- "Larynx Cancer Factsheet" (PDF). Global Cancer Observatory. Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou M, et al. (GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
- "SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Larynx Cancer". NCI. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- Laryngeal cancer at Mount Sinai Hospital
- DeVita VT, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA (2011). Devita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's cancer : principles & practice of oncology (10th ed.). Philadelphia. ISBN 978-1-4511-9294-0.
- "Cancer of the Larynx - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - MedBroadcast.com". Retrieved 2018-01-25.
- Ridge JA, Glisson BS, Lango MN, Feigenberg S, Horwitz EM (2008). "Head and neck tumors.". In Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins W (eds.). Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach (PDF). Vol. 11. p. 369.
- "Laryngeal Cancer". Retrieved April 7, 2019.
- Torrente MC, Rodrigo JP, Haigentz M, Dikkers FG, Rinaldo A, Takes RP, et al. (April 2011). "Human papillomavirus infections in laryngeal cancer". Head & Neck. Head Neck. 33 (4): 581–586. doi:10.1002/hed.21421. PMID 20848441. S2CID 30274997.
- Mirisola V, Mora R, Esposito AI, Guastini L, Tabacchiera F, Paleari L, et al. (August 2011). "A prognostic multigene classifier for squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx". Cancer Letters. 307 (1): 37–46. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.013. PMID 21481529.
Laryngeal Cancer at a Young Age? Manifestations and Causes

Photo source: Getty images
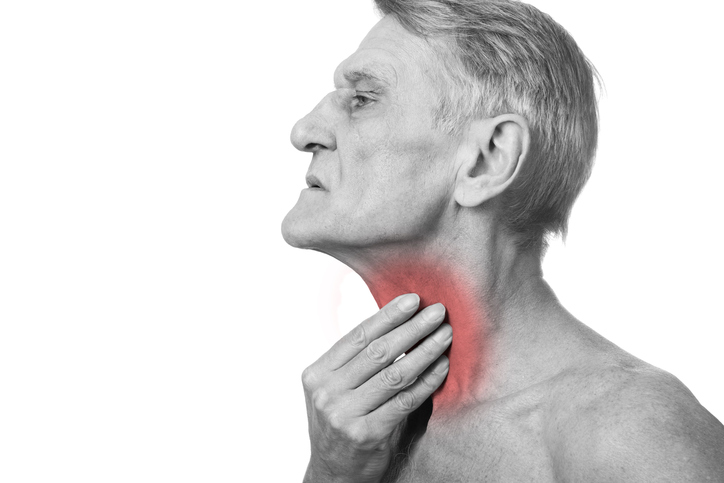
Most common symptoms
- Malaise
- Sore Throat
- Pain when swallowing
- Ear Pain
- Shooting Pain in the Ears
- Hoarseness
- Spirituality
- Bleeding
- Blue leather
- Sweating
- Indigestion
- Malnutrition
- Swallowing disorders
- Dry cough
- Coughing up blood
- Increased body temperature
Show more symptoms ᐯ
Laryngeal cancer treatment: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and more
Show moreLaryngeal Cancer is treated by
Other names
Cancer of the larynx, laryngeal carcinoma