Treatment of uterine polyps: monitoring, medication to surgery
Primarily, we divide the treatment options into 3 types:
- Conservative (follow-up).
- Pharmacological treatment
- Surgical treatment
Preventive monitoring of polyps
In many cases, the doctor will recommend regular monitoring of the nature and size of the polyp. This is especially true if the polyp is not causing the patient any health problems and a malignant tumor has been ruled out.
However, the gynaecologist must assess the risks and possible complications in the light of the patient's individual health and any pregnancy.
Hormonal pharmacotherapy
Another type of treatment is hormonal pharmacotherapy, where the doctor prescribes drugs to eliminate inflammation, irregular bleeding and other undesirable manifestations. They are based on the hormonal-based action of progestin.
This treatment should be short-term. It is indicated especially if the cause of the polyps was a hormonal imbalance. Positively prescribed pharmacotherapy helps to stop the growth and further formation of polyps, relieve symptoms, pain and the inflammatory process.
Surgical treatment
Polyps of larger size with intense symptoms should be surgically removed. This involves hysteroscopy, which involves complete or partial removal (ablation) of the polyp.
Usually, hysteroscopy is used to remove fibroids, adhesions and uterine polyps. In addition to ablating the polyp itself, the surface of the lining (endometrium) of the uterus may also be removed and cleaned, called curettage.
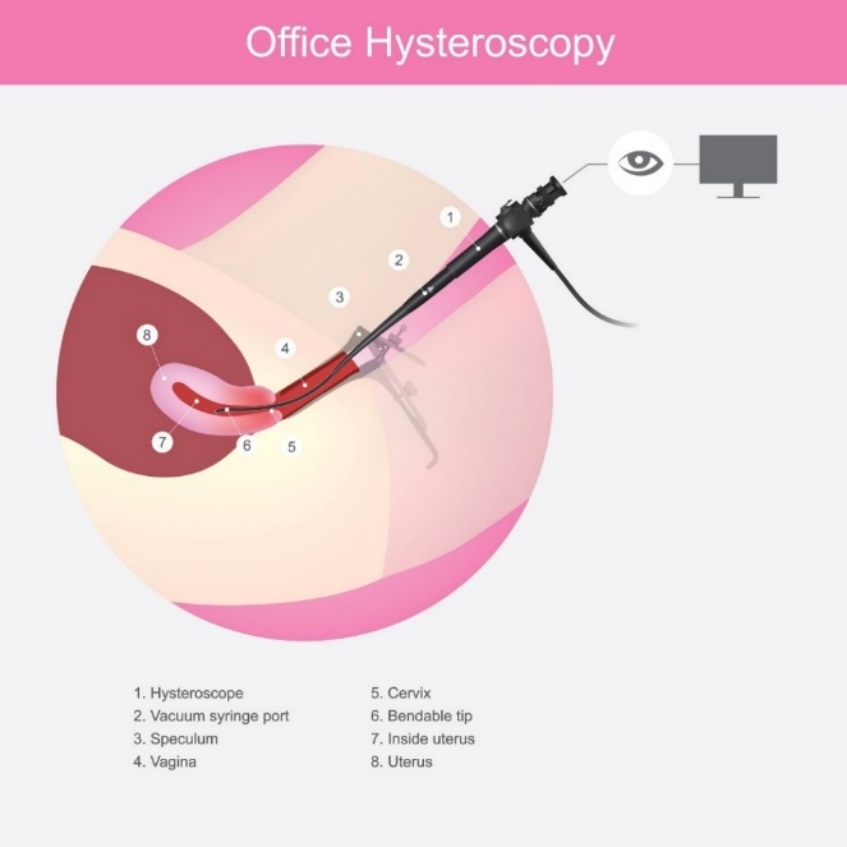
Hysteroscopy is a surgical and diagnostic method that allows many uterine diseases to be identified and, if necessary, operated on at the same time.
Hysteroscopy is a common endoscopic method in which a doctor inserts an endocamera up to 1 cm in diameter into the uterus and then views polyps and structural changes in the uterine lining.
The surgeon uses a special camera on a monitor to see the current state of the cervical canal and uterine cavity.
Using hysteroscopy, the polyps of the uterine cavity can be surgically removed. In this case, it is a surgical type of hysteroscopy or transcervical surgery. The surgery is performed through the vaginal entrance of the patient.
Hysteroscopy is usually performed under general, rarely under local anesthesia of the patient.
Hysteroscopy is an effective method with high diagnostic value. The advantage is the possibility of therapy during the procedure itself.
The surgical procedure is associated with a low complication rate due to the simultaneous optical monitoring of the operation on the monitor.
Curettage is one of the most common diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in the cervix and uterine cavity. The aim of curettage is to obtain material or tissue of the uterine mucosa.
Curettage is one of the common short gynecological procedures. It involves scraping or suctioning the damaged mucosa - endometrium of the patient's uterus.
In hysteroscopy and curettage, if the patient is in good postoperative condition after the procedure, she can leave the medical facility on the day of the procedure.
However, it always depends on the course of the procedure itself, the patient's health and the doctor's decision.
Before going home for treatment, each patient is re-examined, educated about her condition and post-operative instructions. An early post-operative check-up with the gynaecologist is also scheduled.










