- uvzsr.sk - 10 things you should know about flu
- who.int - How can I avoid getting the flu?
- cdc.gov - Flu & Young Children
- hopkinsmedicine.org - Influenza (Flu) in Children
Influenza in children: how to prevent it, what is its course and how is it treated?
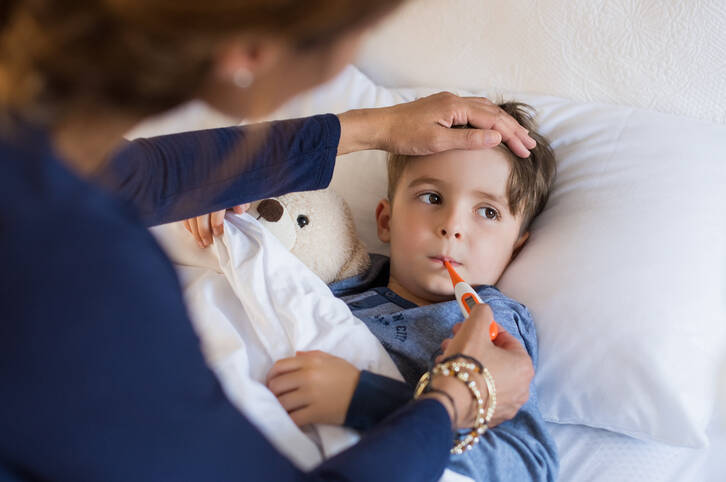

Children have started going to nurseries, schools. The weather has turned colder, the cold season is coming. Among the annual seasonal illnesses is the flu.
Article content
Theflu is a fast-onset illness. It can be mistaken for a cold, but it should not be underestimated.
It can be complicated by other more serious illnesses. For this reason too, your child should be properly treated. There is still time to prevent and prepare before flu season.
Flu in a nutshell
Influenza is a virus-caused disease caused by RNA viruses of types A, B and C. However, type A is the most common type and the one with the best ability to mutate.
Its incubation period is 18-72 hours.
It is highly contagious, infectious.
Transmission is by droplet infection. It is spread by talking, sneezing, coughing, but also by contact such as shaking hands. People at risk are more at risk of complications.
The risk group includes young children with no previous immune experience, preschoolers and children with chronic diseases.
The main flu season peaks in January to February.
Influenza in childhood
As in adulthood, influenza in childhood also has typical symptoms that it manifests. In addition to respiratory tract infection, it also causes systemic symptoms and thus puts even more strain on the body.
The most common symptoms of influenza are:
- Increase in body temperature to fever (38-40 °C)
- chills, shivering
- sweating
- general weakness, fatigue, malaise
- headache
- pain in joints, muscles, limbs
- colds
- sore throat
- cough, irritating, dry, choking
- chest pain, especially when coughing
- eye irritation, painful eye movements
- nausea, vomiting and other intestinal forms (including diarrhoea)
- lack of appetite
It is important to keep children from the collective at home, consult a doctor.
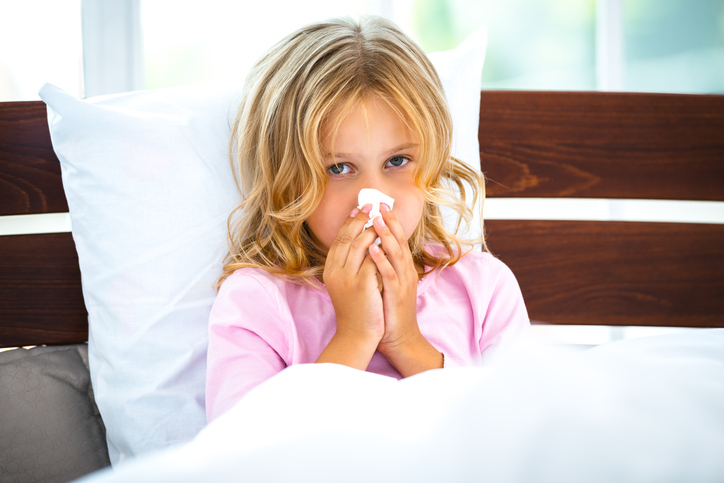

If other problems besides fever are present, a visit to the paediatrician (children's doctor) is essential. Children should be checked more frequently. Children with chronic diseases require special attention.
Repeated body temperature measurements are emphasised in children under three years of age as they may develop febrile convulsions. These are convulsions of the body caused by fever.
Twitching of the eyes, body muscles, limbs, accompanied by unconsciousness are present.
The diaphragm, which is the breathing muscle, may also be affected by convulsions. Then breathing is impaired and the child may turn temporarily blue. First you notice the blueness (cyanosis) on the lips, later on the whole face and fingertips.
In addition to the risk of febrile convulsions, it is important to monitor the body temperature for general exhaustion and the risk of dehydration. It is advisable to keep the body temperature within 38 °C.
Body temperature up to this value is beneficial for the body to fight disease.
But above this value, it is the opposite. It indicates that the organism cannot cope with the fight and needs help.
In young children, measure the temperature in the rectum (buttocks). This is a more accurate measurement than the other methods. Of course, do not forget to take a reading of 0.5 degrees, then you will get the actual body temperature.
Example of how to calculate body temperature:
We measured the child's body temperature in the rectum. The thermometer showed a temperature of 38.5 °C. Then we subtract 0.5 and get a body temperature of 38 °C.
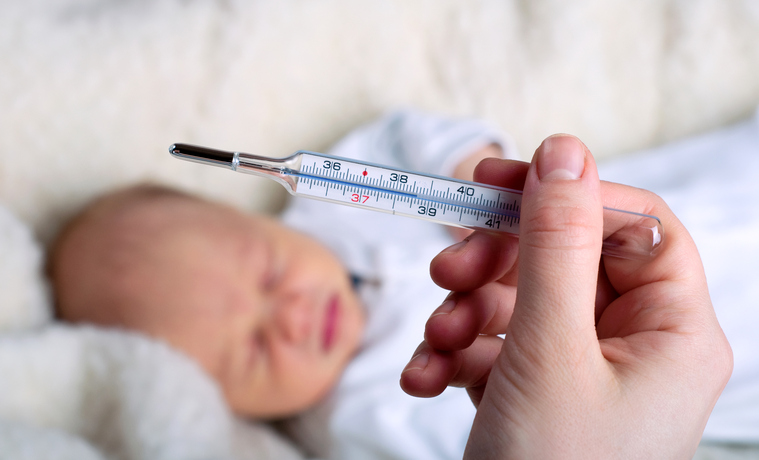
When the body temperature rises, chills are present. It's actually the muscles shivering as the body tries to raise the temperature. When the body temperature is below 38°C, the fight against viruses or bacteria is more effective.
How to manage temperatures?
What should be done when the body temperature is above 38.5 °C?
In this case, you have two options.
One is to try to reduce the temperature from outside the body, by wrapping, bathing or showering. The second option is to administer medication.
The first form of physically lowering the body temperature is all the more preferable because it requires a minimum of aids and is quickly effective.
Body wrap
- the wrap is applied to the torso area, i.e. the chest
- moisten a towel or nappy with lukewarm water (25 °C) and leave on the body for 10-15 minutes
- in the case of high fevers, the towel warms up more quickly (in which case change it)
- they can be repeated several times an hour
- do not cover the child too much, the aim is to lower the temperature, not to maintain it
- the room temperature should be 24 °C
- checking the temperature is a matter of course and a necessity
Bathing or showering
- a bath in a bath or tub
- with water at 29-32 degrees
- may be for 45 minutes in a room at 24 °C
- wash the child with water
- a shower is recommended for larger children
Lowering the temperature with water is not recommended in case of marbling of the skin, bluing (cyanosis) of the lips, fingers, skin rashes.
Drugs for fever
In younger children, they are given rectally (into the anus) in the form of suppositories or as a syrup for the mouth.
In the first case, the onset of action is slightly faster, around 5-10 minutes.
With the second administration, it can be over 15 minutes, depending on the previous meal.
Drugs designed to reduce body temperature are usually a combination of pain-relieving ingredients (paracetamol) or also with an anti-inflammatory effect (ibuprofen).
But!
Strictly follow the package leaflet, dosage and the doctor's or pharmacist's recommendations when administering medication. A possible overdose can seriously endanger and damage the child's health.
It is not recommended to give fever and pain-relieving medicines from the group of medicines that contain acetylsalicylic acid (acylpyrine, anopyrine, aspirin and others) to children.
Why?
When a viral illness is combined with salicylates, there is a risk of a complication. This is rare, but all the more dangerous. It is referred to as Reye's syndrome.
Also for this reason, it is important to consult a doctor, pharmacist about the treatment and read the indications or contraindications of the drugs + the correct dosage.
Other medicines for flu
If your health condition requires it, your doctor or pharmacist can recommend other medicines for the accompanying symptoms of flu. Medicines for a cold, sore throat, vitamins, zinc, probiotics or nutritional supplements to prevent and treat dehydration and nutritional supplements for lack of appetite.
Anti-influenza drugs (antivirals) are only included in the treatment of high-risk patients. Otherwise, symptomatic treatment is chosen. Influenza is not treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics are only effective against bacteria and not viruses.
Antibiotic treatment is only supplemented in the event of a complication, for example, a bacterial superinfection.
Be careful with your drinking regime
In fevers and conditions where the body loses fluid (vomiting, diarrhoea), it is important to ensure that the drinking regime is followed. This should be slightly higher than in health, as the body loses fluid at an increased rate.
It sweats them out, breathes them out.
If vomiting and diarrhoea are associated, there may be a problem in maintaining adequate fluid intake and medical treatment or hospitalisation is necessary. A child's body can become dehydrated very quickly:
- Increased drowsiness, sleepiness of the child
- impaired consciousness
- disorientation
- reduced urination, dark-coloured urine
- dizziness
- distended abdomen
- cyanosis (bluing of lips, fingertips)
- dry mouth
Read also.
Duration of flu treatment
Elevated body temperature readings come on quickly with influenza, but usually subside after 3-4 days.
Other complaints may persist for a week or two. Fatigue may be present for a month.
In children, sufficient convalescence (recovery) is therefore necessary. A total treatment period of two weeks is recommended. During this time, the body is able to heal and regain new energy, recovering from any difficulties.
It is not recommended to start school or kindergarten earlier. There is a risk of another disease breaking out at a time when the organism is still weakened.
During this period it is important that bed rest is maintained. The child should be dressed appropriately and ventilated more often.
Possible complications could manifest as heart, lung, nervous system, brain diseases and also as other diseases. Common complications of influenza include sinusitis and otitis media. Therefore, it is better to follow the recommended duration of treatment.
Prevention of influenza
Prevention of influenza should be the first priority. It is about the health of our children and ultimately our own. Influenza is a highly infectious disease.
Prevention could include a good lifestyle, sport for older children, hardening.
During the influenza epidemic we should avoid places with a higher movement of people, shopping centres. In the pre-influenza period we should supplement our diet with vitamins (especially vitamin C, D), zinc, probiotics and think about vaccination.
Interesting information:
Health effects of vitamin D
Probiotics and their importance for human health

Preventive measures include increased standards of hygiene. Hand washing, appropriate alcohol-based hand wash or other effective hand cleansers.
More frequent washing of surfaces, door handles. Prevent or reduce transmission to others, use disposable paper tissues when coughing, discard after use.
Vaccination
In addition to modern technology, modern times bring modern claims. Information reaches people much more easily and quickly than it once did.
Not all information is true.
Vaccination of any kind has its justification. Therefore, it is not good to neglect it.
Interesting information about vaccinations.
As far as flu vaccination is concerned, a dead flu virus is injected into the body. This then triggers an immune response in the body and the body is ready to defend itself during the flu season. Children from 6 months of age onwards can be vaccinated.
The vaccines are adjusted annually according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Your child and adolescent doctor can give you more information about vaccinations.
Interesting resources
Related










