- prolekare.cz - Skin diseases in athletes
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Clavus
- my.clevelandclinic.org Clavus and calluses
- mayoclinic.org - Clavus and calluses
- dermatologyadvisor.com - Corn/callus
- solen.sk - Warts and their treatment in children, doc. MUDr. Tibor Danilla, CSc. from the Children's Dermatovenerology Clinic of the 1st Medical Faculty of Charles University in Bratislava.
Chicken eye: what is it and what does it look like? + Proven prevention and advice for women
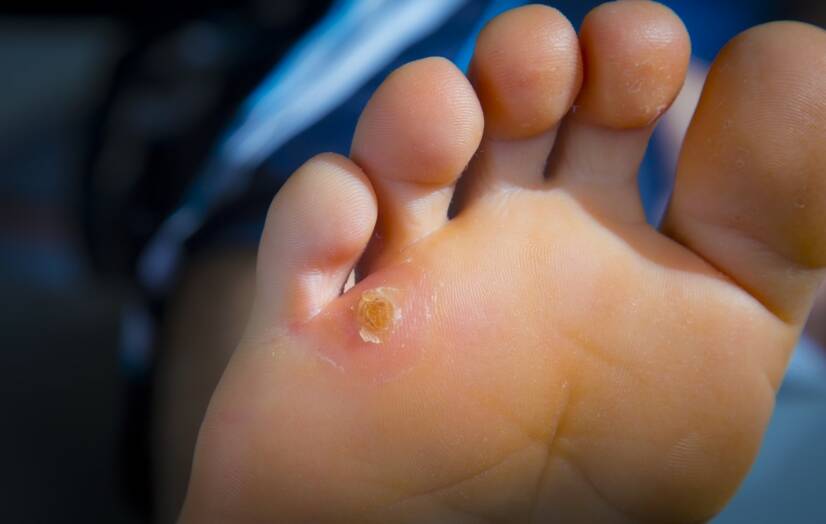
Chicken eye is a non-transmissible mechanical skin lesion. What is the cause of its occurrence? How to get rid of it effectively?
Most common symptoms
Characteristics
Chicken eye is caused by prolonged pressure on a spot on the skin.
A typical example is the pressure of a bad shoe on the big toe, which causes hyperkeratosis (thickening of the corner layer of the skin). A callus later forms on this area. Repeated pressure causes the callus to deepen and develop.
Mechanical damage to the skin in the table
| Diseases | Characteristics |
| Hyperpigmentation | Occurs after prolonged exposure to pressure or friction (belts, braces, prostheses). |
| Blisters | Arise acutely from heat and friction when pressure is applied to the legs after prolonged walking. Arise on the hands from unusual activity (rowing, tennis, etc.). |
| Cerebellum | It is characterized as a focal hyperkeratosis induced by mechanical action. |
| Chicken eye (clavus) | It is defined as painful focal hyperkeratosis over articular or bony prominences |
| Black heel | Is characterized as blue-black spots or streaks caused by blood discharges. Occur in athletes in the callosal area of the heel or on the bellies of the toes. |
| Decubitus ulcers | Arise after prolonged exposure to pressure and subsequent ischemic necrosis (tissue death due to lack of blood supply). |
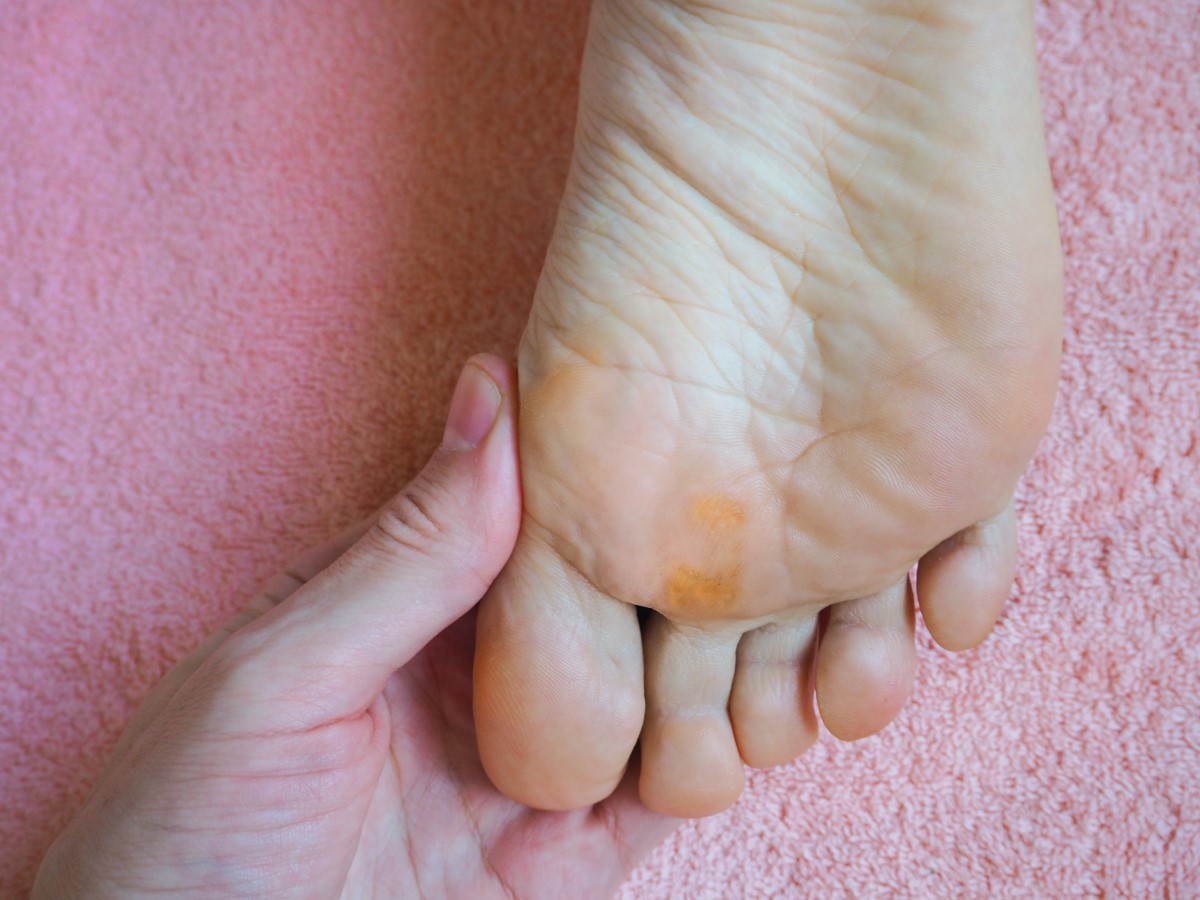
Causes
Who can develop cornea?
Anyone can develop chicken eye.
It particularly affects women who wear narrow fashionable shoes. It is common in patients with orthopaedic problems.
Corns can also occur in children. The cause of corns in children is improperly chosen footwear.
In case of corns in children, it is a good idea to see a doctor to avoid misdiagnosis.
Where can corns form?
Corns are mainly found on the protrusions under the joints, on the heel, between the toes or on the bums of the toes.

What else influences the formation of corns?
There are other factors that contribute to the development of corns, such as:
- Physical activity
- ill-fitting shoes
- foot deformities caused by bone spurs
Patients over 65 years of age are most often affected by painful corns. The skin undergoes many changes with age. The changes result in a thinner and drier protective layer. For this reason, there is a higher incidence in the older population.
People over 65 years of age have a higher risk of developing cornea.
Symptoms
You ask: How will this manifest itself?
The chicken eye consists of two parts:
1. The top layer
The top layer is visible to the naked eye. It is round or elliptical in shape.
The skin is visibly hardened and cornified.
2. Lower layer
The thickened horny layer forms a funnel-shaped, deeply penetrating spine (eye).
The spine is inclined downwards, causing inflammatory and degenerative changes in the joint capsule and surrounding ligaments.
What are the known types of corns?
1. Soft cornea
Occurs mainly in the space between the toes where there is a high moisture content.
It has a characteristic bowl shape and an annular nucleus.
2. Hard cornea
Most commonly found above the joints of the toes, on the lateral side of the foot and on the sole of the foot.
The hard cornea has a dry and rough appearance.
3. Inflamed cornea
As a result of constant irritation, inflammation of the surrounding tissue and the cornea itself occurs.
Initially, it is only reddened, but later on inflammation and suppuration occur. Without professional treatment of an inflamed cornea, the tissue may die (necrotise).
Diagnostics
The histological findings may resemble a callous, but there is parakeratosis (imperfect cornification of the squamous epithelium) in the central part and only hyperkeratosis (thickened skin) at the edges.
Some warts resemble a chicken eye. The wart is visible only after treatment with a salicylic patch.

What is the difference between a chicken eye and a wart?
Warts are a very common skin problem.
Some patients confuse warts with corns.
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus. The disease is transmitted either directly from person to person or indirectly (by using an infected object).
The table below lists the types of warts
| TYPES OF WARTS | CHARACTERISTICS |
| Verrucae vulgares (common warts) |
|
| Verrucae plantares (plantar warts) |
|
| Verrucae filliformes (digitatae) |
|
| Verrucae planae juvenile (flat warts) |
|
| Condylomata accuminata (condylomata) |
|
For more information, see also the article:
Is it a corns or a viral wart?
Prevention of chicken eye
Chicken eyes can be very distressing. They are painful and aesthetically unpleasant. That is why we should think about prevention.
Experts recommend the following preventive measures:
- the right size of shoes (they must not crush or press)
- good quality shoes
- the foot must breathe in the shoe
- regular ventilation of the shoe
- the toe of the shoe is roomy enough
- shoes with flexible soles
- the use of shoe inserts
- the use of creams to soften the feet

Grandma's recipes for home treatments
Here are some homemade recipes...
A table with grandma's advice
| SOURCES | METHOD OF PREPARATION AND APPLICATION |
| Swallowtail |
|
| Banana peel |
|
| Garlic |
|
| Onions with vinegar |
|
| Lemon juice with onion |
|
| Lemon and garlic |
|
| Vinegar s lemon |
|
| Dried raisins |
|

How it is treated: Chicken Eye
Treatment of corns: what works to eliminate it? Drugs, solutions and more
Show moreVšetko o kurom oku (video)
Chicken Eye is treated by
Other names
Interesting resources
Related










