Are you suffering from dry elbows: what do dry elbows mean and how are they treated?
Beautiful skin is everyone's dream. Even men enjoy it. But to keep it beautiful and soft, we need to give it the time and care it needs. Some areas can be more troublesome, others less so.
Article content
Dry and rough elbows look unpleasant and are not pleasant to touch. Often the dryness is at the stage that small scales fall from the skin of the elbows, which can be uncomfortable for a person, especially in company.
The skin on the elbows, which is naturally rougher, is more difficult to care for and tends to dry out more quickly, so it requires special attention.
With proper care and hydration, we can restore its lost softness and smoothness. Enough hiding under your clothes! Show your body in all its glory.
What is the function and structure of the skin?
The skin (cutis, dermis) is the largest organ of the human body. Its total weight is up to 4.5 kg of a person's total weight. It covers almost 1.5m2 to 1.9m2 of external surface area (depending on the height, weight and overall robustness of the individual).
Basic functions of the skin
The skin forms a barrier between the external and internal environment. It protects the body from mechanical, chemical and physical damage.
It is involved in thermoregulation (maintaining body temperature), maintaining body fluids and excreting waste substances and toxins through sweat glands.
Its involvement in respiration (cellular respiration) and sensory properties (receiving stimuli and information via nerve endings) cannot be overlooked.
Skin structure
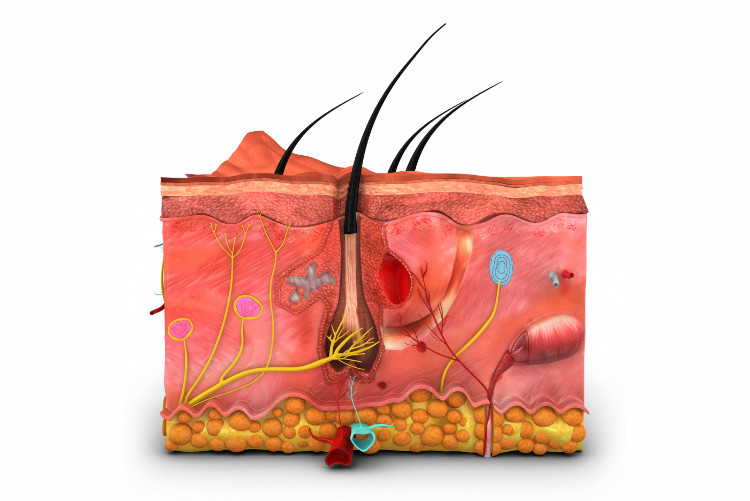
1. The surface of the skin is the epidermis, which is composed of multiple layers of flat cells. These naturally cornify, die and peel off at the surface. This is a natural process of skin regeneration and cell renewal by cell division and replacement by new cells from deeper layers.
This process is of great importance in the case of skin injuries and defects, which are regenerated in this way. The skin also contains the brown skin pigment melanin, a protein that is not soluble in water.
- Interesting fact: The protein found in the skin is insoluble in water. It prevents the penetration of water and water-soluble substances into the skin, together with the sebum (see seam). This fact is a guideline when choosing creams with an oily composition, which has the ability to penetrate deeper.
2. Underneath the skin is the dermis (corium), composed of connective tissue and fat cells. Its elasticity, elasticity, strength and extensibility are provided by elastic fibres passing through the subcutaneous tissue in the direction of the load on the skin. The corium is supplied with blood vessels and innervated by nerve fibres.
The lymphatic and sweat glands are located in the sclera. It is the lymphatic glands running along the hair and hairs that produce sebum, which is key in preventing excessive drying of the skin. It ensures its lubrication and moisturisation. It prevents water from escaping from the skin by its oily composition, which effectively maintains skin hydration.
Sweat glands with their uneven distribution secrete sweat. Sweat is mainly composed of water, sodium chloride, urea, uric acid, fatty acids, amino acids and other substances.
- You may not have known: In sweat there is a certain kind of acid that is very beneficial to the body. This acid has an anti-inflammatory effect when exposed to sunlight. Therefore, it is not advisable to constantly wash off sweat when sunbathing, as this increases the risk of skin inflammation.
3. The deepest layer is the thin subcutaneous connective tissue. It is made up of tough collagen and elastic fibres together with connective tissue cells. It is here that the greatest number of fat droplets are deposited. It is the subcutaneous tissue that is a kind of reservoir of fat.
Differences in the skin according to location
The skin cover is not the same on all parts of the body. In some places the skin is thinner and finer (cubital part - inside of the elbow joint, inside of the forearm and wrist, skin under the knee joint, eyelids, cheek...), in others it is coarser and rougher with more frequent cornification and peeling of the surface layers (knees, elbows...).
- The differences also depend on the location of the sebaceous and sweat glands. The sebaceous glands are found in increased numbers near the hair and hairs. This does not mean that they are not present on other parts of the body. Therefore, they are most numerous on the scalp, in the genital area, on the face, especially around the nose, above the upper lip, on the upper chest and on the back.
To a lesser extent, they are present on the limbs (elbows and knees), the abdomen and are completely absent on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Areas with fewer sebaceous glands are at higher risk of drying out the skin. It is these areas that should be given adequate hydration and regular external lubrication.
- The sweat glands are unevenly distributed in the corium (scrotum). They can produce up to 500 ml of sweat per day, depending on fluid intake, general health, temperature and other factors. They are most abundant in areas where the sebaceous glands are absent, namely on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are also many in the skin of the armpits, forehead, above the upper lip, upper chest and neck.
Specific features of the skin in the elbow area

The elbow area has a minimal number of sebaceous glands and sweat glands. This critical area is therefore very susceptible to excessive cornification of the epithelial surface layers, drying of the skin and flaking. The skin in these areas is drier, rough and scaly to the touch. Excessive dryness is often accompanied by itching.
Another reason that multiplies the drying process is the mechanical stress on the area. In normal daily activities, we constantly bend our arms at the elbow joint and often support ourselves by resting our elbows on a pad.
Under normal circumstances, this is not something that can harm us. However, in individuals who have dry elbows, mechanical pressure against the pad can cause increased peeling, itching, soreness and even cracking of the skin with local bleeding. Cracks are open areas with a high risk of infection and other complications.
- Weather conditions also have a negative effect on the skin as a whole. The effects of the weather have an impact on the overall condition of the skin. Some individuals are more sensitive to heat and sun to develop a sun allergy or, conversely, to cold. Cold is the cause of so-called'cold allergy'. Equally important are the effects of wind, bacteria, moulds and other chemical substances.
What applies to dry elbows?
Why elbows are drier than other parts of the body was described in the article above. How to fight them and win? The basis is to know the anatomy and physiology of the skin and its components, which has already been briefly explained. With this knowledge, you can choose the right procedure and treatment with appropriate products.
Removal of dead, keratinized skin cells
There is little point in applying expensive moisturisers to long dead skin cells. First you need to get rid of these scales. How to do it?

1. Peeling is the most preferred cosmetic method of effectively removing dead skin cells. It is done using cream or gel cosmetic products that contain tiny particles of solid consistency.
Natural home-made peeling mixtures can also be used. With home-made peels, it is important that they contain small particles that abrade the skin (coffee, crushed almonds or oatmeal) and an oil part (almond oil, coconut oil, olive oil...).
Their task is to abrade the top layer of the skin, thus ridding it of dead cells. This way, the skin is cleansed, its blood circulation and oxygenation are improved, allowing better and faster regeneration of the newly formed skin cells.
The peeling method should be carried out once a week. As for the rougher and more problematic parts of the skin, which include the elbows, it can be repeated twice a week if necessary.

2. Cleansing and bathing is best done in water that is not too hot. This can over-dry the skin and worsen the condition of problem areas. Even bath foams and excessive use of shower gels or soaps will ultimately lead to a worsening of the condition. Bathing should be done in slightly warm water; lukewarm showers are great in the summer months.
If your skin is very dry, use a fragrant essential oil as a bath additive to create a protective film on the skin. This prevents the water from drying it out too much. Fragrant oils can also create a pleasant relaxing atmosphere that relaxes the body and mind. They also have a calming, anti-stress effect and help with insomnia and depression. Aromatherapy is a very popular and often used method today.
After the bath, it is time to dry off. The towel we use can also have a negative effect on the condition and appearance of our body. We should only use our own clean towel.
The material should be fine, soft, pleasant to the touch and airy. Cotton materials meet these requirements. They are also suitable for patients suffering from psoriasis, atopic eczema or allergy sufferers. We dry the problem areas only with gentle movements or by applying a cloth.
- Important: Excessive use of shower gels, soaps, but also moisturizing creams and oils, especially if the condition of the skin is not so critical, causes a gradual reduction in the natural activity of the sebaceous glands. Simply put - if we overdo it with lubrication, even if it is not really necessary, the body gets used to the supply of hydration "from the outside" and reduces the production of sebum in the sebaceous glands from the inside. It should be noted that this is an adaptation process that takes several years.

3. Moisturising the skin is very important. Moisturising creams create a protective film on the skin that prevents the penetration of pollutants and excessive drying. However, nothing should be overdone. Even excessive moisturising and lubrication can do more harm than good.
We should only rub larger amounts of oil-based moisturisers (not water) into problem areas of the skin, using gentle circular movements. As soon as the condition of the skin starts to improve, we should reduce the amount of cream and the frequency of use in direct proportion.
Oils or oil-based creams such as those with shea butter, coconut oil, olive oil, castor oil, calendula petroleum jelly, bepanthen, salicylic ointment, dislipping creams and others are suitable.
Beware of skin diseases!
If nothing works for your dry elbows, their condition is serious or you have dry skin in several places of the body, you need to increase attention and see a specialist - a dermatologist. It is not excluded that the cause may also be a skin, infectious or other disease. This needs to be treated differently than mentioned in the article.
The most common disease that causes dryness of the skin, its thickening and peeling, mainly in the area of the elbows or knees, but also the scalp, is psoriasis. This is a chronic autoimmune disease belonging to the hands of a professional. Similar symptoms can be encountered in atopic eczema, seborrhoeic dermatitis, allergy to the sun, as a reaction to cold...
Related










