting metabolism
- Increases blood circulation
- Promotes drainage of waste substances
- Increases immunity
- Increases tissue regeneration
Indications for lymphatic drainage
- Thrombophlebitis
- Varicose veins in the lower body
- Different types of swelling
- Non-inflammatory skin diseases
- Circulatory disorders
- Cellulitis
- Headaches and migraine
- Obesity
- Weight reduction (weight loss)
- Joint disease - arthritis
- Constipation
- Gynaecological problems (painful menstruation, sterility)
- Weakening of the immune system
- Arthritis (gout)
- Scars after surgery
- Post-traumatic conditions
- Post-operative conditions in orthopaedics
- Regeneration of the body
- Helps the body regenerate faster
Contraindications to lymphatic drainage
- Oncological diseases
- Inflammatory skin diseases
- Serious heart diseases
- Lung diseases (asthma, bronchitis)
- Liver, heart, kidney diseases
- High blood pressure
- Presence of infection and inflammation in the body
- Metabolic disorders
- Increased activity of the thyroid gland
- Neurological diseases (stroke, epilepsy)
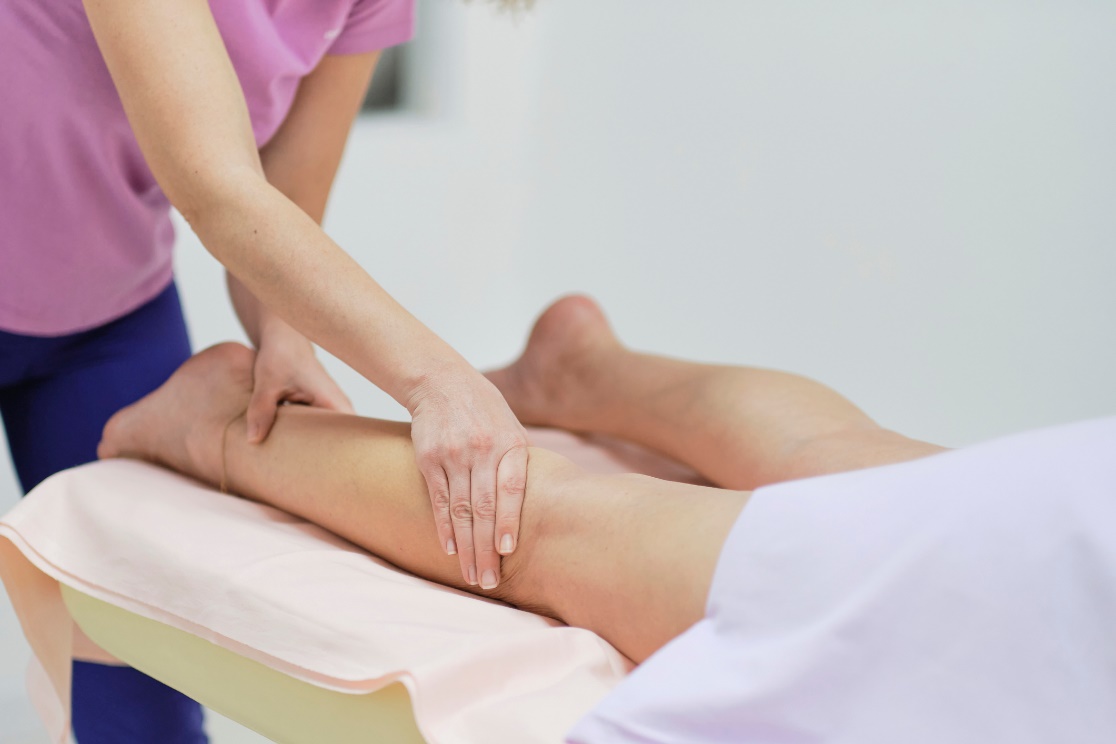
Manual lymphatic drainage
Manual (hand-held) lymphatic drainage is a manual technique consisting of special strokes of a specific pressure and direction that result in the flow of lymph.
The individual strokes use the anatomical distribution of the lymph nodes of the lymphatic system. The pressure of the massaging fingers should not exceed 40 mmHg. The patient perceives this technique as a gentle painless massage.
It is advisable not to get up too abruptly after the massage to prevent the patient from becoming dizzy. A slight headache is possible, which will subside after a while.
A severe, persistent headache after the treatment may be a signal of improperly performed lymphatic drainage, but also a signal of a possible problem in the body. In this case, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
On a given day, it is necessary to observe a resting regime and ensure a sufficient supply of clean water.
Lymphatic drainage has an energy-cleansing effect and rids the body of harmful substances and excess water. Some people may feel tired after the massage and others full of energy. The effect of the therapy is individual.
For the application of manual lymphatic drainage, an extensive therapeutic course and subsequent practice in the field is required. This technique is one of the most sought-after massages for women due to its anti-cellulite effects.
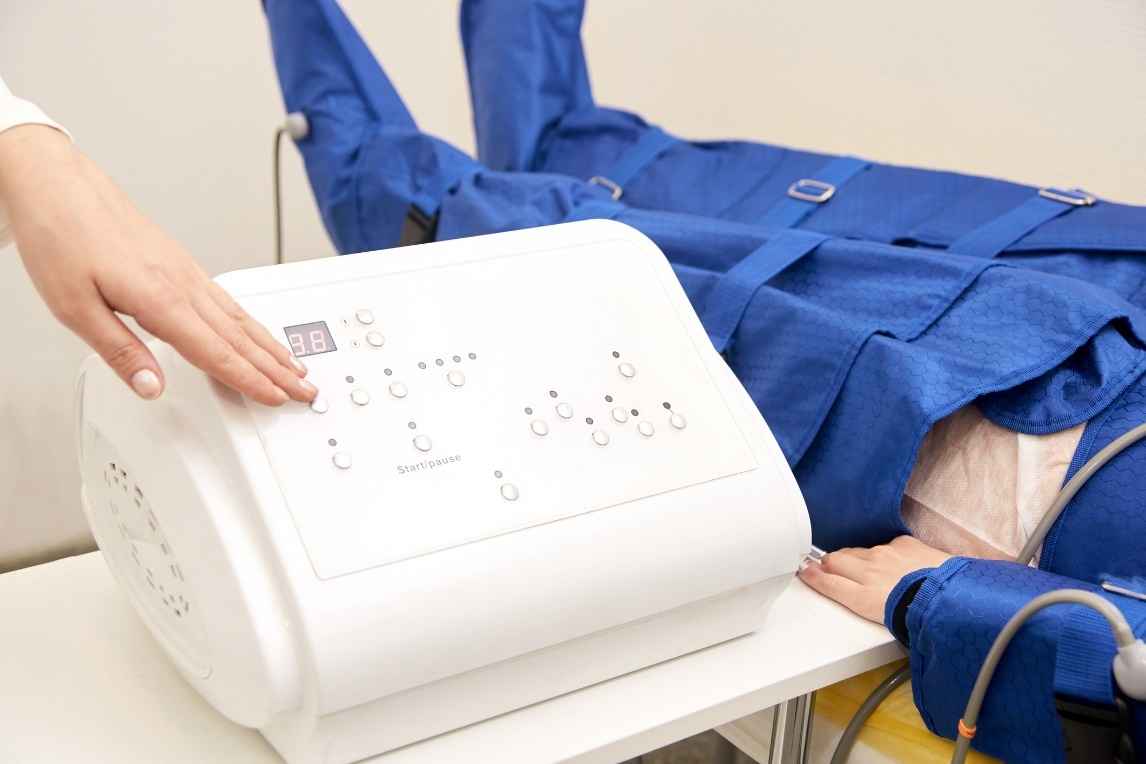
Instrumental lymphatic drainage
Instrumental lymphatic drainage is also known as Pressure Therapy.
It is also known as lymphatic pants.
It is a medical treatment that mimics manual lymphatic drainage by massaging in a special inflatable sleeve. The sleeves contain several air chambers that inflate and deflate in relation to each other.
This creates air (pressure) waves. Most commonly, pressures in the range of 20-40 mmHg are used. During the therapy, the patient's lymph transport and outflow is stimulated.
Lymphatic pants for the lower limbs and sleeves for the upper limbs are most commonly used.
Instrumental lymphatic drainage is also suitable for the prevention of venous inflammation, speeds up recovery after physical exertion, is used in rehabilitation after injuries and operations, improves blood flow to the tissues, helps to eliminate tension in the limbs and feelings of fatigue.
The advantage is the precise adjustment of the pressure and the program that suits the patient. The disadvantage is the impossibility of local targeting of the more problematic part of the body.
Instrumental lymphatic drainage takes 20 to 45 minutes. Approximately 10 repetitions are recommended.
5 tips to know a good lymphatic drainage:
- The therapist will get to know your health condition
- The first step is to relax the lymph nodes
- No oil or emulsion is used
- Lymphatic drainage does not hurt or cause discomfort
- Instructions for the follow-up regime after the treatment
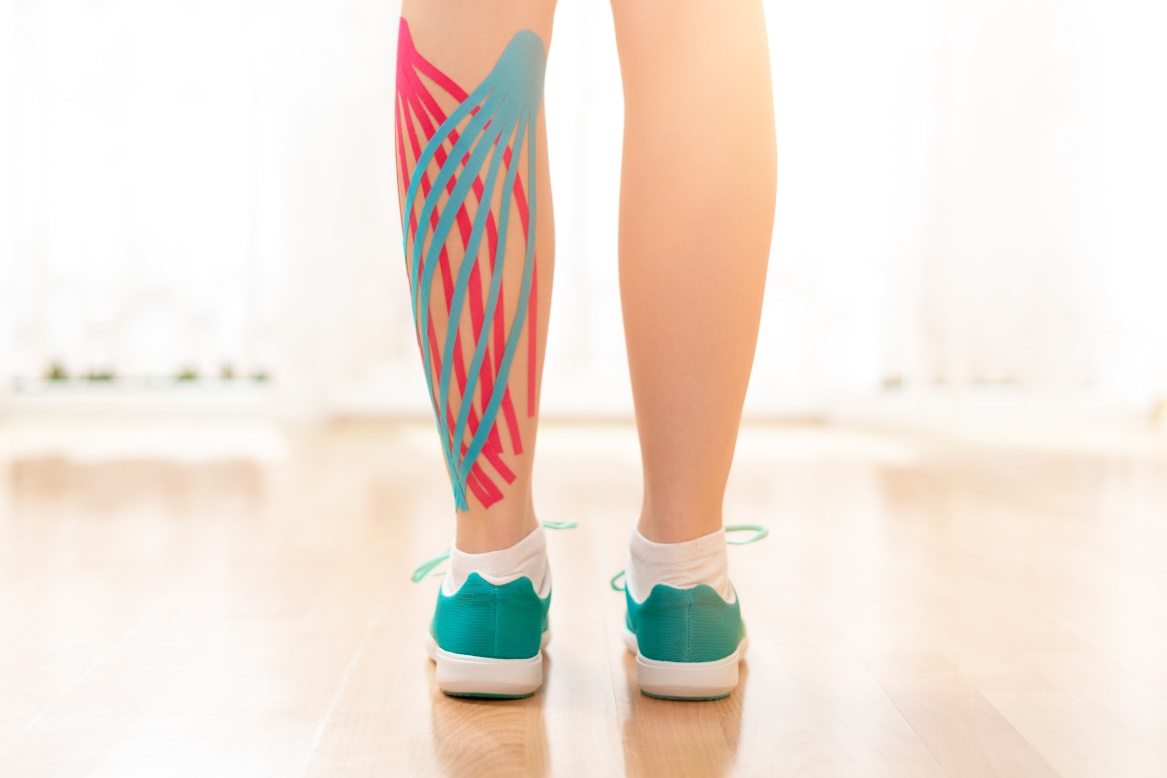
Lymphatic kinesiotaping
Kinesiotaping is a therapeutic method using the healing effect of special strips applied to the patient's skin. The effect is based on the action on the soft structures of the body based on the tension and direction of the kinesiotape.
Lymphatic kinesiotaping is a type of taping that has a beneficial effect on the lymphatic and vascular system. Lymphatic vessels open up and the flow of lymph is facilitated by lymphatic taping. The placement of the tape resembles the shape of the riverbed.
This technique is used locally on problematic swollen areas of the body, especially after injuries and surgery or in the treatment of scars and varicose veins.
Lymphatic taping is often combined with complex lymphatic drainage techniques such as manual or instrumental lymphatic drainage or movement vascular therapy.

Compression bandages
Compression bandages are the most affordable and indispensable part of lymphatic and vascular therapy. External compression creates a barrier to the spread of swelling while promoting lymphatic drainage.
With a properly selected bandage, metabolism and flushing of inflammation mediators is improved.
This is a type of treatment using elastic bandages, compression stockings or instrumented compression that compensates for insufficient muscle pump, reduces congestion of superficial veins and accelerates venous flow.
Compression bandages are mainly used in the short term after surgery.
For long-term preventive wear, special compression underwear is used which can be worn under normal clothing - compression stockings, stockings, stockings, upper limb sleeves, etc.
Vascular kinesiotherapy
The basis of support for the vascular and lymphatic system is movement therapy. The method used is vascular gymnastics, which consists of simple repetitive exercises. Repeated muscle contractions and relaxations are performed.
The aim is to stimulate the muscle pumps and the flow of blood and lymph from the concretions. Vascular gymnastics is combined with conscious breathing and breathing movements.
Hydrokinesiotherapy is also used - active exercise in a water environment using hydrostatic pressure and buoyancy of water to act as a bandage.
Exercising in water results in better toning of the vascular system, reducing the effects of gravity and increasing the work of the muscles against the resistance of the water, which promotes the return of blood from the peripheral areas of the body to the heart.
Care should be taken to perform the exercises slowly and without swaying. Movement in the water gives the patient a pleasant feeling of relief and freedom, both physically and mentally.
Home tips for expanding the lymphatic system
The first type is regular walking, which activates the entire musculoskeletal system and stimulates the lymph nodes in the knee and elbow sockets.
Running is recommended only in good quality soft shoes and on a soft running surface. Hard impacts can adversely affect the vascular system.
Regular exercise is essential to maintain the lymphatic system.
Slower stretching exercises with a greater number of repetitions or contractions and relaxation are suitable to get the lymph flowing. Positions where the lower limbs are higher than the rest of the body are also suitable.
The home method of dry skin brushing is a pleasant self-massage method that expands the lymph while removing dead skin cells.
However, for a positive effect on the lymphatic system, it is necessary to know the principles, appropriate movements and direction of dry brushing (the basis is gentle pressure from the periphery to the centre of the body).
Alternating hot and cold water in the shower is also a home method. The action of hot water dilates the blood vessels and the action of cold water constricts them.
This strengthens the smooth muscles of the vascular wall and stimulates the flow of lymph. This method is not recommended for cardiovascular diseases.
Maderotherapy is a currently used manual method originating in Colombia. It is a modern massage technique using natural wooden rollers that relax mainly the muscles and other soft structures of the body.
By moving the rollers towards the centre of the body, the flow of the lymphatic and venous systems is stimulated. To apply maderotherapy to patients, it is necessary to undergo a professional massage course.
Interesting resources










