- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Cannabidiol (CBD); Hannah Meissner; Marco Cascella
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders; María S. García-Gutiérrez, Francisco Navarrete, Ani Gasparyan, Amaya Austrich-Olivares, Francisco Sala, Jorge Manzanares
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Cannabidiol: Science, Marketing, and Legal Perspectives; Jenny L. Wiley, Camille K. Gourdet, and Brian F. Thomas
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Cannabidiol for Pain Treatment: Focus on Pharmacology and Mechanism of Action; Jakub Mlost, Marta Bryk, and Katarzyna Starowicz
- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - What's new in the management of acne vulgaris; Leon H Kircik
- solen.sk - Cannabinoids - characteristics, distribution, mechanism of action; Marián Nečas
CBD - Cannabidiol: What is it and what are its effects? Is it safe to use?

CBD and also cannabidiol: miracle cure or just another modern hit? Oils, drops, and even teas and foods with CBD have all appeared on the market in recent years. But do you know what CBD actually is and what its effects are?
Article content
What is CBD and where does it come from
Cannabis sativa or Cannabis indica or Cannabis hashish. Three names for the same plant.
It is an annual plant that originally comes from Central and Western Asia.
The plant is cultivated for its medicinal properties. It contains more than 400 chemical compounds. Of these, approximately 80 have an effect on our body.
But the most interesting compounds are the cannabinoids. There are about 60 of them.
The most important psychoactive substance is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Others include..:
- Cannabidiol - CBD
- Cannabigerol - CBG
- Cannabinol - CBN
- Cannabichromene - CBC
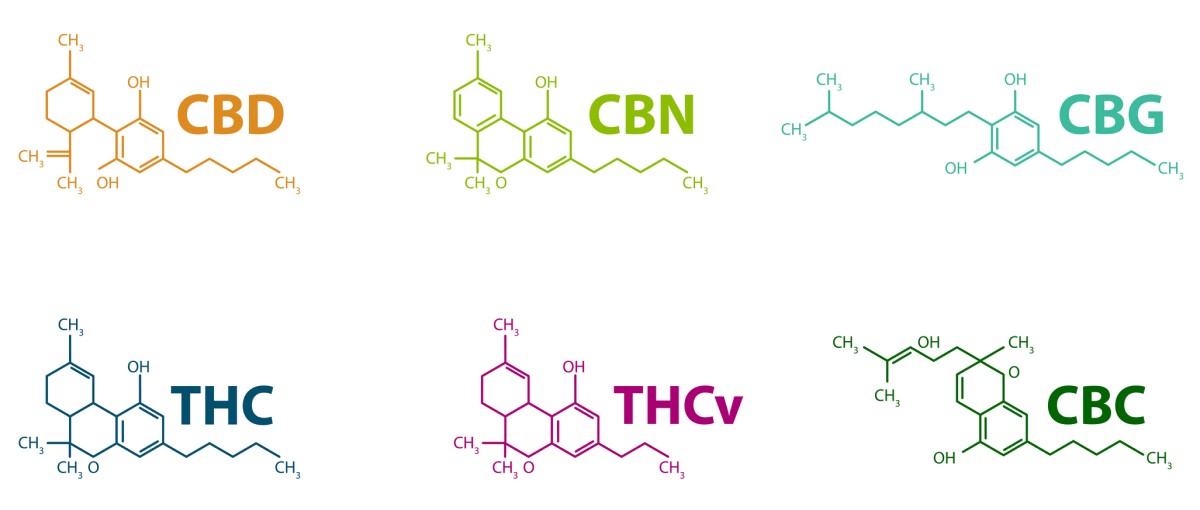
Although increased interest in CBD is relatively recent, it was isolated as early as the 1940s.
CBD can also be extracted from 'industrial hemp' plants. Industrial hemp is used to make rope. Although it is a variant of Cannabis sativa, selective breeding has led to differences between these plants.
The legal cultivation of hemp is judged on the basis of the amount of THC in the dry weight of the plant.
In the USA, a plant may not contain more than 0.3% THC.
The European Union has set the limit slightly lower, at 0.2%.
In the UK too, a grower must be licensed - for 0.2% of hemp.
Otherwise, the limit is set at zero.
But the industry around CBD products is becoming increasingly lucrative. And profits are soaring.
In the U.S., it is estimated that by 2023, profits will be several billion dollars - up from "only" $170 million in 2016. In the U.S., even the food industry has become interested in CBD. So maybe in a few years we'll be buying coffee, wine or even food containing CBD.
Cannabinoid receptors
Cannabinoids are not only found in plants. They also occur naturally in our bodies - in the nervous and immune systems. This type of cannabinoid is called an endocannabinoid.
The effects of these endocannabinoids in the body are mediated by special receptors - cannabinoid receptors.
CB1 and CB2 receptors are two identified cannabinoid-activated receptors that are naturally formed in the body and brain.
CB1 receptors are found primarily in the brain, spinal cord and several peripheral organs - lungs, liver.
The greatest concentration of their occurrence is in the areas of pain perception.
CB2 receptors are found mainly in the immune system and also in the periphery.
Cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 are part of the body system, which is closely involved in physiological processes with:
- maintaining homeostasis
- appetite regulation
- energy balance
- pain perception
- stress response and sleep
Administration of a cannabinoid product, whether natural (phytocannabinoids) or synthetic, replicates these effects.
CBD versus THC
The two substances are very similar in structure, but their effects are not the same. How is this possible?
THC has a planar structure. This allows it to bind to the CB1 receptor, leading to the characteristic subjective sensations of intoxication.
CBD, on the other hand, has a spatial structure that prevents this binding. It has 100 times less ability to act through these receptors. However, unlike THC, activation of the receptors in the brain does not lead to psychoactive effects. CBD is therefore not associated with such effects.
The effects of CBD depend on:
- the dose
- method of administration
- duration of administration - short or long term
- age
- gender
Is CBD safe?
Data to date show that CBD does not induce euphoria or intoxication in healthy volunteers.
Studies in animal models suggest that CBD has a number of positive pharmacological effects.
It is effective in:
- Pain
- inflammation
- anxiety disorders
- vomiting
- psychosis therapy
- problems with falling asleep
- treatment of acne
And it even has neuroprotective and antioxidant properties. Studies suggest that it may have positive effects in the treatment of cancer.
The anti-inflammatory effect is several hundred times greater than that of acetylsalicylic acid.
It may be associated with an increased incidence of suicidal ideation.
However, CBD use may also be associated with an increase in suicidal ideation and/or behaviour.
CBD is currently new to the market. Therefore, further monitoring and study of side and adverse effects is important.
Although the use of pure CBD does not lead to THC-like intoxication, it is not entirely without risk.
It should also be remembered that CBD products on the market are only dietary supplements. Consumers should therefore weigh the benefits and risks of taking CBD. Especially for products of unknown quality.

Uses of CBD
Although CBD has a high fat solubility, its oral administration has poor bioavailability - only 6 to 19%.
This means that only a very small amount is absorbed into the bloodstream. This is mainly due to extensive metabolism in the liver. To increase its availability, it is recommended that CBD is taken with a higher-fat meal.
CBD is also more absorbable when it is smoked, as it does not pass through the liver. However, smoking it carries a number of drawbacks and risks.
Production of CBD oil
In the freshly harvested plant, CBD is present in the form of an acid (CBDa). When the plant is heated to produce the oil, chemical changes take place to produce the active form of CBD.
Extraction is followed by another process that removes unnecessary substances - such as heavy metals and pesticides - from the CBD oil.
Important points to know about the extraction process are:
- It is designed to purify and concentrate the cannabinoids present in the plant, resulting in a higher amount of cannabinoids in the final product (per unit volume).
- During the extraction process, other undesirable substances may be extracted and concentrated into the product.
- If the product is not adequately cleaned at the end, impurities may remain in the product:
- residual solvent (including carcinogenic compounds)
- pesticides (the high heat used in production can change the chemical composition of the pesticide and increase its toxicity)
- heavy metals
- micro-organisms (bacteria and moulds)

CBD and anxiety disorders
Mental stability is a major public health challenge these days and months. And it's a challenge all over the world.
Currently, more than 260 million people worldwide suffer from anxiety and mood disorders.
Approximately one in four people suffer from a mental disorder at least once in their lifetime.
In many countries, neuropsychiatric problems account for 35-45% of absenteeism from work.
Many people are discriminated against,
suffer social stigma or are marginalised because of these problems.
One of the consequences of mental disorders is suicide.
Some mental illnesses are major risk factors for suicide. They claim approximately 800,000 lives worldwide each year. These include:
- major depressive disorder
- bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- alcoholism
Suicide is the second most common cause of death in people aged 15 to 29 years and the first cause in men under 40.
Unlike other illnesses, neuropsychiatric disorders are diagnosed on the basis of individual symptoms. And that's sometimes a big problem.
Different psychiatric problems have common symptoms. In many cases, the individual diseases overlap and a person does not suffer from just one of them.
Because of the limited knowledge of the mechanisms of each disease, pharmacological treatment is non-specific. This ultimately means that the same groups of drugs are used for different mental disorders.
Therefore, the use of Cannabis sativa compounds in the treatment of these disorders is of great interest.
A number of studies have been conducted using THC and CBD.
Unlike THC, CBD does not have addictive effects. It is therefore not abused as a drug. More importantly, the benefits of this drug outweigh its risks.
CBD has no addictive effects.
Studies in animal models have confirmed that CBD has effects in addition to those mentioned above:
- anxiolytic
- antidepressant
- antipsychotic
- antiepileptic
- neuroprotective
CBD was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018 for two diagnoses. It has been shown to be effective and safe in treating seizures - in patients as young as two years old - associated with:
- Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
- Dravet syndrome
This has accelerated research and also its use in other disorders.
The results suggest that CBD may be a potential therapy for other disorders as well.
However, further studies are needed to demonstrate
- the usefulness of
- safety
- efficacy
CBD in psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression and schizophrenia, as well as others.
The use of CBD for pain
CBD deactivates the enzymes involved in the production of inflammatory substances in our body.
Pain in inflammation is caused by substances that are produced during an immune response. Normally, inflammation is a necessary protective mechanism that plays an important role in the wound healing process. It is usually accompanied by redness, warmth, swelling, pain/sensitivity and loss of function. However, in pathological conditions, it can cause long-lasting pain.
CBD also has the potential to act as an anti-inflammatory. However, further research is needed to clarify this effect.
Analgesic effects may vary depending on the dose and route of administration. Studies in animal models suggest that CBD has an effect on reducing different types of pain - neuropathic, inflammatory, arthritic.
CBD and acne treatment
CBD has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on sebocytes. Sebocytes are cells in the sebaceous glands of the skin.
If these cells are over-stimulated or inflamed, excessive sebum production occurs. This can cause inflammation of the skin or acne.
CBD also has high antimicrobial activity against P. acnes bacteria.
Based on these properties, CBD appears to be a suitable choice for the treatment of acne vulgaris.
A new synthetic CBD preparation, BTX 1503, is currently being investigated for use on the skin. External use makes this molecule an excellent candidate for treatment. In this case, there are far fewer side effects than with a centrally acting drug.
CBD and medicines
It should be pointed out that CBD inactivates cytochrome P450. Cytochrome P450 is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of many drugs.
As CBD reduces the action of this enzyme, it may increase the action of other drugs broken down by this enzyme and their side effects.
On the other hand, it may also reduce the effectiveness of some drugs - especially those that are activated by this enzyme.
CBD - depending on the dose - can cause liver damage. People taking e.g. leflunomide or valproate should be careful.
However, caution should also be exercised in patients who:
- are taking medicines that increase liver enzymes
- have a damaged pancreas
May experience a severe impairment of lung function when taking CBD with:
- benzodiazepines
- opiates
Unfortunately,
one of the most common sources of information about appropriate dosing and
side effects of CBD products
is not health professionals.
People prefer to seek advice from friends or acquaintances. They search for advice on the internet or communicate with sellers of CBD products.
Therefore, it is always important to consult CBD use with professionals if you are taking other medications.
Is CBD a miracle cure?
In conclusion, more research and larger studies are needed before CBD can be considered an effective treatment for many ailments.
Studies to date suggest a positive effect of CBD on various diseases, but animal studies cannot always be translated into human results.
If CBD 'treatments' do not achieve the desired results, people lose time and money.
However, in the case of a serious disease or incurable condition (e.g. cancer), the consequences can be much worse - disease progression, and in the worst case, death.
It is also important to note that there are few studies on the chronic administration of CBD in healthy people. There are studies on healthy volunteers that demonstrate the safety and good tolerability of CBD. However, they do not examine long-term use, which is common in chronically ill people. Chronic pain sufferers are often forced to take medication, continuously, for many years.
To date, controlled scientific studies of CBD for human medical indications (other than epilepsy) are rare. Although this is changing rapidly. Especially with the recent relaxation of legal restrictions. The acceptance of CBD use by society is contributing to this.
For example, ClinicalTrials.gov lists several clinical trials in various stages that propose to investigate CBD as a treatment for several conditions - including tremor, anxiety, pain, and substance use disorders.
These results will be crucial in identifying diagnoses for which CBD holds promise as an effective treatment. It is not just a profitable "elixir" with no real therapeutic benefit.
Interesting resources
Related










