What is astigmatism, what are its symptoms and treatment? (for adults and children)

Astigmatism is a common visual acuity disorder. Do you see out of focus, blurry, have headache or have night vision issues?
Most common symptoms
- Headache
- Eye Pain
- Double vision
- Eye irritation
- Cutting the eye
- Squinting
- Itchy eye
- Pressure in the eye
- Head spinning
- Fatigue
- Redness of the conjunctivae
- Blurred vision
- Deterioration of vision
- Increased watery eye
Characteristics
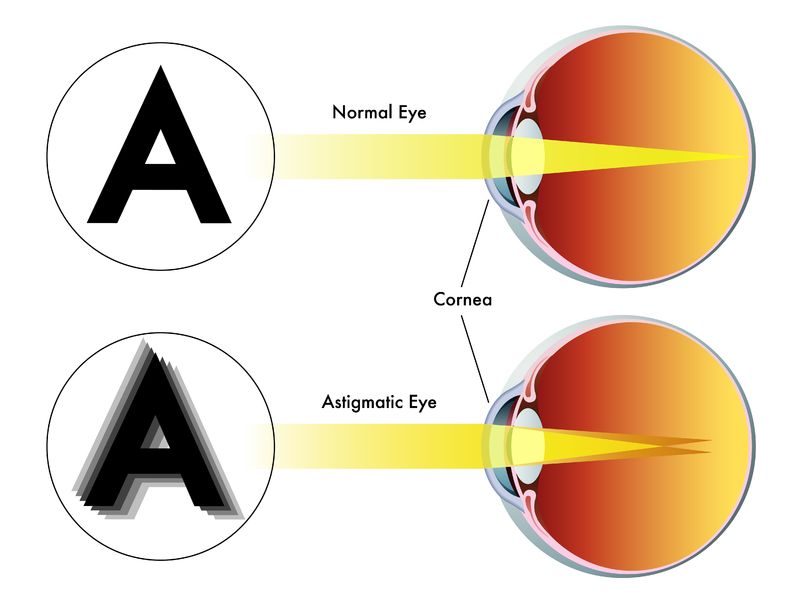
Failure of the curvature of the optical system of the eye poses a problem for the transmission of a focused, uniform and clear image to the retina.
One sees out of focus and blurry.Has issues reading, driving, getting oriented, percept lines.
Refractive errors are caused by a failure of the power of the optical system and refractive environments of the eye. Which causes the rays of light not to fall exactly on the retina, instead have the image created outside. This is responsible for out of focus and blurry vision.
In addition, astigmatism very often occurs in conjunction with another refractive error.
Refractive errors of the eye also include farsightedness (hypermetropia) and myopia (myopia).
Often asked:
What is astigmatism.
What is myopic and hypermetropic astigmatism, so mixed?
Is it hereditary and can it get worse?
Do we know the home test, astigmatism exercises and what is its treatment?
What does it mean that the eye is astigmatic?
In most cases, it is a change in the shape and uniformity of the cornea. Its curvature is irregular, which causes a focusing problem.
A certain degree of corneal irregularity and unevenness is common and normal from birth. That is because the cornea is never absolutely regularly curved. However, it is both a low degree and a physiological phenomenon.
In this case, there is no problem with the focus.
However, higher degrees are pathological and proper treatment is necessary to correct vision. This depends on the diagnosis of the extent of the defect.
What is the cornea?
Cornea is the anterior and transparent part of the eye, which covers the eyeball and thus protects its interior. Due to the communication with the external environment, this is the most stressed part of the eye.
Its transparency ensures perfect penetration of light rays into the eye. It is exposed to dust, dirt and injuries. Tears are responsible for its cleansing as well as moisturizing. Therefore, for the dry eye syndrome, the eye suffers more than it should.
Corneal irritation is manifested by pain, cutting, burning, itching, but also tearing. In addition to chemical effects, it is sensitive to the touch and other irritations.
An example is stinging eyes and tearing when slicing onions.
In addition, when it is irritated, the eyelid reacts and closes reflexively.
It has several layers, although it is only about 1 millimeter thick. Its 5 layers consist of squamous epithelium, Bowman's membrane, stroma, Descemet's membrane and endothelium.
Back to astigmatism ...
Thus, with astigmatism we understand a disorder of the curvature of the cornea. Although, it should have a round shape, in this case, its shape is flattened, thus, oval. For comparison, it has the shape of an egg or a soccer cone (rugby ball or American football).
But...
Other forms of curvature defect exist as well.
Astigmatism can affect:
- cornea - the most common form
- lens - rare
- retina - rare
Astigmatism is divided into regular and irregular. The latter one has both planes perpendicular to each other and a maximally different refraction of light rays.
Forms of astigmatism:
1. simple - simplex
- myopic - light falls into two foci, one on the retina and the other in front of the retina in one plane
- hypermetric - one focus is on the retina and the other behind the retina in one plane
2. compound - compositus
- myopic - foci of light impact are in two planes in front of the retina
- hypermetric - light falls into two planes behind the retina
3. mixed - mixtus, if light falls in two planes, in front of and behind the retina
Irregular, ie irregular, contains various forms of brittleness. Its higher degrees arise mainly after corneal diseases, inflammation, injury or surgery. This type cannot be corrected with glasses.
![Refraction of light rays and optical astigmatism. Photo source: Author I, Sebastian Kroch [GFDL / CC-BY-SA-3.0], Wikimedia Commons explanation of astigmatism of the eye](https://medicspark.com/files/images/choroby/astigmatizmus_1.jpg)
Causes
However, why it occurs is not known. A person can be born with this refractive error. Congenital forms are reported to be relatively common.
Alternatively, it may be a bug acquired during life.
The causes and risk factors are:
- heredity - usually occurs from birth
- eye injury
- eye surgery
- as a consequence of keratoconus - a disease of the cornea, with a change in shape
- and other eye diseases
In addition, astigmatism may progress and increase over time.
Are you interested in:
Can it occur due to eye strain and reading in low light?
Is it possible because of long periods staring at TV and using a computer?
No, rather not.
A closer look at what happens in astigmatism
Under normal conditions, if the eye is perfectly shaped, the rays of light pass through the cornea and lens. These structures refract the rays of light so that they strike the back surface of the eye, i.e. more precisely in retina.
The image, the subject, will be in focus and seen sharply.
However, a problem occurs with a refractive error. That because the rays do not converge exactly, and the resulting image is not displayed on the retina, but instead in front or behind the retina.
In astigmatism, the cornea, or the lens, are rarely unevenly curved. The rays of light are not bent evenly. For this reason, two different images are formed.
As a result, these images overlap or combine in the eye. One perceives this as blurry vision.
The problem can be in horizontal, vertical or diagonal course.
The refractive error can have different degrees.
One does not even have to realize the light forms.
Severe forms of the disease are responsible for blurry vision and other unpleasant difficulties and symptoms.
Symptoms
However, that is not all ...
Symptoms of astigmatism are:
- reduced visual acuity
- blurred vision at any distance
- double vision
- out of focus and blurred lines
- vision of a distorted and distorted image
- squinting
- impaired vision at dusk in night vision
- impaired perception of details
- impaired perception of contrast
- problem with spatial orientation
- closing the eyelids when looking into the distance
- turning the head to a certain position while reading
- headache
- irritability
- tired eyesight and visual discomfort
A good example is the congenital type, when the child is not aware of having vision problem. The child has never seen sharply, hence, does not know what the world around should look like.
He has difficulty reading. They were wrong about characters, numbers and letters.
When reading, it replaces 3 for 8 and H for N or P for F, or K for X.
In young children, it can lead to amblyopia.That is why it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations with children, where the eyesight is also examined.
Diagnostics
Therefore, especially at this age, it is important to attend regular preventive check-ups, which include eye examinations.
An ophthalmologist examines the vision through several methods, such as:
- visual acuity, automatic refractometer
- examination of the anterior segment and the posterior segment of the eye, slit lamp, ophthalmoscope (especially in small children)
- defect detection and preferential vision, eye tests, optotypes after 3rd year of life (E type and after 7th year of life with letters), ophthalmological board
- perimeter, peripheral visionkeratometry, corneal topography, sciascopy (in young children)
- it is examined during cycloplegia, ie the elimination of the accommodation ability of the eye
Course
As mentioned, the problem with congenital forms is that the child has not seen the world clearly before and cannot about the vision problem. It is only at the time of learning reading and writing that can be obvious. At a later stage, it can lead the child to amblyopia.
Values up to +0.5 do not need to be corrected. However, it is an individual assessment, because even the correction of small astigmatism leads to improved visual functions.
Nevertheless, even if it may be a milder defect, over time it may develop more, until one becomes aware about the problem.
No, the eyes strain, because of reading, watching television and using computer has nothing to do with deterioration.
Severe forms, and high astigmatism, are responsible for the perception of double image, and thus double vision, blurred vision, and image distortion. For example, in different directions.
In addition, a person may experience eye strain, blurred vision, visual discomfort, eye tension, eye pain and irritation after prolonged exercise. Headache is associated as well.
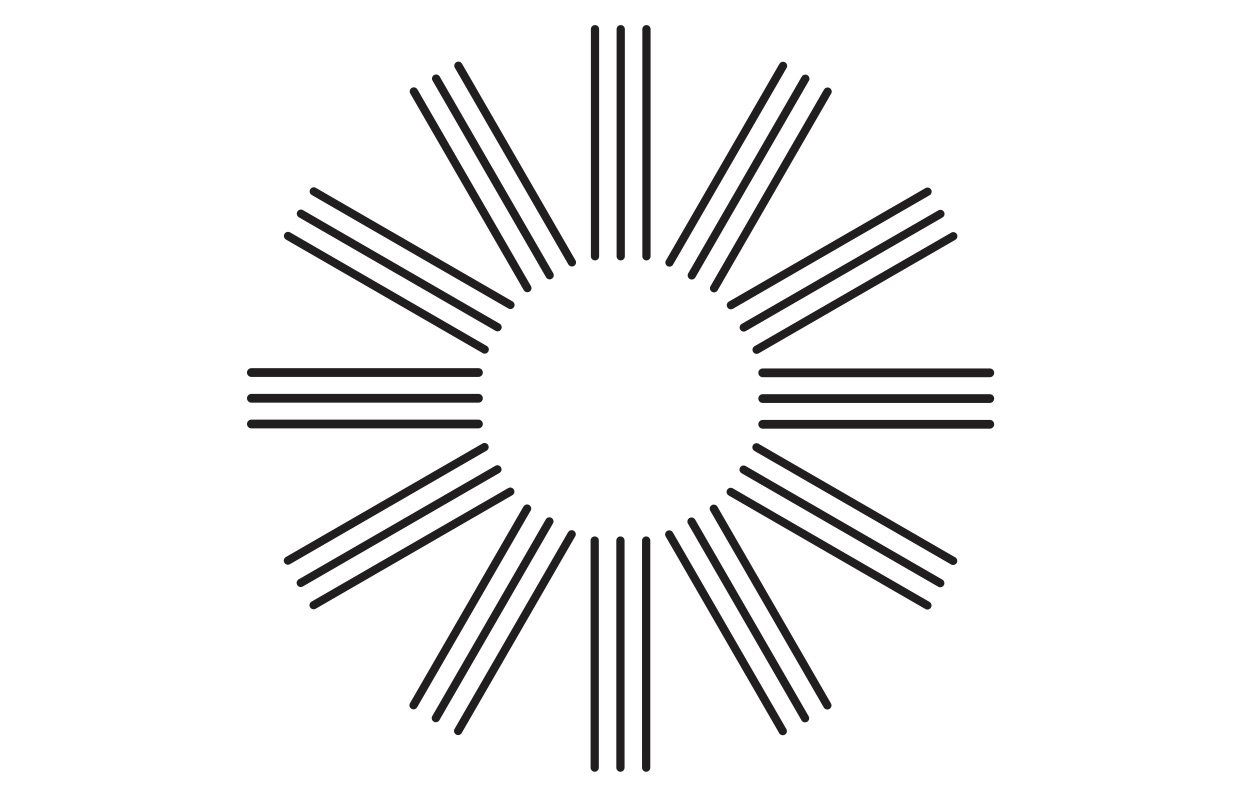
Astigmatism - picture test
A reliable eye examination will be performed by an expert. However, before you decide, you can take a simple test.
All you have to do is print a picture with an astigmatism test on a A4 page in black and white. Hang it on the wall or on the cabinet, stand in front of it 1.5 m, cover one eye with your palm and look at the circle in the picture.
If you see some lines in a picture of a different shade or line, you most probably have astigmatism in that eye and you should see an ophthalmologist who will perform a comprehensive examination to confirm the diagnosis.
Astigmatism in children
Astigmatism is a refractive eye defect that has been present since birth. The incidence is relatively high in children under 1 year of age. It is also a temporary condition that can be corrected by the age of 5.
Above the 5th year, the incidence is similar, as in the case of the adult population. Approximately 10% incidence is reported. Which in practice means that every tenth child suffers from this eye disease.
At the same time, if a child's astigmatism did not occur at all in the first year of life, it is very unlikely that it will happen later.
It is an inherited disease, so if it occurs in parents, it is necessary to pay even more attention and the importance of eye examinations.
A lower degree of astigmatism can correct the eye itself. Neither the child nor the parent knows that it is astigmatism. However, we can observe that, for example, when watching TV, the child tilts his head to the side, up or down to better focus on the image.
However, the most important thing is to detect a refractive error as soon as possible in childhood. Because in older people, the brain is sometimes less plastic and is used to the condition. In this case, the correction will be more complicated.
How to observe it in children?
Children most often complain of overloaded eyes, headaches and distorted or blurred vision, whether they are looking into the distance or at close range.
It affects the child's concentration at school, his mood, causes irritability. A child may have worse results due to a poor ability to read and recognize certain characters, letters and numbers.
Therefore, there is no need to underestimate the symptoms and go for an eye examination.
And remember ...
- the condition is most often corrected in children by spectacle lenses - glasses
- pediatric astigmatism in children over 6 years of age to 2D is corrected only if it causes asthenopic problems
- if visual acuity is normal in young children, and if binocular functions also develop normally, values lower than 2D do not need to be corrected
- regular inspections are carried out twice a year
- for values above 2D, correction is needed in all circumstances for children under the age of 6 years
- because there is present the risk for amblyopia - amblyopia
How it is treated: Astigmatism
How is astigmatism treated? Glasses, lenses, laser...
Show moreis treated by
Interesting resources
Related










