- solen.cz - Fertility disorders in men. Solen. doc. MUDr. Jaroslav Zvěřina, CSc.
- ŠTUDENT, Vladimír, František ZÁŤURA and Zdeněk MUCHA. Základy urologické andrologie. Prague: Institute of Urology and Urology of the CAS, v. v. i.: Galén, 2003. ISBN 80-7262-224-2.
- Urologiepropraxi.cz - Treatment of the infertile man. Urology for practice. Vladimír Kubíček, MD, CSc.
- urologyhealth.org - What is male infertility?
Male infertility: what causes male infertility? How to detect it

Infertility affects up to 15% of couples. Male infertility is becoming a more common problem every year. What are all the possible causes of reduced male fertility?
Characteristics
Male fertility has been declining significantly in recent years. This is due to a number of influences, ranging from physiological and psychological to unhealthy lifestyles. External factors are also intervening.
Male infertility is as common as female infertility. What are the causes of infertility, treatment options and prevention, you will learn in the article.
Infertility in men
Infertility is a condition in which a woman is unable to conceive after regular unprotected intercourse for a year.
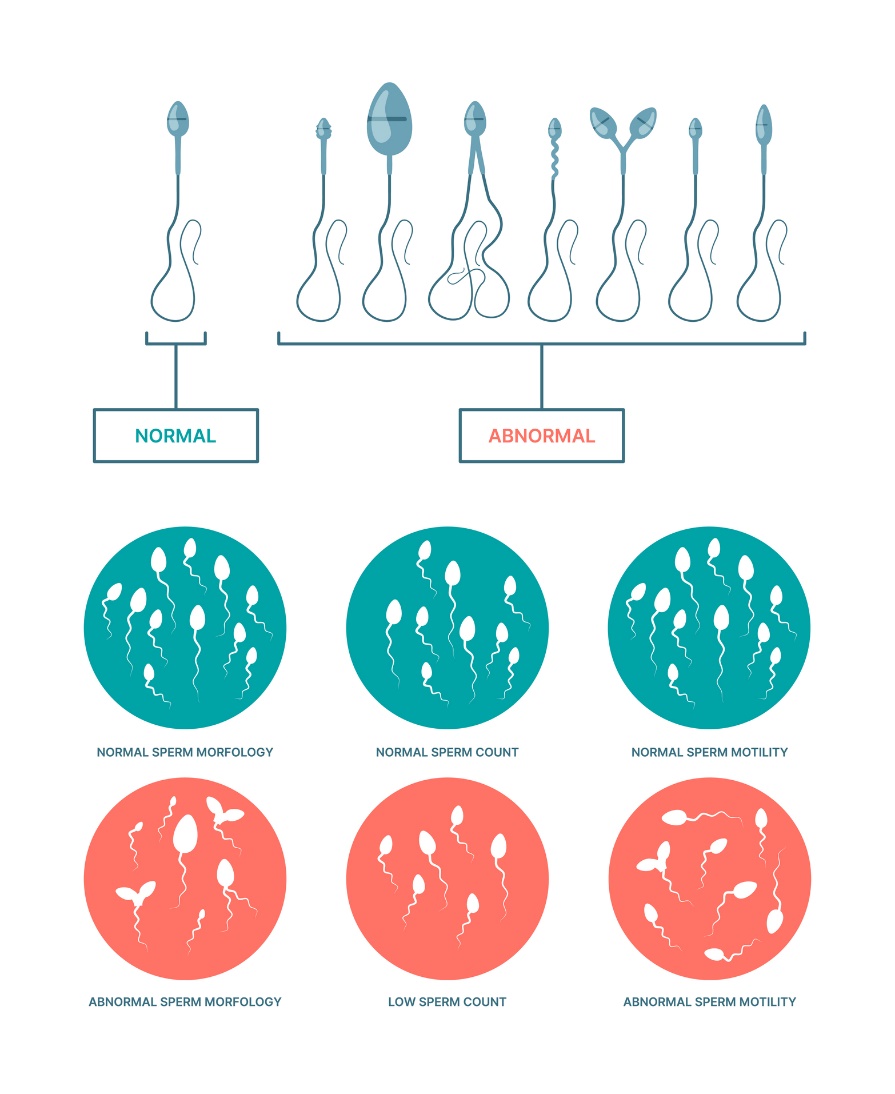
In order for male sperm cells to have quality genetic material, they must meet certain criteria: sufficient production and number, the right shape and the ability to move in the right direction.
The most common cause of infertility is poor sperm quality.
In addition to physical health, psychological state, lifestyle, diet and a number of external factors have a significant impact on male fertility.
A common cause of infertility is a disorder of sperm physiology. Possible causes are congenital defects and deformities of the reproductive organs, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, failure of the testicles to descend into the scrotum, varicocele, hormonal or immunological disorders and many others.
Article.
Causes
The cause of infertility depends on the physiology of sperm itself, erectile and ejaculatory function, hormonal balance, psychosomatics, lifestyle and the influence of external factors.
Disorder of sperm physiology
One of the most common causes of reduced fertility is an insufficient reduction in the number of sperm and, at the same time, a reduction in the chance of fertilization of the egg. Physiologically, there should be at least 15 million sperm in 1 ml of ejaculate. If there are fewer, we speak of oligospermia.
However, a more serious problem is azoospermia. In this case, there are no sperm in the male ejaculate and the child cannot be conceived naturally.
Another reason for infertility may be insufficient motility (sperm motility) or certain morphological defects of the sperm cell. After the age of 45, the quality of sperm in a man decreases significantly.
As men age, blood flow deteriorates and the level of the hormone testosterone decreases. This is very important for libido, sex drive, sperm production and quality, and erectile function.
The most important function of testosterone hormone is to stimulate sperm production in the testes - spermatogenesis. The most significant decline in testosterone occurs after the 50th year of a man's life. This period is also called andropause.
In addition to genetic factors (chromosomal defects, birth defects) and medical diagnoses (diabetes mellitus, obesity, hormonal disorders, cardiovascular disorders, oncological diseases...), the quality of sperm is also negatively affected by an unhealthy lifestyle. Excessive stress, alcohol consumption or smoking tobacco products and drug use have a negative impact.
Developmental defects and genetic factor
Defects of the external genital organs can have a significant negative effect on fertility. Genetic causes are responsible for infertility in approximately 5% of detected cases of male infertility.
Abnormalities on the Y chromosome are the most common cause of azoospermia or severe oligozoospermia with a sperm concentration of less than 5 million/ml.
Epipadia and hypospadias, disorders of the urethral meatus in which an insufficient copulatory organ is formed, are also possible genetic causes.
Erectile and ejaculatory disorders
Absolute erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve an erection - erection of the penis. Thus, ejaculation cannot occur.
Erectile dysfunction, impotence, is a disorder of the process of sexual arousal of a man. In it, there is an incorrect expansion of blood vessels and filling of the penis with blood.
Erectile and ejaculation disorders manifest themselves in various forms, for example, the absence of ejaculation referred to as dry orgasm. In the absence of ejaculation, ejaculate does not get out of the sexual organ.
Retrograde ejaculation, on the other hand, refers to a condition in which climax occurs during intercourse but the ejaculate does not leave the body. It travels instead to the bladder.
Testicular disorder
Unilateral or bilateral testicular disorder is a common factor reducing male fertility. Testicular damage may be mainly related to testicular descent disorder and cryptorchidism, inflammatory process of the testis, infection, hypoplasia or varicocele (enlargement and dilatation of testicular vessels).
As part of the diagnosis, sperm sampling and puncture of the epididymis can be performed to clarify the status of spermatogenesis.
Infertility and other diagnoses
Infertility and reduced fertility may be related to other medical diagnoses.
Reduced fertility is in some cases associated with diabetes, endocrinological disorders, cardiovascular diseases (high blood pressure, cholesterol), neurological diseases or obesity.
In particular, the use of drugs with adverse effects, such as drugs for high blood pressure or antidepressants, is a negative factor.
Risk factors are spinal injuries, pelvic injuries, repeated infections or sexually transmitted diseases.
Unhealthy lifestyle and diet
A long-term unhealthy lifestyle is a risk factor for many diseases. Fertility and sperm quality itself is no exception.
Long-term exposure to stress, an unsuitable unbalanced diet, lack of exercise, excessive alcohol consumption, caffeine, smoking or drug use.
The use of anabolic steroids, drugs, marijuana and psychotropic substances compromises fertility. Overexposure to pesticides, chemicals, heavy metals and hazardous radiation can also have a negative effect.
A negative factor is locally increased temperature of the testicular area. It can be caused by tight clothing, prolonged exposure to heat or frequent and prolonged work on a laptop placed on the pelvis.
In smokers, there is often a problem with blood flow to the penis due to blockage of blood vessels. Toxic substances from cigarette smoke also interfere with the maturation of male sperm, which subsequently lose the necessary mobility.
It is the psychogenic factor that plays a significant role in erection. Impotence is often related to psychological disorders such as depression, anxiety or excessive prolonged exposure to stress.
In addition to the quality of the erection, the psychogenic factor also relates to the sex drive itself, fertility and the achievement of ejaculation.
Factors affecting fertility:
- Older age
- Erectile dysfunction
- Erectile dysfunction
- Loss of the hormone testosterone
- Hormonal disorders and imbalances
- Congenital and developmental defects
- Mechanical damage
- Cardiovascular disease
- Neurological diseases
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Pharmacological treatment
- Smoking tobacco products
- Alcohol and drug consumption
Symptoms
Diagnostics
In most cases, the diagnosis is made by a urologist or andrologist. The examination of infertility consists in taking a comprehensive history of the patient's diseases, diagnoses, manifestations, medications taken, lifestyle and other factors affecting male fertility.
The basic element is an examination of the genital organs by touch and sight. It also includes a palpation examination of the prostate per rectum (with the physician's finger over the patient's anus).
A superficial ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system is common for a more detailed view of the internal structures of the organs.
For erectile dysfunction, a specific ultrasound of the penile arteries and an examination of the pressure and blood flow in the penis is performed. Prostaglandin substances injected into the body artificially induce an erection. Ultrasound is used to demonstrate the ability of the blood vessels of the penis to dilate.
A spermiogram is part of the basic diagnosis. This is a basic examination of a semen sample to determine the values and quality of male sperm (motility, number, morphology).
In case of pathological findings within the spermiogram, a follow-up examination should be performed at an interval of approximately 2-3 weeks.
In case of disorders in the testicular region, sperm collection from the testis and puncture can be performed to clarify the status of defective spermatogenesis.
By culture of the ejaculate it is possible to detect the presence of an infectious disease reducing fertility and sperm quality.
In some cases, hormonal testing of a blood sample may be indicated to determine the level of sex hormones in the body.
The urologist may recommend the patient to see another specialist doctor - endocrinologist, neurologist, psychiatrist, etc.
How it is treated: Male infertility
Treatment of reduced fertility and infertility: what on male fertility?
Show moreMale infertility is treated by
Other names
Interesting resources










