- medicalnewstoday.com - What to know about laser eye surgery. Medical News Today. Grace Zhang, MD
- is.muni.com - Risks and complications of refractive laser eye surgery. Bachelor thesis. Anežka Zemánková. Masaryk University - Faculty of Medicine
- healthline.com - Laser eye surgery. Healthline. Rachael Zimlich, RN, BSN
- ROZSÍVAL, Pavel. Ophthalmology. Second, revised edition. Prague: Oční lékařství: Galén, [2017]. ISBN 978-80-7492-316-6.
Laser eye surgery: how is it done, what are the methods and recovery? + Benefits and risks

Laser eye surgery has become a popular method of diopter correction in recent years. By applying a laser to the cornea of the eye, various eye defects can be corrected. How does the whole process of the procedure work, from pre-operative examination to recovery?
Article content
- How does laser correction work?
- Laser surgery methods
- What eye defects can be treated with laser?
- Who is/is not suitable for the procedure? Indications and contraindications
- The entire course of laser surgery
- Possible postoperative complications and risks
- Success rate of laser surgery
- Cost of laser surgery
The laser beam acts on the corneal tissue of the eye, changing the curvature and shaping of the cornea. Modern eye clinics now offer various methods of laser surgery.
They correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism and other eye defects.
The course of surgery, methods, indications and contraindications, benefits, risks, price and other interesting information can be found in the article.
How does laser correction work?
The basis of eye surgery is a laser current acting on the patient's cornea, which changes the corneal tissue on the principle of vaporization - evaporation.
This breaks the connection between the individual molecules of the corneal tissue. This results in a certain change in the curvature of the cornea. During evaporation, the solid state changes to a gaseous state. It is through this process that the cornea changes its shape and curvature.
This changes the refraction of light on the cornea and the light then hits the retina in the area of sharpest vision.
Laser surgery methods
Based on the type of action on the cornea, laser refractive surgery can be divided into the following:
- Superficial procedures
- Subsurface procedures
Superficial method
Two basic principles are used for laser removal of ocular diopters.
The first older type is called PRK or LASEK. It uses a surface action of the laser. The laser stream acts on the surface of the cornea and vaporizes all the tissues including nerve fibers and endings.
Superficial procedures have a longer recovery time. In the early postoperative period, healing is associated with pain, cutting and burning of the eyes. Significant photophobia is also present.
The method is suitable for lower dioptric defects and especially for patients whose corneas are thin or flat.
Subsurface (deep) method
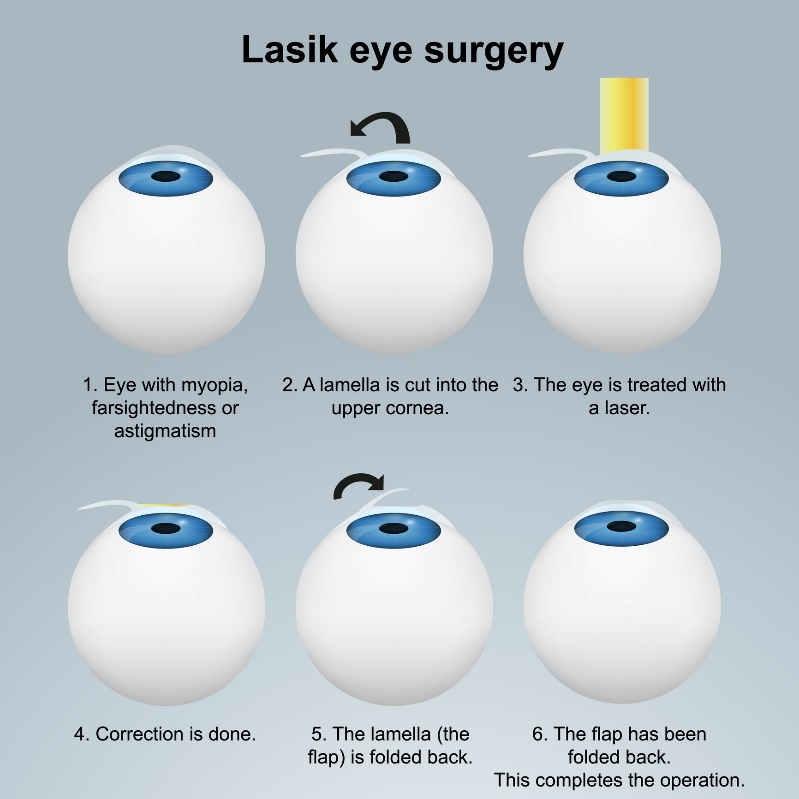
The second type of procedure is called sub-surface(LASIK, FemtoLASIK, Relex Smile...). These procedures are divided into the so-called incisionless method and the incision method.
A common variant of this method is the femtosecond laser. When applied to the eye, the laser creates a thin layer of tissue (flap) in which the nerve endings are located.
The surgeon "lifts" this flap during surgery and performs a laser procedure to curve the cornea. The flap is then returned to its original position.
Since the nerve fibres and endings have not been damaged by the laser, recovery from the procedure is significantly less painful and easier.
These methods are suitable for all patients whose eye defect is stable and have sufficient corneal thickness.
What eye defects can be treated with laser?
Myopia (nearsightedness) - This is impaired distance vision.
The shape of the eye is elongated and the image of vision is already formed in front of the retina. However, a healthy eye forms the image directly on the retina. In most cases, myopia arises in childhood.
Hyperopia (hypermetropia) - This is impaired near vision.
The shape of the eye is shorter and the image of vision is formed behind the retina. In most cases it develops around the age of 40, but it also occurs in childhood.
Astigmatism - Irregular curvature of the cornea and optical surfaces of the eye. It impairs vision at distance and near.
Cataracts - Although not a dioptric defect, through the aging process the lens loses its transparency and transmits less light to the retina. This reduces the quality of vision. Laser surgery is the most advanced method of cataract removal.
Keratoconus - This is a degenerative disease of the eye's cornea in which the cornea slowly and gradually becomes thinner. The manifestation of keratoconus is mainly myopia and irregular astigmatism.
Who is/is not suitable for the procedure? Indications and contraindications
Prior to the actual procedure, the patient undergoes a pre-operative consultation and examination to assess the suitability of laser surgery. Although the procedure may be indicated for most people, there are some exceptions.
Patients must be over the age of 18 to undergo laser refractive surgery. The procedure is waited until full adulthood precisely because of the development of the body and the stabilization of the eye defect itself.
The procedure is not performed on pregnant women.
The patient should not be treated for diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, connective tissue disease, epilepsy, and certain metabolic and immune diseases that impair the healing and recovery process.
The key information for the physician assessing the appropriateness of the procedure is the thickness of the patient's cornea.
Contraindications to the laser procedure may include local skin disease, acute and chronic conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, ocular infections or anatomical abnormalities of the face.
The entire course of laser surgery
1. Preoperative examination
The pre-operative examination is aimed at a complete health check of your eyes (scan, measurement of vision, intraocular pressure, corneal thickness, corneal curvature...).
All examinations are painless for the patient.
In most cases, the pre-operative examination takes place during the initial consultation at the clinic. The patient learns what kind of laser method is suitable for him/her.
During the examination, an appointment for the procedure is arranged. Before the surgery, it is necessary to not wear contact lenses for 2 to 4 weeks and to wear only dioptric glasses.
2. Surgery
Laser eye surgery is performed on an outpatient basis within one day.
Hospitalization is not necessary.
The procedure is performed under local anaesthesia in the form of numbing eye drops. The procedure is painless and the patient does not feel anything thanks to the numbing drops.
In the case of commonly performed laser methods, the procedure in the operating theatre takes a short time, approximately 15 to 20 minutes.
Of these, only a few seconds are spent "shining" the laser into the eye.
During the laser treatment, the patient looks directly into the light - at one specific point.
During the procedure, the eyelid is fixed, the eye is numbed and the laser cameras account for slight movements of the eye. If there is more movement, the laser stops shining, so the patient does not have to worry about any mistakes.
At the end of the procedure, the doctor will place a temporary protective contact lens on the eye for a few days. The patient will receive post-operative drops to promote healing and hydration of the eye.
Approximately 2-3 hours after anesthesia, mild soreness may occur along with a cutting, burning sensation and slight dizziness. These symptoms will subside within 2-3 days.
3. Postoperative treatment and recovery
The patient will wait briefly in the room with eyes closed after the procedure. If all is well, he/she will go home. A ride home by another responsible person should be arranged. The patient cannot drive a car shortly after surgery and it is advisable to keep eyes closed.
The protective lenses remain in the eye for approximately 5 days, after which they are removed at the first follow-up examination.
Subsequent follow-up examinations are usually after 10 (14) days, one month, three months and then after six months. However, this is individual depending on the clinic, the doctor and the patient's condition.
Postoperative drops should be applied for 1 to 3 months depending on the method chosen.
Eyes must be protected from UV sunlight, so wear dark glasses with UV filter when outdoors.
It is not recommended to use eye makeup for at least 2 weeks after surgery and it is a good idea to avoid rubbing your eyes. You should also avoid dusty dirty environments, spas, tanning beds and swimming pools after the procedure.
With superficial methods, sharp vision is corrected in about a month and with deep methods, sharp vision is present shortly after surgery.
However, detailed vision can be corrected up to one year after surgery.
Possible postoperative complications and risks
As with other procedures and surgeries, there are possible post-operative risks with laser refractive surgery. However, the laser method of vision correction is modern, relatively safe and effective.
The most common postoperative complications include:
- Dry eye and insufficient tear production - dry eye syndrome
- Fluctuations in visual acuity
- Reduced visual acuity in the dark
- Poor/long healing of corneal tissue
- Inflammation and infection
- The procedure does not guarantee a lifetime without glasses. A certain degree of dioptres may return with time and age.
Success rate of laser surgery
The success rate of laser eye surgery worldwide is considerable. Doctors consider it a failure if, several months after the procedure, the patient finds that his or her vision is not as sharp as it was shortly after the operation. There are no reported cases of vision loss.
The human body has the ability to correct itself to a certain extent. In some cases, the thinned cornea may "grow back" a little. If this happens, it causes a change of about a quarter or half a dioptre.
The results of the studies may vary because they deal with different laser methods and eye defects. However, in about 50-60% of patients, the quarter to half diopter will return within 3 years after surgery.
Cost of laser surgery
The disadvantage of laser surgery is often its high cost.
Dioptric correction is not considered a necessary procedure and is therefore not covered by insurance. Surgery on one eye costs approximately 400 to 1000 euros - the exact price depends on the specific clinic and the laser method chosen.
In addition to the procedure itself, the total price includes consultation, pre-operative examination, post-operative check-ups as well as eye drops and other equipment.
For some laser methods, clinics offer customers a so-called free lifetime dioptric correction. However, it also depends on the individual thickness of the patient's cornea.
Interesting resources
Related










