- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Translational Investigation of the Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD): Toward a New Age; José A. Crippa, Francisco S. Guimarães, Alline C. Campos, Antonio W. Zuardi
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC); Terence Ng; Vikas Gupta
CBD versus THC: Do you know the difference in effects and uses?
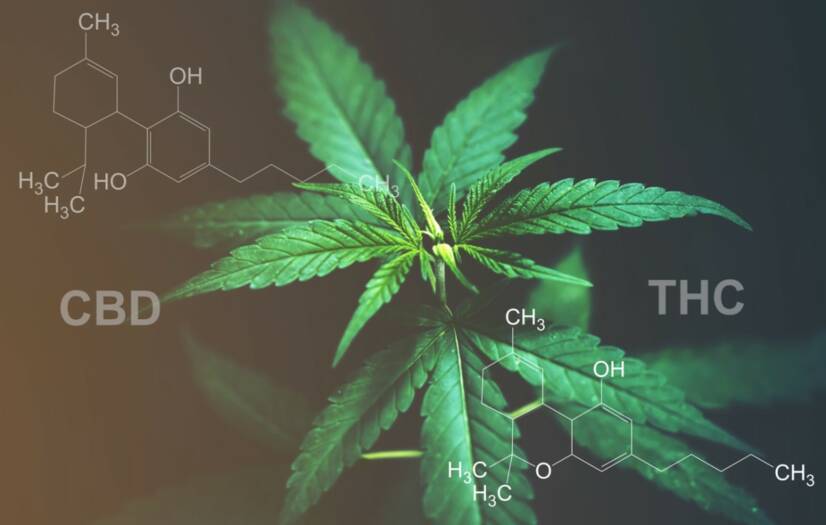

The cannabinoids CBD and THC in Canabis sativa are similar, but have some key differences. Do you know them?
Article content
Although they appear to be almost identical in structure, they differ in spatial arrangement. Therefore, they also differ in their effects.
Studies of interactions between the cannabinoids have shown that CBD blocks and/or enhances the effects of THC in animal tests. The effect depends on the ratio and relationship between the doses of the two cannabinoids.
There is now evidence that the interaction, which leads to a blockade of cytochromes P-450 and thus inhibition of Δ9-THC metabolism, can be overcome by CBD.
This occurs when:
- the CBD/Δ9-THC ratio is high
and/or
- both cannabinoids are administered simultaneously or close together
Several studies have confirmed that acute and chronic administration of CBD by different routes - oral, inhaled, intravenous - to healthy volunteers and patients with different clinical conditions did not produce significant psychological adverse effects.
In humans, there is no conversion of CBD to THC. These results support previous observations from animal studies.
According to them, CBD appears to be a safe compound for use in humans over a wide range of doses.
Interesting information:
CBD - Cannabidiol: What is it, what does it do? Is it safe to use?
Studying interactions between CBD and THC
In healthy people enrolled in the research, high oral doses of THC caused anxiety and psychotic symptoms. These side effects were alleviated when THC was given together with CBD.
These results helped support, for example, the combination of the two cannabinoids in Sativex® (GW-Pharm, UK), a drug used to treat pain and stiffness in multiple sclerosis.
In addition, these observations have contributed to the understanding of the different effects of cannabis in different populations, which is explained by the different concentrations of the constituents of the plant. These findings also suggest that CBD may have anxiolytic and antipsychotic properties. This has prompted a number of studies that continue to this day.
The anxiolytic effect of CBD
CBD has the ability to suppress anxiety, tension, fear, stage fright, and similar conditions.
CBD can prevent the anxiogenic and psychosis-like effects that higher doses of THC induce. This efficacy has been confirmed in both laboratory animals and humans.
Experimental experiments in rats have shown that CBD at lower doses (2.5-10 mg/kg) produces anxiolytic effects in rats. However, at higher doses these effects disappear completely.
Several studies have confirmed that CBD reduces anxiety in rodents after single or repeated administration.
Similar dose-dependent results have recently been confirmed in human clinical trials.
When administered acutely or repeatedly, CBD also has an anti-stress effect.
Antipsychotic effects of CBD
Animal studies suggest that CBD might have antipsychotic effects.
Antipsychotics or neuroleptics are drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders.
Psychoses include:
- Schizophrenia
- Schizotypal disorders
- Mental disorders with delusions
- Acute and transient psychotic disorders
- Schizoaffective disorders
- Hypochondria and other somatogenic disorders
- Other disorders
Its effect is similar to that of the drug haloperidol.
However, unlike this drug, CBD does not induce catalepsy.
Catalepsy is one of the many side effects of antipsychotics. It is a state of muscle rigidity and immobility.
Another side effect is gynaecomastia in men or menstrual cycle disturbances in women. This is usually caused by high prolactin levels. CBD only increases prolactin levels at high doses (more than 120 mg/kg).
Doses of CBD that produce antipsychotic-like effects are usually higher than doses with anxiolytic effects.
Antiparkinsonian, antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of CBD
Findings suggest that CBD may improve the general condition of patients with Parkinson's disease, without associated psychiatric illness.
Studies further suggest that CBD also appears to have antioxidant and neuroprotective properties (protecting brain cell neurons).
Chronic use of cannabis with higher THC and lower CBD concentrations has been associated with a reduction in brain gray matter.
Long-term use + more THC and less CBD = less grey matter...
Hence the reduction in cognitive abilities such as:
- memory
- attention
- thinking
- planning
- organizing
- judgement
- problem-solving ability
- understanding and using language
- express oneself
Conversely, the higher CBD content of cannabis samples consumed has been shown to prevent the neurotoxic effects induced by THC.
CBD also has antioxidant effects. It counteracts the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS, RNS).
This prevents damage to cellular DNA, fatty acids and proteins. Such damage would lead to cell malfunction or death.
Antiepileptic effect of CBD
The antiepileptic effect of CBD was one of the first pharmacological properties to be discovered. It was already confirmed in the 1970s in animals, but also in preliminary clinical studies.
CBD has an effect on seizure control (EPI). It also has protective effects on brain neurons - protecting them from dying.
CBD and sleep disorders
In higher doses, CBD causes a state of sedation - calming. This can be helpful in falling asleep.
A study of the acute effects of 300 mg of CBD on sleep in healthy volunteers showed that this compound does not disrupt the sleep cycle. CBD may therefore be a potentially useful therapy in this case as well.
CBD and THC dependence
There is currently no approved therapy for the treatment of cannabis-related disorders.
Based on findings from animal studies, it appears that CBD could be useful in this case.
Similarly, the lack of an effective treatment for cocaine dependence is a clear indication of the need for further research in this area. In an animal study, CBD was found to protect against cocaine-induced seizures.
Further...
In addition to the above effects, CBD has anti-inflammatory effects. It deactivates enzymes involved in the production of inflammatory substances in our bodies.
It is also used in the treatment of acne. CBD has been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect on the cells in the sebaceous glands of the skin - called sebocytes.
If these cells are over-stimulated or inflamed, excessive sebum production occurs. This can cause inflammation of the skin or acne.
CBD also has high antimicrobial activity against P. acnes bacteria.
Comparison of the effects of CBD and THC in the table below
| Effect | CBD | THC |
| Anxiolytic | v | X |
| Antipsychotic | v | X |
| Antiparkinsonian | v | X |
| Neuroprotective | v | X |
| Influencing the perception of reality | X | v |
| Neurotoxic | X | v |
| Antiepileptic effect | v | v |
| Sedative - calming | v | v |
| Anti-inflammatory | v | X |
| Treatment of acne | v | X |
| Appetite | X | v |
| Pain suppression | v | v |

Nabilone and dronabinol are synthetic THC compounds approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
The most common side effects of THC use that require its discontinuation are:
- Dysphoria - a state of anxiety
- hallucinations
- paranoia
Other common side effects include:
- Sedation - calming down
- confusion
- headache
- dry mouth
- euphoria
- hypotension - lowering of blood pressure
Seizures have also been known to occur in patients using THC.
A syndrome characterised by uncontrollable vomiting is also seen with chronic THC use. The hallmark of this syndrome is relief from hot showers.
Compared to CBD and THC, cannabidiol (CBD) appears to be a more versatile molecule. At the same time, CBD has fewer side effects. However, further research is still needed to clarify the individual diagnoses and doses for which CBD will become a treatment.

Interesting resources










